Anatomy: The Orbit and the Eye Flashcards


where is the optic canal


how many bones make up the orbit
6
what is the thinnest bone of the optic canal
ethmoid - medial wall
where is the apex of the bony orbit located
nasal side
what bones form the orbital margins

what forms the orbital rim
combiend orbital margins
what function does the orbital rim have in respect to orbital trauma
nothing wider than diameter of orbital rim can hit the eye
describe the angle of the orbital rim

orbital blowout fracture
force on orbital rim damages medial wall (ethmoid) and orbital floor (maxilla) which are extremely thin
can damage the infraorbital NVB resulting in general sensory deficit of facial skin
typically entraps the inferior rectus - patients will complain of pain on upward gaze
which direction does a fractured zygoma tend to rotate, and what can this result in clinically
medially towards orbit floor
as the suspensory ligament of the eye attaches to the zygoma laterally, the eye may be lowered towards the orbital floor
results in diploplia (double vision)

what is the difference between notch and foramen
notch is an incomplete circle
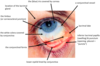
outer eyelid:
name the 2 parts of the orbicularis oculi


describe the functions of the orbital and paplebral parts of the orbicularis oculi
orbital part closes the eye tightly
palpebral part is involved in normal blinking

what is the orbicularis oculi innervated by
CNVII
what is another name for the superior tarsal muscle (connective tissue?)
Muller’s muscle
medial eyelid layer:


what is the orbital septum made of and what is its function
sheet of fascia
helps to prevent spread of infection from superficial to deep
inner eyelid layer:
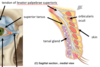
tarsal glands
also called Meibomian glands
glands embedded in the tarsal muscles, responsible for lipid secretion
they secrete a layer of oil on top of tears to stop them from evaporating


tears:
- antibacterial properties
- pH
antibacterial properties due to action of lysozyme
pH of around 7.6
describe the conjunctiva - 2 types and where they meet
the inner surface of the eyelid is lined by palpebral conjunctiva
the eyeball is lined by bulbar conjunctiva
meet at the fornix

conjunctival fornix
connects the conjunctiva lining the inside of the eyelid with that covering the eyeball

describe the features of the palpebral conjunctiva
has follicles and papillae
contains goblet cells which secrete part of the tear film