Neuroradiology Flashcards
What was newly approved in 2011 regarding MRI studies?
- MRI-safe pacemakers.
- Safe for patient; cannot scan over the pacemaker region
- Good records, serial no. of pacemaker, etc. are required.
What is the significance of the origin of the opthalmic artery?
- It is the marker that the Internal Carotid Artery (ICA) is in the subarachnoid space, so the artery at this point is completely encased in the dura.
- Thus, at this point and beyond, an aneurysm that leaks or bursts would cause a subarachnoid hemorrhage.
Describe the complications caused by subarachnoid hemorrhage.
- Arachnoid granulations are blocked,
- CSF is not resorbed, ventricles expand (hydrocephalus), which leaves less room for cerebral blood, causing ischemia.
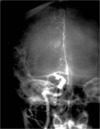
Identify the tagged artery in the following lateral carotid angiogram.
Ophthalmic artery
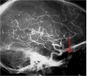
Identify the tagged artery in the AP carotid angiogram.

Posterior communicating artery
Identify the tagged artery.

Pericallosal artery (branch of the anterior cerebral artery)
What is the clinical significance of the pericallosal artery?
It courses above the corpus callosum, which is above the ventricular system, so the position of the pericallosal artery provides information about the ventricular system.
Identify the tagged artery.

Middle cerebral artery
What is tagged in this image?

The Sylvian point
What is the Sylvian point?
The most posterior and the most medial point of the MCA. The “end” of the MCA.
Where is the Sylvian triangle in the following image?

Sylvian triangle.

Describe the Sylvian triangle.
- Identifies all the branches as they come out of the Sylvian fissure (top line of triangle; coming “toward you”).
- Bottom line shows origin of the vessels.
- Must be in the normal location and shape. If the top line is “bowed up” there is a mass elevating it, and vice versa.
Identify the tagged artery.
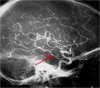
Posterior communicating artery.
What artery is the origin of PICA?
Vertebral a. (not Basilar!)
Identify the tagged artery.

Posterior inferior cerebral artery (PICA)