Neurooncology Flashcards
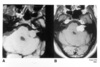
young adult presenting with back pain (with or without radicular features)
- slow growing glial tumor
- arise almost exclusively in the conus medullaris + filum terminale
myxopapillary ependymoma
What disease process is pictured?
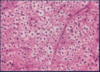
Oligodendroglioma
Tumor composed of cells with monotonous round nuclei, surrounded by prominent perinuclear halos
= “fried egg” appearance
What metastatic tumors to the brain have a propensity to bleed?
Melanoma
Choriocarcinoma
Renal cell
Lung
Thyroid
Breast
(“My Cancer Really Likes To Bleed”)
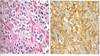
56YOFM w/ hx of NHL treated w/ chemo had L sided weakness & dysarthria over 2 mos. A brain bx showed the following. He was probably infected with
–JC Virus
–Herpes Virus
–Rabies
–CMV
–HIV

JC Virus
Picture shows enlarged oligodendrocytes filled with virions
What condition did this patient probably have?
–PML
–HIV
–Rabies
–HSV
–CMV
What % of patients with this biopsy are asymptomatic?
–70-90%
–10-20%
–50%
–1-5%

PML
70-90% are asymptomatic
JC virus – causes multifocal demyelination; giant oligos (filled with virions)
Primary infection at kidney -> to CNS via infected mononuclear cells – affects astrocytes
Viral latency & reactivation during immunosuppression
Patient presents w/ HA and obstructive hydrocephalus. A mass is found in the lateral ventricle on neuroimaging, with the biopsy results below. Which IH stain would be most useful in dx this tumor?
a) Epithelial Membrane Antigen
b) GFAP
c) Neurofilament
d) S-100
e) Ki-67

Central Neurocytoma
c) Neurofilament
–Stains tumor of neural origin
–Neurocytoma
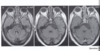
What disease process is pictured?
Central Neurocytoma
- Usually presents w/ increased ICP / HA
- Often intraventricular esp @ Foramen of Monro
- Young adults – btw 2nd & 4th decades
- Treatment – resection
- Benign prognosis
A patient presents with an ipsilateral decrease in smell, ipsilateral optic atrophy with decreased visual acuity & color vision, and contralateral papilledema.
1. What is this syndrome called?
- What type of lesion would cause this syndrome and where?
- Why?

- Foster Kennedy Syndrome
- Meningioma Olfactory Groove
- Increased Intracranial Pressure
Patient has a history of cancer suffered from his first seizure and has post-ictal hemiparesis. His BP is 205/100, fingerstick blood glucose = 60, Na 125. What is the likely cause of his seizure?
Metastasis
A seizure with postictal hemiparesis in a patient with known cancer should be presumed to be related to brain metastases until proven otherwise. Paraneoplastic limbic encephalitis would be much less likely, and hypertensive encephalopathy, hypoglycemia, and hyponatremia would be unlikely to produce focal deficits. Moreover, the patient does not have severe enough hypertension, hypoglycemia, or hyponatremia to produce a seizure.
What antibodies are associated with the following conditions?
- Sensory Neuronopathy
- Lambert-Eaton myasthenic syndrome
- Paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration
- Stiff-person syndrome
- Polymyositis
- Anti-Hu
- Calcium channel antibodies
- Anti-Yo (PCA-1)
- Anti-amphiphysin antibodies/GAD-65
- Anti-Jo-1
What would happen if you withdrew bromocriptine from a patient that you were treating for her prolactinoma?
a) Prolactinoma would re-expand
b) Prolactinoma would decrease in size
c) No effect
a) Prolactinoma would re-expand
Bromocriptine is a dopamine agonist.
Dopamine inhibits prolactin production -> Thus the prolactinoma would re-expand.
What is pictured?

Glioblastoma Multiforme
CLOSED RING of enhancement
List 4 tumors that can occur at the cerebellopontine angle
- Schwannoma (acoustic neuroma)
- Meningioma
- Epidermoid (Cholesteatoma)
- Mets
Meningioma, Schwannoma, or Both
1) Common tumor of the CPA
2) Epithelial membrane antigen, (EMA) +
3) Cells joined by many desmosomes
4) S-100 + on immunohistochemistry
5) Antoni A and B areas and Verocay bodies
6) Contrast Enhancing
1) Both
2) Meningioma
3) Meningioma
4) Schwannoma
5) Schwannoma
6) Both
What type of tumor is pictured?

Schwannoma
- Most common nerve sheath tumor
- Commonly arises from CN VIII à “Acoustic Neuroma”
- Benign (often single)
- If bilateral think NF2 on chromosome 22