Behavioral Neurology Flashcards
hyperintensity of the caudate and putamen; cortical ribbon on MRI
CJD
- rapidly progressive mental deterioration
- myoclonus (provoked by startle)
- extrapyramidal signs (hypokinesia, rigidity)
- cerebellar manifestations (nystagmus, ataxia)
- visual disturbance
- akinetic mutism
CJD
positive 14-3-3 protein in CSF
CJD
Pathology: loss of neurons, spongiform degeneration, or plaques positive for PrPSc
CJD
Clinical features of CJD
- rapidly progressive mental deterioration
- myoclonus (provoked by startle)
- extrapyramidal signs (hypokinesia, rigidity)
- cerebellar manifestations (nystagmus, ataxia)
- visual disturbance
- akinetic mutism
What clinical symptoms are most compatible with the disease process seen in the picture?
a) Dementia, social disinhibition
b) Memory loss, language deficits, visuospatial impairment
c) Acute course of hypersalivation, hydrophobia, encephalopathy & death
d) Writhing fluid movements, ataxia, psychosis
e) Parkinsonism, hallucinations, neuroleptic sensitivity

Lewy Body Dementia
e) Parkinsonism, hallucinations, neuroleptic sensitivity
What clinical symptoms are most compatible with the disease process seen in the picture?
a) Dementia, social disinhibition
b) Memory loss, language deficits, visuospatial impairment
c) Acute course of hypersalivation, hydrophobia, encephalopathy & death
d) Writhing fluid movements, ataxia, psychosis
e) Parkinsonism, hallucinations, neuroleptic sensitivity

Alzheimer’s Disease
b) Memory loss, language deficits, visuospatial impairment
What are 5 things that can be seen on pathology in Alzheimer’s Disease?
Neuritic Plaques
Neurofibrillary Tangles
Hirano Bodies
Neuronal Granulovacuolar degeneration
Deposition of Amyloid in blood vessel walls
What clinical symptoms are most compatible with the disease process seen in the picture?
a) Dementia, social disinhibition
b) Memory loss, language deficits, visuospatial impairment
c) Acute course of hypersalivation, hydrophobia, encephalopathy & death
d) Writhing fluid movements, ataxia, psychosis
e) Parkinsonism, hallucinations, neuroleptic sensitivity

Rabies
= Negri Bodies
c) Acute course of hypersalivation, hydrophobia, encephalopathy & death
What is the pathology pictured?

Negri Bodies
seen in Rabies
Acute course of hypersalivation, hydrophobia, encephalopathy & death
What clinical symptoms are most compatible with the disease process seen in the picture?
a) Dementia, social disinhibition
b) Memory loss, language deficits, visuospatial impairment
c) Acute course of hypersalivation, hydrophobia, encephalopathy & death
d) Writhing fluid movements, ataxia, psychosis
e) Parkinsonism, hallucinations, neuroleptic sensitivity

Pick’s Disease (FTD)
a) Dementia, social disinhibition
What clinical symptoms are most compatible with the disease process seen in the picture?
a) Dementia, social disinhibition
b) Memory loss, language deficits, visuospatial impairment
c) Acute course of hypersalivation, hydrophobia, encephalopathy & death
d) Writhing fluid movements, ataxia, psychosis
e) Parkinsonism, hallucinations, neuroleptic sensitivity
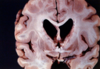
Caudate Atrophy
seen in Huntington’s Disease
d) Writhing fluid movements, ataxia, psychosis
Man presented with visual hallucinations and altered mentation for 6 months before becoming bed-bound. A brain biopsy was conducted. What statement about the patient’s disease is most accurate?
a) It’s treatable w/ PCN
b) Immunosuppression is a primary risk factor for this
c) The patient had signs of Parkinsonism
d) This disease was caused by a tick
e) CSF would likely reveal 14-3-3 positivity

Spongiform change - prion disease
e) CSF would likely reveal 14-3-3 positivity
spongiform change, gliosis, & neuronal loss = classic triad
Misfolding maybe induced by mutation or exposure of normal cellular prion protein to pathogenic prions;
Misfolding alters 2ndary structure so that the protein becomes highly resistant to chemical or thermal methods of sterilization.
36YOF s/p gastric bypass who 3 months later developed confusion, feeling off balanced and shaky eyes. Her brain biopsy is shown.
- What did she have?
- What could have prevented her symptoms?
- What structure was affected?
- What nucleus of the thalamus is the damage connected to?

Wernicke’s Encephalopathy
Thiamine intake
Mammillary Bodies
Anterior Nucleus
What are the alpha-synucleinopathies?
L = LBD A = alpha synucleinopathies M = MSA P = PD
All the rest are tauopathies


