Neuromuscular Flashcards
- What nerve is involved?
- The above nerve is a branch of what nerve?
- What muscles does the nerve innervate?

- Anterior Interosseus Nerve
- Median Nerve
- Flexor pollicis longus, flexor digitorum profundus 1&2, pronator quadratus
The C4 dermatome lies adjacent to which dermatome on the trunk?
T2

Damage to long thoracic nerve causes what
scapular winging due to weakness of serratus anterior muscle
gene mutation seen in 10-20% AD familial cases of ALS
SOD1 (Superoxide Dismutase)
- chromosome 21q22
- toxic gain of function of affected gene
Emery-Dreifus Muscular Dystrophy
-X-linked
Defect in gene encoding for EMERIN protein
- contractures at the elbows, ankles, & neck
- cardiac involvement is prominent & have serious conduction abn often requiring a pacemaker
- muscle weakness in upper arms 1st then later pelvic girdle & distal legs
- What does this picture represent?
- Name the associated genetic mutation
- Clinical presentation
- Patients are at increased risk of what with anesthesia?
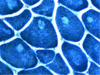
- Central core myopathy
- Autosomal Dominant
- mutation in the ryanodine receptor gene RYR1, chromosome 19 - weakness & hypotonia soon after birth
- proximal weakness worse in the pelvic girdle (facial, bulbar, ocular usually spared) - increased risk malignant hyperthermia w anesthesia
This biopsy is consistent with what NM disease?
Genetics of condition?
Typical age of onset?
Clinical Features?

Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy
Genetics: Most common hereditary NM disease
X-linked recessive disorder due to absence of dystrophin
- out-of-frame deletion in the dystrophin gene at Xp21 site
-1/3 of cases result from new mutations
Clinical Features: Prox musc weakness btw 3 & 5 yrs
Waddling gait, toe walking, difficulty arising from floor, frequent falls
Pseudohypertrophy of calves
Increased lumbar lordosis
Hip girdle weakness
(Dystrophic changes on biopsy)
What conditions is the following seen in?

Ragged red fibers
Seen in:
Mitochondrial myopathies
AZT induced myopathy
This biopsy is consistent with what NM condition?
What are the clinical features?

Kearns-Sayre Syndrome (Mitochondrial Myopathy) :
Biopsy features: Myofiber w red subsarcolemmal staining on the Gomori Trichrome prep - histologic appearance of a “ragged-red fiber” corresponds to abnormal subsarcolemmal mitochondrial accumulations
Clinical Features:
Progressive external ophthalmoplegia
Retinal degeneration
Heart block*
Hearing loss
Ataxia
Dementia
Short stature
Hypoparathyroidism
Hypothyroidism
Peripheral neuropathy
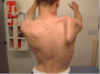
Fascioscapulohumeral muscular dystrophy (FSH)
- Genetics?
- Clinical Presentation?
- Pathology?
- Autosomal Dominant
chromosome 4q35 - Onset infancy to adulthood; 3rd most common muscular dystrophy
Present w facial weakness & scapular winging
Tibialis anterior is affected early
Deltoid is spared
Later the biceps & triceps are affected, sparing the forearm muscles, giving arms Popeye appearance
- Biopsy: necrotic fibers, inflammatory infiltrate, connective tissue proliferation


