Neurology: TBL Questions Flashcards
(50 cards)
Which lamina of the trilaminar embryo does the nervous system derive from?
A. Ectoderm
B. Endoderm
C. Mesoderm
D. Neural crest
A. Ectoderm
- CNS neurons
- Ependymal cells (inner lining of ventricles, make CSF)
- Oligodendrocytes
- Astrocytes

The neural crest cells go on to form which cell types?
A. Brain
B. Spinal cord
C. Ventral motor neurons
D. Dorsal root ganglia
D. Dorsal root ganglia
In addition to:
- PNS
- Sensory ganglia
- Autonomic ganglia and plexuses
- Neural glia
- Schwann cells
During regionalisation which statement is true?
A. Bone Morphogenic Protein helps to specify the ventral/motor part of the spinal cord.
B. Bone Morphogenic Protein helps to specify the dorsal/sensory part of the spinal cord.
C. Bone Morphogenic Protein is released by the notochord to pattern the sensory nerves.
D. Bone Morphogenic Protein is released by the notochord to specify the identity of motor neurons.
B. Bone Morphogenic Protein helps to specify the dorsal/sensory part of the spinal cord.

The lateral ventricles develop from the cavity of which of the following?
A. Diencephalon
B. Mesencephalon
C. Rhombencephalon
D. Telencephalon
D. Telencephalon
- Cerebral hemispheres
- Basal ganglia
- Lateral ventricles

A typical peripheral nerve when observed in cross section in a stained section under the light microscope will be seen to consist of bundles of axons contained within fascicles. Which cell defines or forms the boundary of the fascicle?
A. Endoneurium
B. Epineurium
C. Schwann Cell
D. Perineural cell
D. Perineural cell

The discriminatory function of the blood brain barrier is a consequence of:
A. Capillary fenestrations
B. Tight junctions between endothelial cells
C. Endothelial basement membrane thickness
D. Gap junctions between endothelial cells
B. Tight junctions between endothelial cells
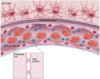
CSF production involves which of the following?

A. Arachnoid granulations
B. Choroid Plexuses
C. Transudate from small cerebral veins in the cerebral hemispheres into ventricles
D. Production by cells within the pia mater on the surface of the brain
B. Choroid Plexuses produced here by specialised ependymal cells
A superior sagittal vein thrombosis is likely to have what effect upon CSF pressure?
A. Reduced absorption of CSF across the arachnoid granulations and a rise in CSF pressure
B. A decrease in the CSF pressure because of a drop in venous pressure inside the skull
C. No change in CSF pressure as there is no connection between the CSF and the cerebral venous system
D. As the production of CSF is pressure dependent any increase in venous back pressure will reduce CSF production. There will be no overall change in CSF pressure

A. Reduced absorption of CSF across the arachnoid granulations and a rise in CSF pressure
CSF production is pressure indepependent, CSF absorption is pressure dependent

How does a Chiari 2 malformation cause hydrocephalus?

A. By causing obstruction to CSF flow at point A
B. By causing obstruction to CSF flow at point B
C. By causing obstruction to CSF flow at point C
D. By causing obstruction to CSF flow at point D
B. By causing obstruction to CSF flow at point B
- Smaller posterior fossa in cranium
- Herniation of cerebellar vermis and tonsils through foramen magnum with aqueductal stenosis: non-communicating hydrocephalus.
- Usually associated with lumbosacral myelomeningocele

Which is correct about hydrocephalus?
A. Hydrocephalus is defined as an increase in CSF volume
B. Hydrocephalus does not cause localising signs
C. In children papilledema is a common sign
D. Hydrocephalus is defined as an increase in CSF pressure
A. Hydrocephalus is defined as an increase in CSF volume
Sympathetic pre-ganglionic neurones are located in which of the following regions?
A. Nucleus of the solitary tract in the medulla
B. Parabrachial nucleus in the pons
C. Paraventricular nucleus in the hypothalamus
D. Preoptic area in the hypothalamus
E. Intermediolateral cell column in the spinal cord
E. Intermediolateral cell column in the spinal cord

Which of the following spinal tracts is most involved in skilled movement?
A. Dorsal column
B. Reticulospinal
C. Vestibulospinal
D. Corticospinal
D. Corticospinal
A 62 year old man complains of trouble walking. On examination, he cannot stand on tip toes and has weakness of dorsiflexion of both ankles. His calves and anterior tibial compartments are wasted. His ankle jerks are absent. These signs are consistent with which type of syndrome?
A. Extrapyramidal
B. Lower motor neurone
C. Neuromuscular junction
D. Upper motor neurone
B. Lower motor neurone
Anterior horn, brainstem or spinal cord out
Which are the three layers of the cerebellar gray matter?
A. Axonal, dendritic and cell body layers
B. Basket cell, interneuron and synaptic layers
C. Dura mater, arachnoid and pia mater
D. Molecular, purkinje and granular layers
D. Molecular, purkinje and granular layers
With reference to the spinal cord image, which of the following would be a likely sign after a lesion to X (shaded area)?
A. Contralateral motor weakness
B. Ipsilateral analgesia
C. Contralateral spasticity
D. Ipsilateral motor weakness
E. Contralateral paraesthesia

D. Ipsilateral motor weakness
A lesion to which of the following ascending tracts in the spinal cord generates the signs or symptoms described: A patient has reduced ability to detect pin-prick on the skin of their right leg.
A. Left spinothalamic tract
B. Right spinothalamic tract
C. Left dorsal column tract
D. Right dorsal column tract
A. Left spinothalamic tract
Which of the following symptoms commonly occurs during the initial stages following a spinal cord injury?
A. Hyperreflexia
B. Hypertension and tachycardia
C. Hypertonia
D. Hypotonia
E. Hypertension and bradycardia
D. Hypotonia
After traumatic injury to the brain or spinal cord, which substance is released from the traumatised tissue that can lead to further damage to surrounding tissue?
A. Glutamate
B. Ketones
C. Lactic acid
D. Prostaglandin E
A. Glutamate
Excitatory neuron: acts on NMDA and AMPA receptors which are over-expressed = excess calcium release
A patient experiences decreased proprioception in the left lower limb. A lesion to which of the following ascending tracts in the spinal cord generates the signs or symptoms described?
A. Left dorsal column tract
B. Right dorsal column tract
C. Left spinothalamic tract
D. Right spinothalamic tract
A. Left dorsal column tract

Hyperalgesia is defined as which of the following?
A. Decreased sensitivity to pain
B. Increased sensitivity to touch
C. Increased sensitivity to pain
D. Pain response to non-noxious stimulus
C. Increased sensitivity to pain
The posterior communicating artery connects which of the following vessels?
A. Vertebral artery to basilar artery
B. Left vertebral artery to right vertebral artery
C. Posterior cerebral artery to anterior cerebral artery
D. Posterior cerebral artery to internal carotid artery
E. Left anterior cerebral artery to right anterior cerebral artery
D. Posterior cerebral artery to internal carotid artery

The major neurotransmitter that characterises the cells of the brainstem raphe nuclei is which of the following?
A. Glutamate
B. Noradrenaline
C. Dopamine
D. Acetylcholine
E. Serotonin
E. Serotonin
- Contributor to feelings of well-being and happiness
- Regulates the sleep cycle along with melatonin
- Regulates intestinal movements.

A 70-year old woman was admitted to the emergency department with a suspected stroke. Radiology showed an infracted region corresponding to the shaded area shown in the photograph. Occlusion of which of the following arteries may have caused infarction in this area?
A. Internal carotid artery
B. Middle cerebral artery
C. Posterior cerebral artery
D. Anterior cerebral artery
E. Lenticulostriate artery

D. Anterior cerebral artery

A 68-year-old male presents to the Emergency Department 2 hours after the onset of symptoms suggestive of acute stroke. With regard to the immediate management of this patient, which of the following statements about medical imaging is correct?
A. Non-contrast computed tomography is performed to detect brain ischaemia
B. Contrast enhanced computed tomography is performed if the patient has had nil by mouth for 4 hours
C. Carotid Doppler ultrasound is performed to assess the patency of the carotid arteries
D. Skull x-ray is performed to exclude bony trauma
E. Non-contrast computed tomography is performed to exclude haemorrhage
E. Non-contrast computed tomography is performed to exclude haemorrhage









