Neurology: Embryology Flashcards
What does the neural plate give rise to?
- Neural tube
- Neural crest cells
What does the notochord become?
Nucleus pulpous of intervertebral disc in adult
What induces overlying ectoderm to differentiate into neuroectoderm and form neural plate?
Notochord
Is the alar plate (dorsal) sensory or motor?
Sensory
Is the basal plate (ventral) sensory or motor?
Motor
What are the three primary vesicles in the developing brain (superior to inferior)?
- Forebrain (prosencephalon)
- Midbrain (mesencephalon)
- Hindbrain (rhombencephalon)

What are the five secondary vesicles in the developing brain (superior to inferior)?
- Telencephalon (from forebrain)
- Diencephalon (from forebrain)
- Mesencephalon (from midbrain)
- Metencephalon (from hindbrain)
- Myelencephalon (from hindbrain)

What are the adult derivatives of the walls and cavities of the telencephalon?
Walls
- Cerebral hemispheres
- Basal ganglia
Cavities
- Lateral ventricles

What are the adult derivatives of the walls and cavities of the diencephalon?
Walls
- Thalamus
- Hypothalamus
Cavities
- Third ventricles

What are the adult derivatives of the walls and cavities of the mesencephalon?
Walls
- Midbrain
Cavities
- Cerebral Aqueduct

What are the adult derivatives of the walls and cavities of the metencephalon?
Walls
- Pons
- Cerebellum
Cavities
- Upper part of fourth ventricle

What are the adult derivatives of the walls and cavities of the myelencephalon?
Walls
- Medulla
Cavities
- Lower part of fourth ventricle

What develops from the neuroepithelia in the neural tube?
- CNS neurons
- Ependymal cells (inner lining of venticles, make CSF)
- Oligodendrocytes
- Astrocytes
What develops from the neural crest?
- PNS neurons
- Schwann cells
What develops from the mesoderm?
- Microglia (like Macrophages)
- Failure of caudal neuropore to close, but with no herniation
- Usually seen at lower vertebral levels
- Dura is intact
- Associated with tuft of hair or skin dimple at level of bony defect
Spina bifida occulta
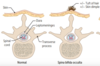
Meninges (but no neural tissue) herniate through bony defect
Meningocele

Meninges and neural tissue (eg. cauda equina) herniate through bony defect
Myelomeningocele

- Increased alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) in amniotic fluid and matternal serum
- Increased acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in amniotic fluid
Neural tube defects (except spina bifida occulta = normal AFP)
- Neuropores fail to fuse (4th week)
- Persistant connection between amniotic cavity and spinal canal
Neural tube defects
What deficiencies are neural tube defects associated with?
- Maternal diabetes
- Folate deficiency
Exposed, unfused neural tissue without skin/meningeal covering
- Myeloschisis
- Also known as rachischisis
- Failure of rostral neuropore to close → No forebrain, open calvarium
- Clinical findings: polyhydramnios (no swallowing centre in brain)
Anencephaly
MRI:
- Monoventricle
- Fusion of basal ganglia (star)

Holoprosencephaly














