Neurology: Anatomy and Physiology Flashcards
What is myelin synthesised by in the CNS (including CN II)?
Oligodendrocytes
“COPS: CNS = Oligodendrocytes, PNS = Schwann cells”

What is myelin synthesised by in the PNS (including CN III-XII)?
Schwann cells
“COPS: CNS = Oligodendrocytes, PNS = Schwann cells”
What is the function of myelin?
Wraps and insulates axons: increased space constant and increased conduction velocity

Where along a myelinated axon do action potentials occur?
Nodes of Ranvier, where there are high concenttrattions of Na+ channels
What embryotic structure are Schwann cells derived from?
Neural crest
What is the function of Schwann cells?
Promote axonal regeneration
How many PNS axons does each schwann cell myelinate?
One
“Each “Schwone” cell myelinates only one PNS axon”

What cells are affected in Guillain-Barré syndrome?
Schwann cells
What embryotic structure are oligodendrocytes derived from?
Neuroectoderm
How many CNS axons does each oligodendrocyte myelinate?
Approximately 30

What is the predominant type of glial cell in white mattter?
Oligodendrocyte
What conditions can result from injured oligodendrocytes? (3)
- Multiple sclerosis
- Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)
- Leukodystrophies
What cells are affected in Multiple Sclerosis?
Oligodendrocytes
What sensory receptors exhibit the following:
- Fast twitch
- Myelinated fibres
- Found in all skin, epidermis, some viscera
- Carries pain and temperature
Free nerve endings: A-delta
“A delta plane is fast, but a taxC is slow”

What sensory receptors exhibit the following:
- Slow twitch
- Unmyelinated fibres
- Found in all skin, epidermis, some viscera
- Carries pain and temperature
Free nerve endings: C
“A delta plane is fast, but a taxC is slow”

What sensory receptors exhibit the following:
- Large, myelinated fibres
- Adapt quickly
- Found in hairless skin
- Carries light touch and position sense
Meissner corpuscles

What sensory receptors exhibit the following:
- Large, myelinated fibres
- Adapt quickly
- Found in deep skin layers, ligaments, joints
- Carries vibration and pressure
Pacinian corpuscles

What sensory receptors exhibit the following?
- Large, myelinatted fibres
- Adapt slowly
- Found in fingertips and superficial skin
- Carries pressure, deep static touch and position sense
Merkel discs
What sensory receptors exhibit the following?
- Dendritic endings with capsule
- Adapt slowly
- Found in finger tips and joints
- Carries pressure, slippage of objects along skin surface and joint angle change
Ruffini corpuscles

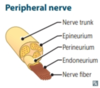
Thin, supportive connective tissue that ensheaths and supports individual myelinated nerve fibres
Endoneurium
“Endo = inner”

Blood-nerve permiability barrier that surrounds a fasicle of nerve fibres
Perineurium
- “Peri = around”*
- “Perineurium: blood-nerve permeability”*

What part of the nerve sheath needs ot be rejoined in microsurgery for limb reattachment
Perineurium
Dense connective tissue that surrounds entire nerve (fascicles and blood vessels)
Epineurium
“Epi = outer”
What cell has a “fried egg” appearance histologically?

Oligodendrocytes







































