Neuro: Somatosensation I Flashcards
What sensations does the somatosensory system provide?
- Touch (tactile sensation)
- Proprioception (sense of body position)
- Temperature
- Pain (Nociception)
Describe the structure of a peripheral nerve
- A peripheral nerve contains multiple bundles of axons each surronded by a connective sheath called perineurium
- Each bundle of axons surronded by perineurium is called a fasicle
- Space between each fasicle filled with epineurium
- Each individual axon within a fasicle is surronded by endoneurium
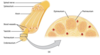
Do peripheral nerves contain incoming sensory axons or outgoing motor axons?
Peripheral nerves contain both incoming sensory axons and outgoing motor axons
Describe the features of the peripheral nerves at the point that they enter the spinal cord
- When a peripheral nerve enters spinal cord it forms a dorsal root ganglion
- This dorsal root ganglion then splits into dorsal roots and ventral roots which enter the spinal cord at different points
Are dorsal root ganglion cells sensory or motor receptors?
Dorsal root ganglion cells are the sensory receptors of the somatosensory systems
What are the 2 broad classes of somatosensory afferent fibre (fibres that run from recptor endings to spinal cord)?
- Large fibres - Myelinated and fast conducting
- Small fibres - Thinly myelinated or unmyelinated and slow conducting

What sensations are each class of afferent somatosensory fibre responsible for?
- Large fibres - Tactile sensations (touch) and proprioception
- Small fibres - Temperature, nocieception

What does the quality of sensation provided somatosensory system depend on?
- Quality of sensation depends on the type of afferent fibre and the stimulus they respond to
- E.g. Some thermosensitive afferent fibres only respond to cooling and so won’t respond to warming
Somatosensory afferent fibres have receptors within the skin called cutaneous receptors. Name the different types of cutaneous receptor
- Meissner corpuscle
- Ruffini corpuscle
- Pacinian corpuscle
- Merkel’s disk
- Free nerve endings

For the different cuteaneous receptors of the somatosensory sysyem state whether they’re superficial or deep?
- Meissner’s corpusule - superficial
- Merkel’s disc - superficial
- Ruffini corpuscle - deep
- Pacinian corpuscle - deep
Another type of somatosensory receptor are proprioceptors, where within the body are proprioceptors located?
Prorioceptors are the muscle spindle found within the muscle fibres of flexors and extensors

Name the receptor type responsible for detecting each type of sensation provided by the somatosensory system
- Propreoception: A-α afferents (Muscle spindle)
- Tactile sensation (discriminative touch): A-β afferents, these include:
- Superficial cutaneous - Meissner’s corpuscle and Merkel’s disc
- Deep cutaneous - Ruffini corpuscle and Pacinian corpuscle
- Temperature, pain and low-resolution tactile sensation: A delta fibres and C fibres
What are the relative conduction speeds for each of the afferent fibres of the somatosensory system?
- A-α afferents - fastest conducting
- A-β afferents - 2nd fastest conducting
- A delta fibres - Moderate conduction speed
- C fibres - slow conducting
Each of the 4 cutaneous tactile receptors are responsible for sensing a different type of tactile sensation, name these tactile sensations
- Merkel’s disc - Very fine tactile discrimination (e.g. discriminating different bumps in braille)
- Meissner’s corpuscle - Fine tactile discrimination (lesser extent than merke’s disc)
- Ruffini corpuscle - Stretch of skin in response to touching surface
- Pacinian corpuscle - Vibration, stretch of skin in response to touching surface
Each of the 4 cuteneous tactile receptors have receptive fields, what is a receptive field?
- Area of the skin that needs to be stimulated in order to produce a response from the cutaneous tactile receptors

What are the relative sizes of the receptive fields for each of the 4 cutaneous tactile receptors?
- Merkel’s disc - lots of really small receptive fields
- Meissner’s corpuscle - Lots of small receptive fields
- Ruffini corpuscle - Large receptive field, small number of them
- Pacinian corpuscle - Large receptive field, small number of them
What are the 2 major pathways of the somatosensory system?
- Dorsal column - medial lemniscal system (DCML)
- Spinothalamic tract (STT) or Anterolateral system
What afferent fibres are part of the dorsal column-medial lemniscal system (DCML)?
- A-α afferent fibres
- A-β afferent fibres
What somatosensory sensations are provided by the dorsal-column medial lemniscal system?
- Proprioception
- Tactile sensation (discriminative touch)
What afferent fibres are part of the spinothalamic tract?
- A-delta fibres
- C fibres
What somatosensory sensations are provided by the spinothalamic tract?
- Temperature
- Pain
- Low-resolution discriminative touch
Describe the pathway of the dorsal column-medial lemniscal system
- Peripheral axon of A-α or A-β-afferent fibre runs from the receptor endings in skin or muscle to their cell body in dorsal root ganglion
- At cell body peripheral axon becomes central axon and runs from the cell body into dorsal column of spinal cord and up to the dorsal column nuclei in the medulla
- At dorsal column nuclei central axon of afferent fibre synapses with dorsal column nuclei neurons
- Axons of dorsal column nuclei neurons ascend up medial lemiscus through the midbrain and terminate in ventral posterior nuclear complex in the thalamus
- At ventral posterior nuclear complex axons of dorsal column nuclei neurons synapse with thalamic neurons
- Thalamic neurons run from ventral posterior nucleus complex of thalamus to the primary somatosensory cortex

Describe the pathway of the spinothalamic tract (anterolateral system)
- Peripheral axons of A-delta or C fibres run from receptor endings in skin to their cell body in dorsal root ganglion
- At cell body peripheral axon becomes central axon which runs from into dorsal column of spinal cord and synapses with 2nd order neuron
- 2nd order neuron crosses to other side of spinal cord and ascends up anterolateral column through the spinal cord, through the medulla, through the midbrain to the ventral posterior nuclear complex of thalamus
- At ventral posterior nuclear complex 2nd order neuron synapses with 3rd order neuron
- 3rd order neuron runs from ventral posterior nuclear complex to primary somatosensory cortex

Describe the pathway of Dorsal column-medial leminiscus system from head and face
- In head and face sensory info comes from cranial nerves rather than spinal nerves e.g. trigeminal nerve
- Peripehral axon of trigeminal nerve runs from face to cell body in trigeminal ganglion
- Peripheral axon becomes central axon and runs from trigeminal ganglion to principal nucelus of trigeminal complex
- At principal nucleus central axon synapses with trigeminal complex nuclei neurons
- Trigeminal complex nuclei neurons run up trigeminal lemniscous to ventral posterior medial nucleus of thalamus
- Here the trigeminal complex neurons synapse with thalamic neurons
- Thalamic neurons run from ventral posterior nucleus complex of thalamus to the primary somatosensory cortex




