Neuro: Neurotransmitters Systems III: Monoamines Flashcards
What systems control behaviour in the CNS?
- Autonomic nervous sytem
- Hypothalamic-pituitary neurohormones
- Diffuse monoamine system
What are the 4 main systems that make up the diffuse monoamine pathway?
- Noradrenergic Locus Coeruleus
- Serotonergic Raphe Nuclei
- Dopaminergic Substantia Nigra and Ventral tegmental Area
- Cholinergic Basal Forebrain and Brain Stem Complexes
What are the common principles of the 4 diffuse monoamine systems?
- Small set of neurons at core
- Arise from the brain stem
- One neuron influences many others
- Synapses release neurotransmitter molecules into extracellular fluid
Describe the Noradrenaline pathway within the brain
- Synthesised in the Locus coeruleus
- Gets released via adrenergic neurons into the cortex, cerebellum, amygdala, spinal cord and hypothalamus
What are some of the effects of Noradrenaline on the body?
- Increases arousal, wakefullness and exploration
- Increases heart rate and blood pressure
- Plays a role in addiction/gambling
Are Adrenergic receptors pre-synaptic (autoreceptors) or post-synaptic?
Noradrenergic receptors can be either pre-synaptic (autoreceptors) or post-synaptic
What type of receptor are Noradrenergic recptors?
Metabotropic receptors
What are the different types of Adrenergic receptor? - for each receptor name the G protein its coupled to and by extension what enzyme each of those G proteins activates or inhibits
- α1 - Gq which activates Phospholipase C
- α2 - Gi/o which inhibits adenylate cyclase
- β - Gs which activates adenylate cyclase

What effect does the activation of each type of Adrenergic receptor have on the body?
- α1 - Causes smooth muscle contraction and glycogenelysis
- α2 - Inhibits Noradrenaline release (autoreceptor) and inhibits smooth muscle contraction
- β - Causes smooth muscle relaxation, cardiac muscle contraction and Glycogenelysis
What transporter is responsible for the reuptake of Noradrenaline back into the pre-synaptic neurone?
- Noradrenaline transporter (NET)

Once Noradrenaline is taken back up into pre-synaptic neurone via NET what happens to it?
Noradrenaline is then broken down by Monoamine oxidase (MAO)

What effect does reserpine have on Noradrenaline?
- Inhibits vesicular uptake of NA causing NA stores to deplete
What effect does Amphetamine have on Noradrenaline?
- Displaces NA within vesicles causing NA concentration within cytoplasm to increase
- This causes more NA to be released into synaptic cleft
What effect does Cocaine have on Noradrenaline?
- Blocks NA re-uptake
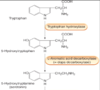
Explain how Dopamine is synthesised
- Tyrosine is converted into DOPA via tyrosine hydroxylase
- DOPA is converted into Dopamine via DOPA decarboxylase

What are the 2 families of Dopamine receptor? What receptors are included in each family?
- D1-like family - Includes D1 and D5 receptors
- D2-like family - Includes D2, D3 and D4 receptors

What G protein are the D1-like receptors and D2-like receptors coupled to and what enzyme do these type of receptors activate/inhibit?
- D1-like receptors: Gs - Activates adenylate cyclase
- D2-like receptors: Gi/o - Inhibits adenylate cyclase
There are dopamine receptors that are heterodimers containing a D1-like receptor and a D2-like receptor. What G protein is this type of receptor coupled to?
Gq - activates phospholipase C

What transporter is responsible for the re-uptake of Dopamine?
Dopamine transporter (DAT)
What happens to doapmine once it’s re-uptaken into pre-synaptic neuron?
It gets broken down by Monoamine oxidase B (MAOB)
Describe the 4 different dopamine pathways within the brain
- Nigrostriatal pathway - Substantia nigra (SN) - Striatum (Str)
- Tubero-hypophyseal pathway - Hypothalamus - pituitary gland (via hypophyseal portal system)
- Mesocortical pathway - Ventral tegmental area - Frontal cortex (includes nucleus accumbens)
- Mesolimbic pathway - Ventral tegmental area (VTA) - Nucleus accumbens, Amygdala and hippocampus

What does the binding of dopamine to the pituitary gland cause?
It prevents the release of prolactin from the pituitary gland
What disease develops as a result of the degeneration of the dopaminergic neurons within the nigrostriatal pathway?
Parkinson’s disease
What condition is caused by hyperactivity of the dopaminergic neurons within the mesolimbic pathway? Why is this?
- This leads to Schizophrenia due to hyperactivity resulting in huge surge of dopamine release