Neuro Flashcards
What is the organization of the meninges in the spinal cord?
What structure in the ventricles of the brain produces CSF?
choroid plexus
Blood-brain barrier structure

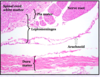
The arrows are pointing to what?
activated microglia
Cell Type

Gitter cells (aka microglia ingesting myelin- foamy cytoplasm)

chromatolysis
Alive or dead neuron?

dead

neuronophagia

spheroid
Steps of wallerian degeneration

Why can regeneration of neurons occur in the PNS but not in the CNS?

Cell type

Reactive astrocytes

gemistocytic astrocytes
Cell type and commonly associate dz

Alzheimer’s type II astrocytes: enlarged, vesicular nuclei; hepatic encephalopathy

microglial nodules
VIRAL infections
premature degradation of normally formed tissues?
abiotrophy
What type of CNS malformation is shown?

hydrocephalus
What type of CNS malformation is shown?

hydrocephalus
What type of CNS malformation is shown?

microencephaly
A lhaso apso presents with this

Lissencephaly

Prosencephalic hypoplasia

Prosencephalic hypoplasia

Cranium bifidum
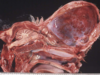
Cranium bifidum
Meningoencephalocele

Cranium bifidum
Meningocele

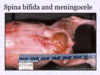

hydranencephaly

porencephaly
A cow presents with this. Likely Disease?

BVD
cerebellar hypoplasia
What toxin causes this and what day?

cyclopia
veratrum californicum
sheep day 14 gestation
How are storage disorders named? Give a couple examples.


storage disorder
Describe the process of ceroid lipofuscin.

What are the histo characteristics of cerebral edema?

Gross characteristics of cerebral edema
herniation of cerebellum
flattening of gyri & sulci

infarct d/t vascular occlusion

Fibrocartilagenous embolism

polioencephalomalacia


polioencephalomalacia
A pig presents with head pressing
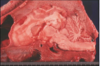
cerebral edema d/t salt poisoning in swine
A cat
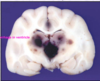
polioencephalomalacia d/t thiamine def

Location of
Globus pallidus
Substantia nigra


nigropallidal encephalomalacia
Cause and C.S. of leukoencephalomalacia?


leukoencephalomalacia
A dog presents after consuming gasoline

Lead poisoning- white matter edema
A dog that consumed gasoline

demyelination

Bacterial meningitis

Equine bacterial meningitis

calf bacterial meningitis
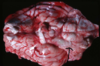
purulent meningitis in a pig 2nd to otitis externa/media

goat brain abscess
Sheep circling
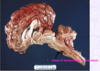
listeriosis in a sheep


ITME


ITME
Describe other lyssaviruses associated w/ disease

Lesions for rabies virus

DDX?
Carnivore or herbivore?

rabies (negri bodies)
purkinje cell= herbivore
A pig presents with a mild fever.

pseudorabies
A horse presents with CNS signs.

EEE
Gross and histo lesions of Canine Distemper virus

DDX?

Canine Distemper virus
DDX? horse



Crypto

Cryptococcus neoformans
Lesions of Equine protozoal encephalomyelitis


A horse presents with ataxia and lameness.

Equine protozoal encephalomyelitis


Lesions of Toxoplasmosis


Toxoplasmosis
cyst in a dog not near the site of inflammation

neospora caninum
Characteristics of neospora in canines and cattle?


bilateral & asymmetrical
NME & NLE

scrapie


meningioma

astrocytoma
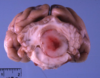
oligodendroglioma
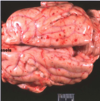
metastatic hemangiosarcoma

metastatic melanoma

metastatic mammary carcinoma


