Liver Flashcards
(82 cards)
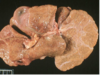
What infectious agent caused this hepatitis?
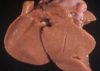
letpospirosis
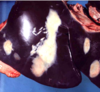
What is the response of the liver to chronic injury? (aka what changes will be observed in the liver?)

fibrosis and nodular regeneration

What is occuring at the portal areas?
Why?

arteriole hyperplasia, oval cell hyperplasia, lobular atrophy
PSS
What are the additional vessels seen going from the portal v. to the vena cava?
Why do they form in this case of acquired PSS?

shunting vessels
form as a result of increase heptic blood flow resistance from chronic hepatic injury that causes secondary fibrosis.
Describe the area of necrosis?

massive hepatocellular necrosis
The picture below shows a viral inclusion body for a dog that presented with acute hepatic necrosis and blue eye. What is the likely DDX?

CAV-1 (infectious CN hepatitis)
In which two species is lipidosis of the liver common?
cats and cows
Histo from liver (gross morph- reticular pattern, local hemorrhage, edges rounded, hepatomegaly)
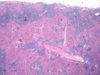
lymphoma in the liver
Liver Pattern?
Cause?

Reticular pattern
aka nutmeg liver
Chronic passive congestion results in centrilobular atrophy & fibrosis
R-heart failure (HCM) or vena caval obstruction (HW)

With a random hepatocellular pattern, what is the likely cause?
hematogenous infection (bacteria, viruses)
ex: salmonella
Morphologic forms of toxic hepatic injury
1. Acute injury
a. Generally cytotoxic
b. Necrosis – CCl4, mycotoxins
c. Degeneration – steroids
d. Lipidosis – anticonvulsants, antineoplastic drugs 2. Chronic Injury
a. Cytotoxic – multifocal necrosis, degeneration, lipidosis
b. Fibrosis and cirrhosis – pyrrolizidine alkaloids, aflatoxins
c. Chronic active hepatitis – copper
3. Vascular injury
a. Hepatic v injury – pyrrolizidine alkaloids
* *4. Neoplasia**
a. Carcinomas – aflatoxins, nitrosamines
b. Adenoma
c. Sarcomas – vinyl chloride-induced hemangiosarcoma
adenocarcinoma or adenoma?

biliary adenocarcinoma
(umbilicated [aka naval like center, pit depresson] necrotic centers)
What is more common in cats- biliary or liver cysts?
biliary cysts
Biliary hyperplasia and fibrosis in the liver is commonly seen with which toxicosis?

Pyrrolizidine alkaloids

cholelithiasis
Why are palm nuts toxic to the liver?
contain cycasin which is converted to toxic methlazoxymethanol by bacteria in GI
Causes of hepatomegaly?
- congestion
- lipidosis
- amyloidosis
- neoplasia
- acute diffuse hepatitis
What infectious cause of hepatitis can be observed with this staining?
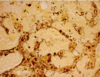
leptospirosis
This pattern in the liver is indicative of what?
Potential Causes?

Chronic Passive congestion
Cz: heartworms, HCM
Top three causes for this condition in animals?

cirrhosis (chronic damage)
- pyrrolizidine alkaloid toxicosis
- chronic drug therapy (ex: anticonvulsants)
- chronic R sided heart disease
Which zone of the liver is affected here?

centrilobular (most susceptible to ichemic damage)
Why are the kidney and urine from a bedlington terrier gunmetal grey/black?

Copper tox causes intravascular hemolysis (hemoglobunuria)
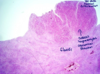
What is observed in the histo slide of liver?
What leads to this?

nodular hyperplasia
response to chronic injury to liver
Differentiate between hepatitis, cholangitis, cholangiohepatitis.
- Hepatitis – inflammation of liver parenchyma
- Cholangitis – inflammation of the biliary system
-
Cholangiohepatitis – inflammation of the portal areas and biliary system with extension into
the liver parenchyma