midterm 1 Flashcards
(95 cards)
Where was the first psychology lab established? By whom? When?
In Leipzig, Germany by Whilhelm Wundt, in 1879
Who wrote “Principles of Psychology” and how was the book regarded “then” as well as today?
William James,
- Very well regarded “then”
- Still very well regarded, but not really used
How do physiology and philosophy relate to roots of psychology?
Physiology is the study of the brain and philosophy is the study of thought. (Psychology) is the study of human thought and behavior.
Who is considered the first U.S. psychologist? Discuss his endeavors.
William James,
considered the first psychologist
-Studied all aspects of human behavior(The James-Lange Theory of Emotion)
-Principles of Psychology in 1890
Who said “It is our attitude at the beginning of a difficult task which, more than anything else, will
affect its successful outcome.”
William James
What is the perspective of structuralism?
feelings and sensations combine systematically to produce the same experience for each person: What people do( Early School of Thought)
What is the perspective of functionalism?
Function of mental processes, including consciousness: How and Why behavior occurs
what is the perspective of gestalt?
(Whole/ Form) naturally seek out patterns
ex. Lisa formed by hearts
an approach to psychology that saw experience as different than the sum of its elements.
Why did structuralism not last as a major school of thought?
What is the definition of psychology?
The science of behavior and mental processes (Study of mind & Behavior(Mental))
What precisely is a perspective? Describe the different foundational perspectives.
(one person’s point of view)
- Structuralism (Basic elements that for a thought, memory,feeling,or sensation)
- Functionalism(How and why ppl behave)
- Gestalt (Whole/Form seek out pattern)
- Evolutionary (Instinct/Habits ex. Survival of the fittest)
- Humanistic 1900’s(Gandhi all humans are good and want to do their best)
- Psycho dynamic(Sigman Froyd ex. when someone is mad at someone else but take it out on others)
- Behavioral (Overt Dependent on punishment/Reward ex. If you see a cop at a stop sign do you stop)
- Cognitive 1900’s(William James Thinking Component- behaviors are influence by the way ppl think about the world)
What are the three different types (categories) of psychology?
- Clinical
- Academic
- Applied
*Know the names and basic description of psych’s sub-fields.
- Clinical Psychology(assessment and treatment of mental illness and disability.)
- Cognitive and perceptual psychology(How we perceive and process information)
- counseling psychology(encompasses research and applied work)
- Developmental psychology( the social and mental development of children)
- Experimental psychology(scientific investigation of basic psychological processes such as learning, memory, and cognition in humans and animals.)
- Health psychology(psychological and behavioral processes in health)
- Industrial/ Organizational psychology(scientific study of employees, workplaces, and organization)
- Neuropsychologists and Behavioral Neuropsychology( relationships between the brain and behavior)
- Quantitative and measurement psychology( methods and techniques of human attributes, the statistical and mathematical modeling of psychological processes)
- Social Psychology.(social interactions, including their origins and their effects on the individual)
Why are the words “it depends” so important for psych questions?
Because it depends on individual and situation given
Why can psychology be considered a science?
Psychology uses systematic observations and experimentation just like other sciences.
empirical evidence
Data and observations collected through scientific processes; basis of scientific explanations
*Know the steps of the scientific method
1-Ask a question
2- research topic
3-state hypothesis
4-test hypothesis
5-analyze data
6-report results
Population:
The entire group of individuals about whom we desire to collect information.
sample:
the subset of the population from which you are actually collecting data
random sample:
every member of the sample population has the same probability of being included. (This ensures a representative sample.)
double blind:
neither the researcher nor the subjects know which treatment a subject is receiving(use to prevent bias)
Research methods - problems & benefits of each ?Which method is best ?
-Survey(Quick & Cheap/ Not reliable info)
-Interview(Reliable info/ Expensive & time consuming)
-Naturalistic Observation(Sit back& view/ Not controllable)
-Experiment(Lab)(Controllable/ expensive & Time Consuming)
And it depends on the situation, what researcher hypothesizes
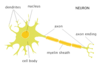
Parts of a neuron:
(Know the location, structure and function)
- Dendrites (Branchlike parts of a neuron around cell body that are specialized to receive information.)
- Axon (A long, thin fiber that transmits signals away from the neuron cell body to other neurons, or to muscles or glands.)
- Synapse (A physical gap between two neurons that functions as the site of information transfer from one neuron to another.)
How many neurons do we have ?
100 billion


