mandibular molars Flashcards
(181 cards)
Has the greatest mesiodistal dimension of any tooth in the mouth
mandib 1st molar
number of cusps for
mand 1st molar
5
Mand 1st molar
Anchor tooth of Mandibular arch
3 buccla and 2 lingual cusps
mand 1st molar
4 cusps
mand M2
tf Mand M2 is smaller than mand M1
T
C-shaped canal is a special feature of some
lower second molars.
Some or all of the canal orifices are joined in the form of a groove or isthmus with a shape of the letter C.
mand M2
The continuous C-shaped canal
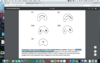
Type I C shaped canal

type 2 c shaped canal
The semicolon shaped canal

Two discrete and separate canals.
Type III : c shaped canal

the shape is an uninterrupted ‘C’ with no separation or division.
c1 melton

the canal shape resembles a semicolon resulting from a discontinuation of the ‘C’ outline.
Category C2: Melton

two separated canals.
Category C3a:

three separated canals. C
Category C3b: Melton

Category C4:
only one round or oval canal.
PERICORONITIS (Acute or Chronic)
Inflammation of the soft tissues surrounding the crown of a partially erupted tooth
Mand M3
tf Third Molars Have a High Incidence of Pathology
F
Not more than 12% of impacted teeth have associated pathology
tf Early Removal of Third Molars Is Less Traumatic
F
Early removal of third molars is actually more traumatic and painful than leaving asymptomatic, nonpathologic teeth in situ
tf Third molars do not possess sufficient force to move other teeth or cause crowding, overlapping
T
tf There is no evidence of a significant increase in third-molar pathology with age
T
tf There is Little Risk of Harm in the Removal of Third Molars
F
Days of “standard discomfort or disability”—pain, swelling, bruising, and malaise result postoperatively, and more than 11,000 people suffer permanent paresthesia
mand 1st molar
has — buccal cusp separateed by — grooves
3;2
names of grooves that separate the 3 buccal cusps of mand
1st molar
mesiobuccal developmental groove and distobuccal developmental groove


