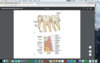
all Flashcards
All Incisors are formed by—-developmental lobes
—– on facial, —- on lingual
All Incisors are formed by four developmental lobes three on facial, one on lingual

Most dominant tooth of “smile zone”
Maxillary Central Incisor
Single central incisor most challenging to restore esthetically
Maxillary Central Incisor
tf max. central incisor facial surface
Crown is slightly longer incisogingivally than mesiodistally
T
tf max central inc facial surface; Root is conical and straight; may incline mesially
F
distally
Correct the following; max central incisor–>
Mesial outline relatively round with contact at incisal 2/3 • Distal outline straight with contact at junction of incisal and middle thirds
Mesial outline relatively straight with contact at incisal 1/3 • Distal outline more rounded with contact at junction of incisal and middle thirds
max. central incisor–>Incisal edge straight with —- mamelons;
mesio-incisal angle —–, distoincisal angle more ——-
Incisal edge straight with 3 mamelons;
mesio-incisal angle sharp, distoincisal angle more rounded
correct the following;
Maxillary central incisor
Two deep developmental depressions between the 4 facial lobes
Two shallow developmental depressions between the three facial lobes
TF Lingual aspect of max. central incisor is narrower than facial aspect mesiodistally
T
Cingulum (bulky convexity at cervical 1/3 of lingual aspect) formed by lingual developmental lobe
on lingual aspect of max central incisor
TF max central incisor;
the central portion of the cingulum is typically located mesial to the center on the crown
F distal
lingual fossa is created by 3 ridges in the max central incisor
F
4–> cingulum, mesial, distal, incisor
TF lingual fossa of max central inc. May have developmental grooves in fossa and lingual pit
T
Crown roughly triangular or wedge shaped
max central incisor(mesial)
tf
max central inc –> Incisal tip and root apex lingual to bisecting line
Incisal tip and root apex on bisecting line
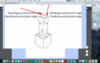
mesial aspect of max central incisor
CEJ line curves greatly toward —-
CEJ line curves greatly toward incisal (
tf incisal ridges are visible from mesial surface of max central inc.
T
which is false about max central incisors from distal surface?
Shorter incisocervically than mesial
CEJ line more pronounced than mesial
Contact area more cervically positioned than mesial
B
CEJ line less pronounced than mesial
Max central incisor
tf
Due to the turn of the tooth along the arch, you see more of the facial surface of the crown from the distal view. Also, the mesial marginal ridge is not visible from this view
t
incisal of max central incisor
Roughly triangular outline
wider mesiodistally than faciolingually
max central inc (incisal view)
tf
only has max central incisor has only Distinct mesio-facial line angles
Distinct mesio-facial and distofacial line angles
max lat incisors
Termed incisal —- when newly erupted (slightly rounded); after wear it becomes flattened and is termed incisal —-
Termed incisal ridge when newly erupted (slightly rounded); after wear it becomes flattened and is termed incisal edge