M2. U5. RF. Flashcards
Excretion
3

66% water passively reabsorbed
Dialysis
- blood leaves artery in arm to vein in same arm
- add heparin - prevent clotting
- blood circulates through tubes with selectively permeable walls
- membranes keep protein and blood cells in
- tubes make large SA
- dialysis fluid - NB components of blood - flows opposite blood around tubes
- counter-current system - max exchange of substance
- excess substance in blood diffuses into dialysis fluid
- dialysis fluid replenishes lacking blood components
- steep concen. gradient for waste into fluid - needs replacing
- blood circulates several times per 1 treatment
- 6 hours
- before re-entering body, blood filters to lose bubbles
12

urine
the second convoluted part of the renal tubule
distal convoluted tubule
the blood vessel which carries oxygenated blood rich in metabolic waste products to the kidney
renal artery
1

malpighian body
specialised cells with filtration slits out of which the inner wall of the bowman’s capsule consists
podocytes
C

medulla
the hormone which regulates the water content of the blood
ADH or antidiuretic hormone
13

medulla
the blood vessel that transports blood to the glomerulus
afferent arteriole
H

renal artery
8

H+
the process in the functioning of the kidney during which foreign substances are actively added to the filtrate
tubular excretion
6

descending limb of henle
6

water and salts reabsorbed
E

renal capsule
skin excretes:
- sweat
- excess water, salts, urea
the process in the functioning of the kidney during which glucose is reabsorbed into the bloodstream
tubular reabsorption
B

pyramid
4

branch of renal vein
9

loop of henle
5

left kidney
1

vena cava inferior
6

proximal convoluted tubule
Homeostatic control of blood pH.
- regulate with distal convoluted tubule
- too low: H+ ions secreted from blood. H+ ions thus leave blood, pH returns to normal
- too high: fewer H+ ions secreted from blood.
11

impermeable to water
the hormone which regulates the concentration of sodium ions of the blood
aldosterone
adaptations of the proximal convoluted tubule for reabsorption
- long and convoluted - SA
- peritubular cap. network surrounding renal tubule
- lining cells contain mitochondria
- also have microvilli
F

calyx
kidneys receive oxygenated blood from:
renal arteries.
4

glomerulus
2

efferent arteriole
9

distal convoluted tubule
renal pelvis
the renal calyces open into this.
Tube connecting the bladder to the kidneys
ureter
adaptations of the malpighian body for filtation.
- afferent wider than efferent
- capillary network of glomerulus - large surface area
- bowman’s capsule c-shaped - large SA
- endothelial layer of caps.
- podocyte layer of bowman’s capsule
- endothelial layer has pores
- podocytes have filtration slits
Homeostatic control of blood salt concentration.
- aldestorone from adrenal gland regulates blood salt concentration
- too low: adrenal cortex secretes more aldestorone. more sodium reabsorbed into blood. blood sodium concentration increases - decreases in urine.
- too high: less aldestorone. fewer sodium ions reabsorbed. blood sodium concentration decreases - more in urine.
9

K+
the part of the renal tubule which extends down into the medulla and forms a hairpin loop
loop of henle
3

afferent arteriole
external structure of the kidney.
- concave side faces vertebral column
- hilum - renal artery and vein arrive and leave; ureter leaves
- enclosed in fat
10

passive reabsorption of water
the first convoluted part of the renal tubule
proximal convoluted tubule
Kidney stones
- when nitrogenous waste and salts don’t dissolve
- solid crystals
- can block ureter
- can be broken by ultrasound waves
- or surgery
the removal of metabolic waste from the body
excretion
1

glomerulus
the structural and functional units of the kidney
nephrons
12

cortex
G

ureter
the removal of undigested substances
egestion
liver and intestines excrete:
- liver excretes urea, bile
- urea transported through blood to kidneys
- bile pigments excreted as bile salts through faeces
the part of the kidney directly below the renal capsule
cortex
a chemical substance that resists pH changes
buffer
7

efferent arteriole
the sum total of all the chemical reactions that occur in a cell
metabolism
the widened region of the ureter into which the renal calyces open
renal pelvis
the Duct into which the distal renal tubules of a number of nephrons open
collecting duct
functions of the kidney
glomerular filtration, tubular reabsorption, tubular excretion
Bilharzia
- schistosoma parasite
- bleeding in gut or bladder
- liver damage, renal failure, bladder cancer
1

wider afferent arteriole
12

peritubular capillary network
reabsorption in the proximal convoluted tubule
- gl, A-acids, water soluble vitamins - actively reabsorbed
- mineral salts and fat soluble vitamins - actively reabsorbed
- water passively reabsorbed by osmosis
renal cortex
Under capsule, red brown
4

water passively withdrawn by osmosis
the apex of each pyramid
renal papilla
a disease where the kidney is so damaged that it can no longer function
renal failure
4

glomerulus
renal capsule
Protective membrane around kidney.
1

gl., A-acids, water soluble vitamins fully reabsorbed
8

proximal convoluted tubule
excretory organs
kideys and bladder, liver and intestines, skin, lungs
medulla
Inner region of kidney. lighter. contains tubes which form pyramids facing the cortex
lungs excrete:
- CO2
- water vapour
- heat
2

branch of renal artery
D

renal pelvis
the process in the functioning of the kidney that occurs in the malpighian body
glomerular filtration
5

bowman’s capsule
a surgical procedure during which the diseased kidney other patient is removed and replaced with a healthy donor kidney
kidney transplant
the metabolic waste product that is formed in the liver from deamination of excess amino acids
urea
the structure on the end of the nephron consisting of the glomerulus and bowman’s capsule
malpighian body
functions of kidney.
- excretion
- osmoregulation
- blood salt content
- blood pH
the release of useful substances
secretion
the process whereby the blood of patients with renal failure is purified artificially by a kidney machine
dialysis
3

afferent arteriole
solid crystals that form in the kidneys from nitrogenous waste and mineral salts
renal stones
3

narrower efferent arteriole
13

ascending limb of henle
the connective tissue membrane which surrounds and protects each kidney
renal capsule
the blood vessel that transports blood away from the glomerulus
efferent arteriole
the blood vessel which carries deoxygenated blood minus waste products from the kidney
renal vein
5

bowman’s capsule
2

right kidney
3
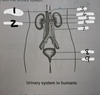
aorta
5

bowman’s capsule
9

urethra
7

ureter
11

collecting duct
renal calyx
renal papilla opens into this
Renal failure
- disfunctional kidney
- acute RF: sudden loss of use - injury, overdose
- chronic RF: develops slowly. caused by diabetes/ high blood pressure. genetic
- waste and water accumulate in body
- possibly fatal
8

bladder
deoxygenated blood leaves the kidneys via the:
renal vein
A

cortex
10

collecting duct
7

final addition of creatinine and urea
11

ascending limb of henle
6

renal vein
Osmoregulation
- regulated by ADH (anti-diuretic hormone)
- too low: osmoreceptors stimulated. more ADH secreted into blood. makes dis.con.tub. more permeable to water. more water reabsorbed. urine concentrates. also stimulate thirst. water content rises to normal.
- too high: osmoreceptors not stimulated. less ADH secreted. dis.con.tub. less permeable to water. less water reabsorbed. urine less concentrated. water content lowers to normal.
renal papilla
The apex of each pyramid
14

duct of bellini
1

vena cava inferior
2

podocytes
Kidneys excrete:
- urine
- excess water
- mineral salts
- nitrogenous wastes (urea, uric acid, creatinine)
8

loop of henle
6

squamous epithelium
7

descending limb of henle
5

Na+ ions actively pumped out
a disease that is caused by the schistosoma parasite
bilharzia
2

mineral salts, fat soluble vitamins partially reabsorbed
4

renal artery


