M2. U2. RF. Flashcards
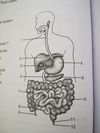
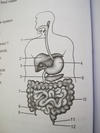
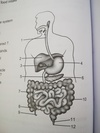
Animal nutrition
a round ball of chewed food that is pushed in the direction of the oesophagus during swallowing
food bolus
functions of the pancreas
- secretes pancreatic juice and enzymes
- secretes insulin and glucagon
8

ileum
2
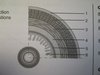
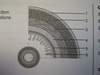
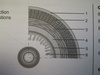
longitudinal muscles
Stomach structure.
- sickle shaped organ below diaphragm
- thick, muscular wall
- opening to oes. closed with cardiac sphincter
- opening to small intest. closed with pyloric sphincter
process in nutrition when food is taken in and enters the alimentary canal
ingestion
process in nutrition when the end products of nutrition are absorbed into the bloodstream
absorption
12

anus
Absorption of water
- passive transport (osmosis)
- capillaries
jejunum
middle part of small intest.
the structures on the tongue that ensure that it can function as a taste organ
taste buds
structures in the small intestine mainly responsible for the absorption of nutrients
Villi
the harmful effect of excess alcohol on The Unborn foetus
foetal alcohol syndrome
group of enzymes involved in the chemical digestion of proteins
proteases
group of enzymes involved in the chemical digestion of carbohydrates
carbohydrases
the maintenance of a constant internal environment in the body
homeostasis
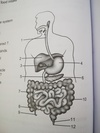
the three parts of the small intestine
duodenum, jejunum, and ileum
end product of protein digestion
amino acids
5

duodenum
Carnivore volume of food intake?
Low. Meat is high in protein and fat.
a metabolic disease characterised by high glucose levels in the blood
diabetes mellitus
Duodenum
- 1st part of small intest.
- connected to gall bladder, pancreatic duct
process in nutrition when undigested remains are removed from the body
Egestion
the group of animals that feed only on animal material
carnivores
4

common bile duct
the three parts of the large intestine
Caecum colon rectum
a diet which contains all the necessary nutrients in the correct quantities
balanced diet
cells in the pancreas which secrete insulin and glucagon
Islets of Langerhans ( alpha and beta cells)
exocrine gland
excreted through ducts
Pharynx function.
passage for food and air from the mouth.
group of enzymes involved in the chemical digestion of fats
lipases
Stomach functions.
- muscles churn food to crush and mix with gastric juices
- glands secrete gastric juices
- food becomes chime
chemical digestion of fats
- pancreas, small intest.
- pancreatic and intestinal juices
- becomes glycerol, fatty acids
Chemical digestion of carbs
- carbohydrases
- mouth, pancreas, small intest.
- saliva, pancreatic and intestinal juice
- becomes glucose
9
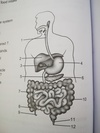
appendix
5

duodenum
11

rectum
Carnivore teeth adaptations.
- incissors - sharp to bite
- canines - long. strong. pierce.kill. tear.
- pre / molars - sharp edges (cusps) to cut
medication used to treat diabetes
insulin
2

liver
nutrients mainly responsible for growth and repair of damaged tissues
proteins
3
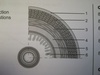
circular muscles
chemical digestion of protein
- proteases
- tummy, pancreases
- becomes amino acids
the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the muscles in the Wall of the alimentary canal that helps move the food particles forward
peristaltic movements
Homeostatic control of blood glucose levels
- HUSH
*
Three parts of the small intestine
- duodenum
- jejunum
- ileum
Absorption of glucose
- active transport
- blood capillaries
active and passive transport
against and down the concentration gradient respectively.
functions of the liver
- produce bile
- glucose converted to glycogen
- excess glucose becomes fat
- deamination: breaks down A. acids to form urea and glucose
- neutralises toxins
- stores vitamins
- prevents blood clotting
Herbivore alimentary canal structure.
- no true stomach
- long intestinal tract
- continuous eating
- long digestive system to digest cellulose
- large caecum ; holds cellulose-digesting bacteria