LOWER LIMB ANATOMY Flashcards
What are the main branches of the lumbo-sacral plexus? And what nerves are involved?
Femoral Obturator Sciatic = Tibial - Medial and Lateral Plantar = Common Fibular -Deep and Superficial Fibular
Describe the role of the sacro-iliac joint. And what ligaments support said joint anteriorly and posteriorly.
Extremely limited movement, essentially for weight transference. Synovial anteriorly and supported by the anterior sacro-iliac ligament Fibrous posteriorly, linked by the interosseous ligament
Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for PECTINEUS.
(i) Superior ramus of pubis
(ii) Pectineal line of femur (just inf to lesser trochanter)
(iii) Adducts & flexes thigh, assists with medial rotation of thigh
(iv) Femoral nerve (L2, L3) - may receive branch from obturator

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for ILIOPSOAS.
(i)PSOAS MAJOR = Sides of T12-L5 vertebrae & discs between them; transverse processes of all lumbar vertebrae
ILIACUS = iliac fossa
(ii) Lesser Trochanter
(iii) Flexing hip & stabilising this joint
(iv) PSOAS MAJOR = (Ant rami of lumbar nerves (L1, L2, L3)
ILIACUS = femoral nerve (L2, L3)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for PSOAS MINOR.
(i) Sides of T12 - L1 vertebrae & intervertebral discs
(ii) Pectineal line, iliopectineal eminence via iliopectineal arch
(iii) Acts with iliopsoas in flexing hip & stabilising hip joint
(iv) Anterior rami of lumbar nerves (L1, L2)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for SARTORIUS.
(i) ASIS & superior part of notch inferior to it
(ii) Superior part of medial surface of tibia
(iii) Flexes, abducts & laterally rotates thigh at hip joint; flexes leg at knee (medially rotating ONLY when knee is flexed)
(iv) Femoral nerve (L2, L3)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for QUADRICEPS FEMORIS (rectus femoris, vastus lateralis, vastus medialis & vastus intermedius).
(i)RF: AIIS & ilium superior to acetabulum
VL: Greater trochanter & lateral lip of linea aspera of femur
VM: intertrochanteric line of linea aspera of femur
VI: anterior & lateral surfaces of shaft of femur
(ii) Via common quadriceps tendon (which attaches to base of patella)
(iii) Extend leg at knee, RF also steadies hip joint & helps iliopsoas flex the thigh
(iv) Femoral nerve (L2, L3, L4)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for ADDUCTOR LONGUS.
(i) Body of pubis inferior to pubic crest
(ii) Middle third of linea aspera fo femur
(iii) Adducts thigh
(iv) Obturator nerve (branch of anterior division) (L2, L3, L4)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for ADDUCTOR BREVIS.
(i) Body & inferior ramus of pubis
(ii) Pectineal line & proximal part of linea aspera of femur
(iii) Adducts thigh, to some extent it also flexes it
(iv) (same as longus!) Obturator nerve (branch of anterior division) (L2, L3, L4)
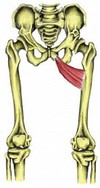
Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for ADDUCTOR MAGNUS.
(i) ADDUCTOR PART: inf ramus of pubis, ramus of ischium
HAMSTINGS PART: ischial tuberosity
(ii) ADDUCTOR PART: gluteal tuberosity linea aspera, medial supracondylar line
HAMSTINGS PART: adductor tubercle of femur
(iii) Combined, they adduct the thigh
ADDUCTOR PART: flexes thigh
HAMSTINGS PART: extends thigh
(iv) ADDUCTOR PART: (same as brevis&longus!)Obturator nerve (branches of posterior division) (L2, L3, L4)
HAMSTINGS PART: tibial part of sciatic nerve (L4)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for GRACILLIS.
(i) Body & inf ramus of pubis
(ii) Superior part of medial surface of tibia
(iii) Adducts thigh; flexes leg; helps rotate leg medially
(iv) Obturator nerve

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for OBTURATOR EXTERNUS.
(i) Margins of obturator foramen & obturator membrane
(ii) Trochanteric fossa of femur
(iii) Laterally rotates thigh & steadies femoral head in acetabulum
(iv) Obturator nerve (L3, L4)
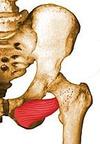
What muscles make up the (i) Anterior Compartment (ii) Lateral Compartment of the leg? What nerves supply the (a) Anterior Compartment (b) Lateral Compartment of the leg?

(i) Tibialis anterior Extensor hallucis longus Extensor digitorum longus Peroneus(fibularis) tertius (ii) Peroneus (fibularis) brevis Peroneus (fibularis) longus
(a) Deep fibular nerve (L4, L5)
(b) Superficial fibular nerve (L5, S1, S2)

What muscles make up the (i) Posterior Superifical Compartment (ii) Posterior Deep Compartment of the leg? What is their common innervation?

(i) Gastrocnemius
Soleus
Planatris
(ii) Popliteus
Flexor Hallucis Longus
Flexor Digitorum Longus
Tibialis Posterior
TIBIAL NERVE (L4 - S3)

What muscles make up the medial thigh? What nerve (majority) supplies these muscles?
Adductor Longus, Brevis, Magnus
Gracillis
Obturator Externus
MAJORITY: Obturator nerve (L2 - L4)
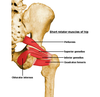
Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for GLUTEUS MAXIMUS.
(i) Ilium posterior to posterior gluteal line; dorsal surface of sacrum and coccyx; Sacrotuberous ligament
(ii) Most fibres end in the Iliotibial tract, which inserts into lateral condyle of tibia; some fibres insert on gluteal tuberosity
(iii) Extends thigh (especially from fixed position) & assists lateral rotation of thigh; steadies thigh & assists in rising from sitting position
(iv) INFERIOR gluteal nerve (L5, S1, S2)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for GLUTEUS MEDIUS.
(i) External surface of ilium between anterior and posterior gluteal lines
(ii) Lateral surface of greater trochanter of femur
(iii) Abduct and medially rotate thigh; keep pelvis level when ipsilateral limb is weight-bearing and advance opposite (unsupported) side during swing phase
(iv) Superior gluteal nerve (L5, S1)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for GLUTEUS MINIMUS.
(i) External surface of ilium between anterior and inferior gluteal lines
(ii) Anterior surface of greater trochanter of femur
(iii) SAME AS MEDIUS: Abduct and medially rotate thigh; keep pelvis level when ipsilateral limb is weight-bearing and advance opposite (unsupported) side during its swing phase
(iv) SAME AS MEDIUS: Superior gluteal nerve (L5, S1)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for TERNSOR FASICA LATAE.
(i) Anterior superior iliac spine; anterior part of iliac crest
(ii) Iliotibial tract, which attaches to the lateral condyle of tibia
(iii) SAME AS GLUT MED & MIN: Abduct and medially rotate thigh; keep pelvis level when ipsilateral limb is weight-bearing and advance opposite (unsupported) side during its swing phase
(iv) SAME AS GLUT MED & MIN: Superior gluteal nerve (L5, S1)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for PIRIFORMIS.
(i) Anterior surface of sacrum; Sacrotuberous ligament
(ii) Superior border of greater trochanter of femur
(iii) Laterally rotate extended thigh and abduct flexed thigh; steady femoral head in acetabulum (pirifomis, obt. int, sup & inf gemelli & quadratus femoris all have same action)
(iv) Branches of anterior rami of S1, S2

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for OBTURATOR INTERNUS.
(i) Pelvic surface of obturator membrane and surrounding bones
(ii) Medial surface of greater trochanter (trochanteric fossa) of femur
(iii) Laterally rotate extended thigh and abduct flexed thigh; steady femoral head in acetabulum (pirifomis, obt. int, sup & inf gemelli & quadratus femoris all have same action)
(iv) Nerve to obturator internus (L5, S1)
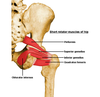
Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for SUP & INF GEMELLI.
(i)SUPERIOR: ischial spine
INFERIOR: ischial tuberosity
(ii) Medial surface of greater trochanter (same as obt internus)
(iii) Laterally rotate extended thigh and abduct flexed thigh; steady femoral head in acetabulum (pirifomis, obt. int, sup & inf gemelli & quadratus femoris all have same action)
(iv) SUPERIOR: Same as obt internus (nerve to…)
INFERIOR: Same as quadratus femoris (nerve to …)
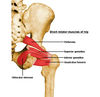
Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for QUADRATUS FEMORIS.
(i) Lateral border of ischial tuberosity
(ii) Quadrate tubercle on intertrochanteric crest of femur and area inferior to it
(iii) Laterally rotate extended thigh and abduct flexed thigh; steady femoral head in acetabulum (pirifomis, obt. int, sup & inf gemelli & quadratus femoris all have same action)
(iv) Nerve to quadratus femoris (L5, S1)
Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for SEMITENDINOSUS.
(i) Ischial tuberosity (common hamstrings origin)
(ii) Medial surface of superior part of tibia
(iii) Extend thigh; flex leg & rotate it medially when knee is flexed; when thigh and leg are flexed, these muscles can extend the trunk
(iv) Tibial division of sciatic nerve of tibia (L5, S1, S2)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for SEMIMEMBRANOSUS.
(i) Ischial tuberosity (common hamstrings origin)
(ii) Posterior part of medial condyle of tibia; reflected attachment forms oblique popliteal ligament
(iii) (Same as tendinosus) Extend thigh; flex leg and rotate it medially when knee is flexed; when thigh and leg are flexed, these muscles can extend the trunk
(iv) (same as tendinosus) Tibial division of sciatic nerve of tibia (L5, S1, S2)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for BICEPS FEMORIS.
(i) LONG HEAD: Ischial tuberosity (common hamstrings origin)
SHORT HEAD: linea aspera & lat supracondylar line of femur
(ii) Lateral side of head of fibula; tendon is split at this site by fibular collateral ligament of knee
(iii) Flexes leg and rotates it laterally when knee is flexed; extends thigh
(iv) LONG HEAD: tibial division of sciatic nerve (L5, S1, S2)
SHORT HEAD: common fibular division of sciatic nerve (L5, S1, S2)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for TIBIALIS ANTERIOR.
(i) Lateral condyle & superior half of lateral surface of tibia & IO membrane
(ii) Medial & inferior surfaces of medial cuneiform and base of 1st metatarsal
(iii) Dorsiflexes ankle & inverts foot
(iv) Deep fibular nerve (L4, L5)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for EXTENSOR DIGITORUM LONGUS.
(i) Lateral condyle of tibia & superior 3/4’s of medial surface of fibular & IO membrane
(ii) Middle & distal phalanges of lateral 4 digits
(iii) Extends lateral 4 digits & Dorsiflexes ankle
(iv) Deep fibular nerve (L4, L5)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for EXTENSOR HALLUCIS LONGUS.
(i) Middle part of anterior surface of fibula & IO membrane
(ii) Dorsal aspect of base of distal phalanx of great toe (hallux)
(iii) Extends great toe & Dorsiflexes ankle
(iv) Deep fibular nerve (L4, L5)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for FIBULARIS TERTIUS.
(i) Inferior 1/3 of anterior surface of fibula & IO membrane
(ii) Dorsum of base of 5th metacarpal
(iii) Dorsiflexes ankle & aids in eversion of foot
(iv) Deep fibular nerve (L4, L5)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for FIBULARIS LONGUS.
(i) Head & superior 2/3rds of lateral surface of fibula
(ii) Base of 1st metatarsal & medial cuneiform
(iii) Everts foot & weakly plantar flexes ankle
(iv) Superficial fibular nerve (L5, S1, S2)
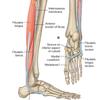
Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for FIBULARIS BREVIS.
(i) Inferior 2/3rds of lateral surface of fibula
(ii) Dorsal surface of tuberosity on lateral side of base of 5th metatarsal
(iii) same as fib longus - Everts foot and weakly plantarflexes ankle
(iv) same as fib longus - Superficial fibular nerve (L5, S1, S2)

What muscles make up the lateral compartment of the leg? What is their common (i) action and (ii) innervation?
Fibularis (peroneus) longus & brevis
(i) Everts foot & weakly plantarflexes ankle
(ii) Superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve (L5, S1, S2)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for GASTROCNEMIUS.
(i) LAT HEAD: lateral aspect of lateral condyle of femur
MED HEAD: popliteal surface of femur; superior to medial condyle
(ii) Posterior surface of calcaneus via calcaneal tendon (Common attachment of sup post compartment)
(iii) Tibial nerve (S1, S2)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for SOLEUS.
(i) Posterior aspect of head & superior 1/4 of posterior surface of fibula; soleal line & middle 1/3 of medial border of tibia; & tendinous arch extending between the bony attachments
(ii) Posterior surface of calcaneus via calcaneal tendon (common attachment of sup post compartment)
(iii) Plantarflexes ankle independent of position of knee; steadies leg on foot
(iv) Tibial nerve (S1, S2)

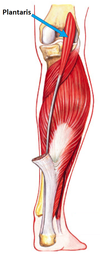
Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for PLANTARIS.
(i) Inferior end of lateral supracondylar line of femur; oblique popliteal ligament
(ii) Posterior surface of calcaneus via calcaneal tendon (common attachment of sup post compartment)
(iii) Weakly assists gastrocnemius in plantarflexing the ankle
(iv) Tibial nerve (S1, S2)
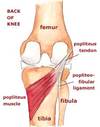
Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for POPLITEUS.
(i) Lateral surface of lateral condyle of femur & lateral meniscus
(ii) Posterior surface of tibia, superior to soleal line
(iii) Weakly flexes knee & unlocks it by rotating the femur 5 degrees on fixed tibia; medially rotates tibia of the unplanted limb
(iv) Tibial nerve (L4, L5, S1)
Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for FLEXOR HALLUCIS LONGUS.
(i) Inferior 2/3rds of posterior surface of fibula; inferior part of IO membrane
(ii) Base of distal phalanx of great toe (hallux)
(iii) Flexes great toe at all joints; weakly plantarflexes ankle; supports medial longitudinal arch of the foot
(iv) Tibial nerve (S2, S3)
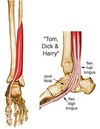
Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for FLEXOR DIGITORUM LONGUS.
(i) Medial part of posterior surface of tibia inferior to soleal line; by a broad tendon to fibula
(ii) Bases of distal phalanges of lateral 4 digits
(iii) Flexes lateral four digits; plantarflexes ankle; supports longitudinal arches of foot
(iv) Tibial nerve (S2, S3)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for TIBIALIS POSTERIOR.
(i) IO membrane; posterior surface of tibia inferior to soleal line; posterior surface of fibula
(ii) Tuberosity of navicular, cuneiform, cuboid and sustentaculum tali of calcaneus; bases of 2nd, 3rd, and 4th MT.
(iii) Plantarflexes ankle & inverts foot
(iv) Tibial nerve (L4, L5)

What muscles make up the 1st layer of the sole of the foot?
Adductor Hallucis
Flexor Digitorum Brevis
Adductor Digiti Minimi
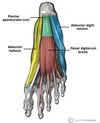
Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for ADDUCTOR HALLUCIS.
(i) Medial tubercle of tuberosity of calcaneus; flexor retinaculum; plantar aponeurosis
(ii) Medial side of base of proximal phalanx of 1st digit
(iii) Abducts and flexes 1st digit (hallux)
(iv) Medial plantar nerve (S2, S3)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for FLEXOR DIGITORUM BREVIS.
(i) Medial tubercle of tuberosity of calcaneus; plantar aponeurosis; intermuscular septa
(ii) Both sides of middle phalanges of lateral four digits
(iii) Flexes lateral four digits
(iv) Medial Plantar Nerve (S2, S3)

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for ABDUCTOR DIGITI MINIMI.
(i) Medial & lateral tubercles of tuberosity of calcaneus; plantar aponeurosis; intermuscular septa
(ii) Lateral side of base of proximal phalanx of 5th digit
(iii) Abducts and flexes little toe (5th digit)
(iv) Lateral Plantar Nerve (S2, S3)

What muscles make up the 2nd layer of the sole of the foot?
Quadratus Plantae
Lumbricals
Tendons of FDL

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for QUADRATUS PLANTAE.
(i) Medial surface & lateral margin of plantar surface of calcaneus
(ii) Posterolateral margin of tendon of FDL
(iii) Assists flexor digitorum longus in flexing lateral four digits
(iv) Lateral plantar nerve (S2, S3)
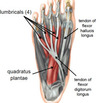
Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for LUMBRICALS.
(i) Tendons of FDL
(ii) Medial aspect of expansion over lateral 4 digits
(iii) Flex proximal phalanges, extend middle and distal phalanges of lateral four digits
(iv) Medial 1: medial plantar nerve (S2, S3)
Lateral 3: lateral plantar nerve (S2, S3)

What muscles make up the 3rd layer of the sole of the foot? (HINT: there’s 3)
Flexor Hallucis Brevis
Adductor hallucis
Flexor digiti minimi brevis
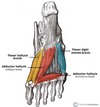
Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for FLEXOR HALLUCIS BREVIS.
(i) Plantar surfaces of the cuboid and lateral cuneiforms, tendon of the posterior tibialis tendon.
(ii) Base of proximal phalanx of great toe at the metatarsophalangeal joint
(iii) Flexes the proximal phalanx of the great toe at the metatarsophalangeal joint.
(iv) Medial plantar nerve

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for ADDUCTOR HALLUCIS.
(i) OBLIQUE HEAD: base of first 4 metatarsals
TRANSVERSE HEAD: plantar ligaments of MTP joints
(ii) Lateral base of proximal phalanx of hallux
(iii) Adducts hallux, assists in forming transverse arch of foot
(iv) DEEP branch of lateral plantar nerve

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for FLEXOR DIGITI MINIMI BREVIS.
(i) Base of 5th MT
(ii) Base of proximal phalanx of 5th digit
(iii) Flexes proximal phalanx of 5th digit
(iv) SUPERFICIAL branch of lateral plantar nerve

What muscles make up the 4th layer of the foot? What is their common innervation?
Plantar & Dorsal Interossei
Lateral Plantar Nerve
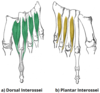
Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for PLANTAR INTEROSSEI.
(i) Medial side of MT’s 3-5
(ii) Medial sides of phalanges of digits 3-5
(iii) Adducts digits 3-5 & flex MTP joints
(iv) Lateral plantar nerve

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for DORSAL INTEROSSEI.
(i) Sides of MT’s 1-5
(ii) 1st: medial side of proximal phalanx of SECOND digit
2nd - 4th: lateral sides of proximal phalanxes of digits 2-4
(iii) Abducts digits 2-4 & flex MTP joints
(iv) Lateral Plantar Nerve

What muscles make up the dorsal aspect of the foot? What is their common innervation?
Extensor Digitorum Brevis
Extensor Hallucis Brevis
Deep Fibular Nerve

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for EXTENSOR DIGITORUM BREVIS.
(i) Calcaneus, interosseus talocalcaneal ligament & the inferior extensor retinaculum
(ii) Long extensor tendons of lateral 4 digits
(iii) Aids the extensor digitorum longus in extending the medial 4 toes at the MTP and IP joints

Give the (i) Origin (ii) Attachment (iii) Action and (iv) Innervation for EXTENSOR HALLUCIS BREVIS.
(i) Calcaneus, the interosseus talocalcaneal ligament & the inferior extensor retinaculum
(ii) Base of the proximal phalanx of the great toe
(iii) Aids the extensor hallucis longus in extending the hallux at the MTP joint.
(iv) Deep fibular nerve



