Lower Extremities Flashcards
Name the components of the anterior compartment of the lower leg.
Extensor muscles: 1.) tibialis anterior 2.) extensor digitorum longus 3.) extensor hallucis longus 4.) fibularis (peroneus) tertius Anterior tibial artery and veins Deep fibular (peroneal) nerve [Plate 510]
Name the components of the lateral compartment of the lower leg.
Fibularis (peroneus) longus muscle Fibularis (peroneus) brevis muscle Superficial fibular (peroneal) nerve [Plate 510]
Name the components of the superficial posterior compartment of the lower leg.
Superficial flexor muscles: Soleus Gastrocnemius Plantaris (tendon) [Plate 510]
Name the components of the deep posterior compartment of the lower leg.
Deep flexor muscles: Flexor digitorum longus Tibialis posterior Flexor hallucis longus Popliteus Posterior tibial artery and veins
Name the 4 muscles which make up the quadriceps femoris (from lateral to medial)
- Vastus lateralis
- Rectus Femoris
- Vastus intermedius (deep to rectus femoris)
- Vastus medialis
Name the muscles which comprise the anterior thigh muscle group.
From lateral to medial
- Quadriceps:
- vastus lateralis
- rectus femoris
- vastus intermedius
- vastus medialis
- Sartorius
- IIiopsoas

origin of the vastus medialis
intertrochanteric line, medial lip of linea aspera of femur [From Netter’s Anatomy, Table 7]
insertion of the vastus medialis
base of patella and to tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament [From Netter’s Anatomy, Table 7]
innervation of vastus medialis
femoral nerve [From Netter’s Anatomy, Table 7]
main action of vastus medialis
extends leg at knee joint [From Netter’s Anatomy, Table 7]
blood supply of vastus medialis
femoral and profunda femoris arteries
origin of the vastus lateralis
greater trochanter, lateral lip of linea aspera of femur
insertion of the vastus lateralis
base of patella and to tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament
innervation of the vastus lateralis
femoral nerve
main action of the vastus lateralis
extends leg at knee joint
blood supply of the vastus lateralis
lateral circumflex femoral and profunda femoris arteries
origin of the vastus intermedius
anterior and lateral surfaces of body of femur
insertion of the vastus intermedius
base of patella and to tibial tuberosity via patellar ligament
innervation of the vastus intermedius
femoral nerve
main action of the vastus intermedius
extends leg at knee joint
blood supply of the vastus intermedius
lateral circumflex femoral and profunda femoris arteries
The ________ ________ is the only extensor of the knee joint.
quadriceps femoris [From https://www.kenhub.com/en/videos/vastus-medialis-3d-anatomy]
What does musculus rectus femoris mean?
straight muscle of the thigh [From https://www.kenhub.com/en/videos/rectus-femoris-muscle-3d-anatomy]
The femoral nerve originates from the lumbar plexus, specifically the ________ ____ of the ___ through ___ lumbar nerves.
anterior rami 2nd through 4th lumbar nerves [From https://www.kenhub.com/en/videos/rectus-femoris-muscle-3d-anatomy]
The rectus femoris has a double origin on the _____. The first is a straight tendon which arises from the ________ ________ _____ _____, while the other is a reflected tendon which arises just superior to the __________.
ilium anterior superior iliac spine acetabulum
The rectus femoris muscle is the only member of the quadriceps femoris group that crosses both the ___ and ____ joints.
hip and knee [From https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/the-quadriceps-femoris-muscle]
Just like the femur, the proximal end of the tibia is formed by two condyles. On each of these condyles, you have an articular area which articulates with the corresponding condyle of the femur, and these are also collectively known as the ______ _______ especially in the clinical setting. The two areas are separated by a non-articular, irregular intercondylar area with the rugged raised area called the ________ ________.
tibial plateau intercondylar eminence [From Knee Joint video transcript, https://www.kenhub.com/en/start/anatomy-knee-joint]
The patellar ligament is strong flat band, which is actually just a continuation of the ________ _______ ______. It stretches from the apex of the patella to the tibial tuberosity. It’s joined medially by the medial patellar retinaculum and laterally by the lateral patellar retinaculum.
quadriceps femoris tendon [From Knee Joint video transcript, https://www.kenhub.com/en/start/anatomy-knee-joint]
A few bursae are actually continuous with the synovial cavity and that means that if there is an infection in one of the bursae, especially the large suprapatellar bursa, it can spread into the knee joint.
The sartorius muscle is a long, slim, superficially running muscle, formally belonging to the extensors of the thigh. The sartorius muscle moves both the hip and knee joint. Even though it is located in the anterior compartment of the thigh, it should not be confused as an _________ of the thigh.
extensor
Name the 4 muscle groups which comprise the gluteal muscles.
Gluteus maximus Gluteus medius Gluteus minimus Tensor fasciae latae
The posterior hip musculature can be found underneath the gluteal muscles. The four muscles which make up the posterior hip musculature are:
Piriformis Internal and external obturators Superior and inferior gemelli Quadratus femoris
The gluteus maximus is the ________ extensor of the hip joint, as well as the ________ rotator of the hip joint.
strongest external
The gluteus maximum originates from 3 places:
the sacrum, the ilium, and the sacrotuberous ligament.
The caudal fibers of the gluteus maximus insert at the….
….gluteal tuberosity of the femur.
The cranial fibers of the gluteus maximus insert on the….
….iliotibial fascia (the iliotibial tract on the fascia lata).
The gluteus maximum originates from 3 places:
the sacrum, the ilium, and the sacrotuberous ligament.
The caudal fibers of the gluteus maximus insert at the….
….gluteal tuberosity of the femur.
The cranial fibers of the gluteus maximus insert on the….
….iliotibial fascia (the iliotibial tract on the fascia lata).
What are the functions of the gluteus maximus? What do the cranial fibers vs what the caudal fibers do?
extension of the hip external rotation of the hip stabilization of the hip joint The cranial fibers abduct. The caudal fibers adduct.
The gluteus maximus is innervated by the…
…inferior gluteal nerve which comes from the sacral plexus.
what muscles insert onto the pes anserinus
the pes anserinus looks like a duck foot and the mneumonic is SGT (picture: marching duck sargeant) which stands for
- sartorius
- gracilis
- semiTendinosus

what is the function of the sartorius muscle?
Hip joint: thigh flexion, thigh abduction, thigh external rotation
Knee joint: leg flexion, leg internal rotation
all are shown in the attached picture.. its basically all the actions you use to look for gum on the bottom of your shoe.

The femoral nerve comes from what lumbar innervations?
L2-4
mn: 2 legs, 4 quad muscles
femoral nerve is the one in NAVL mn.

femoral triangle
bordered by the sartorius, inguinal line, and gracilis
clinical significance: access to heart, injection site

origin and insertion of rectus femoris
anterior inferior iliac spine (NOT ASIS like the sartorius)
shown in orange (attached).. notice that it crosses two joints (hip joint and knee joint) wherease all the other quadriceps muscles only cross the knee joint

what are the muscles of the medial thigh
pectinuius, adductor longus, gracilis

origin, insertion, and innervation of adductor longus
origin: pubic symphysis
insertion: mid shaft of humerus via aponeurosis
innervation: obturator nerve

adductor magnus
the femoral artery and vein go through the adductor hiatus

what are the occluded nerves

green = femoral nerve
blue = obturator nerve
what muscle is highlighted

pectinius
lateral leg muscles (2)
fibularis longus and fibularis brevis

what 2 tendons are shown?

the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis
what muscle is shown

adductor magnus (posterior view) - hamstring ischioportion
what muscle is occluded

quadratus femoris
what muscle is occluded

inferior gemellus
what muscle is occluded

superior gemellus
what muscle is occluded

piriform muscle
what muscle is occluded

tensor fasciae latae
what muscle is shown

adductor magnus (anterior view) - pubofemoral portion
what muscle is occluded

adductor magnus (pubofemoral part) in posterior view.

what are the actions of the adductor magnus muscle (3)
*some sources also say it does lateral rotation but this is in contention

where do the superior and inferior gemellus originate and insert?
what muscle is shown

tensor fasciae latae
obturator externus vs obturator internus comparison

what muscle is shown

obturator internus
what muscle is shown

adductor longus
what muscle is shown

adductor brevis
what muscle is shown

obturator externus
what muscle is shown

pectinius
vastus medialis versus vastus lateralis muscles

what muscle is shown

vastus intermedius

what muscle is shown and what is its function

biceps femoris
action: flexion of knee joint (“flirty foot pop”)

what muscle is shown

semitendinosus muscle (one of the pes anserinus muscle insertions)
semitendinosis versus semimembranosus muscles
semimembranosus (right) is deep to semitendinosus (left)

what muscle is shown and what is its function

ileopsoas
function: flexion of hip past 35 degrees and some adduction

what muscle is shown in green and where does it insert
soleus
inserts onto calcaneus

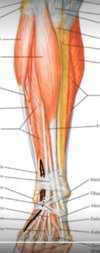
what muscle is shown in green and where does it insert?

tibialis posterior
inserts onto the plantar surface of the tarsal bones of the foot, mainly onto the tuberosity of navicular bone and the medial cuneiform bone.

flexor digitorum longus versus flexus hallucus longus
left = flexor hallucis longus
right =flexor digitorum longus

what muscle is shown (black)
fibularis tertius
what pathology is shown

ACL tear
Acetabular labrum is a fibrocartilaginous
rim that increases the articular area by
almost 10%
what position are the ligaments of the hip best suited for?
quadruped position
how would a patient present if she had been in a head on collision and sustained a posterior hip dislocation

what is this and what does it innervate?

deep fibular nerve –> innervates all muscles of the anterior compartment of the leg (meaning that it excludres the fibularis longus and fibularis brevis, which are lateral compartment muscles)
Other than the _____________ and the __________, which are innervated by the superficial fibular nerve, the anterior compartment muscles of the leg are innervated by the deep fibular nerve
fibularis longus, fibularis brevis
Deep fibular nerve: tibialis anterior, extensor digitorum longus, extensor digitorum brevis, extensor hallucis longus, extensor hallucis brevis and fibularis tertius muscles.


