LL: Leg Flashcards
Attachments for meniscus and cruciate ligaments on tibia
Anterior horn of medial meniscus attaches most anteriorly
PCL attaches most posteriorly

Attachment of collateral ligaments
Tibial collateral: medial condyle of femur to medial tibia
Fibular collateral: lateral condyle of femur to fibular head

Which structure separates the PCL from popliteal artery
oblique popliteal tendon

Lower femur bony anatomy

Proximal tibia bony anatomy

Proximal fibula bony anatomy

Popliteal fossa content
From superficial to deep
Common peroneal nerve (medial to biceps femoris)
Tibial nerve (lateral to popliteal vessels)
Popliteal vein
Popliteal artery
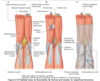
The membranes separatign the compartments of the leg

Which tissues stabilise tibiofibular joint
Interosseous membrane
Anterior and posterior tibiofibular ligaments

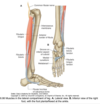
Muscles of posterior compartment of leg
Superficial: gastrocnemius, plantaris, soleus
Deep: popliteus, flexor hallucis longus, flexor digitorum longus, tibilais posterior
Origin and insertion of gastrocnemius
Medial and lateral condyle to calcaneus

Origin and insertion of plantaris
Lateral supracondylar line of femur to calcaneus

Origin and insertion of soleus
Soleal line/medial tibia to calcaneus
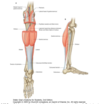
Innervation to posterior compartment of leg
tibial nerve
Function of gastrocnemius and plantaris
Plantar flex
Flex knee
Function of soleus
Plantar flex
Origin and insertion of popliteus
Lateral femoral condyle to posterior tibia

Origin and insertion of flexor hallucic longus
posterior fibula to distal phalanx f big toe

Origin and insertion of flexor digitorum longus
Tibia to distal phalanges of lateral 4 toes
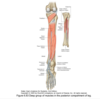
Origin and insertion of tibialis posterior
Interosseus membrane to tuberosity of navicular bone

Function of popliteus
Stabilises knee joint (resists lateral flexion of tibia on femur)
Unlocks knee joint (laterally rotates femur on fixed tibia)

Action of flexor hallucis longus
Flexes great toe
Action of flexor digitorum longus
Flexes lateral four toes
Action of tibialis posterior
Inversion
Plantarflexion