H&N - Face and Scalp Flashcards
Surface marking for parotid gland
Starts around tragus
Follows inferior to zygomatic arch
Drops down to angle of mandible and wraps around it
Climbs to inferior part of lobule

Parotid duct aka
Stensen’s duct
Surface marking of Stenson duct
Middle third of a line between intertragic line (between tragus and anti tragus) and philtrum

How does parotid duct get into mouth
After masseter muscle, dives into buccal fat and pierces buccinator muscle

End point of parotid duct
Near the second upper molar tooth

Structures through the parotid gland
Facial nerve
External carotid artery (and its branches; the maxillary and superficial temporal)
Retromandibular vein
Auriculotemporal nerve

Branches of facial nerve in facial canal
- greater petrosal nerve
- nerve to stapedius
- chorda tympani

Facial nerve branches through the stylomastoid foramen
Posterior auricular
Digastric
Stylohyoid
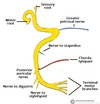
Facial nerve branches after entering parotid gland
The Zebra Buggered My Cat
Temporal branch
Zygomatic branch
Buccal branch
Marginal mandibular branch
Cervical branch

Functions of facial nerve
Face, ear, taste, tear
Taste: anterior 2/3
Tear: PSN to lacrimal and salivary glands
Facial nerve end branches motor test
Temporal: raise eyebrow
Zygomatic: close eyes tightly
Buccal : blow cheeks
mandibular: show lower teeth
cervical: tense skin under your chin

External carotid artery branches
Some attendings like freaking out potential medical students
Sup thyroid
Ascending Pharyngeal
Lingual
Facial
Occipital
Post auricular
Maxillary
Sup temporal

Tribuaries of retromandibular vein
superficial temporal and maxillary veins

Arterial supply of parotid
External carotid artery
Venous supply of parotid
Retromandibular vein
Lymphatic drainage of parotid
deep cervical
Innervation of parotid gland
Glossopharyngeal -> otic ganglion -> Auriculotemporal
Branches of opthalmic nerve
Supra-orbital
Supratrochlear
Infratrochlear
Lacrimal
External nasal

Branches of maxillary nerve
Zygomaticotemporal
zygomaticofacial
Infra-orbital

Branches of mandibular nerve
Auriculotemporal
Lingual
Inferior alveolar
Nerve to the mylohyoid
Mental

Layers of scalp
Skin
Connective tissue (dense)
Aponeurotic layer of occipito frontalis (Galear layer)
Loose connective tissue
Pericranium (ie periosteum)

Innervation of scalp
Anterior to vertex: trigeminal
Posterior to vertex: C2 and C3 (great auricular, lesser and greater occipital, third occipital)

In which layer of scalp do blood vessels and nerves lay
In dense connective tissue
Scalp blood supply
Opthalmic artery (internal carotid): supratrochlear and supraorbital
External carotid: Post auricular, superficial temporal, occipital



















