Lecture 8: GI Radiology Flashcards
What is the search strategy for image interpretation of the abdomen?
- Solid organs: Liver, spleen, pancreas, adrenal glands, and kidney
- Gallbladder/biliary system
- Lymph node chains: hepatogastric lig, periportal region, mesentery
- Stomach, duodenum, rest of small bowel, colon
- Fat planes, abdominal wall, bones
In a T1-weighted vs T2-weighted MRI, how does fluid show up?
T1: fluid is dark
T2: fluid is bright (best for fluid)
Which structures on CT will show up best at level of T11?
Spleen, stomach, liver, aorta, IVC, inferior aspects of lung well defined
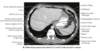
Which structures on CT will show up best at level of T12?
- Pancreas, spleen, kidney (particularly left)
- Gallbladder, portal triad
- Bifurcation of celiac trunk, possibly SMA, left renal vein, aorta, IVC
- View of small bowel, stomach

Identify this structure; seen best at what level?

Gastric fundus (stomach)
*Seen best at T11

Identify this structure; seen best at what level?
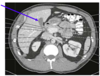
- Gallbladder
- Seen best at T12

Identify this structure; seen best at what level?

- Colon
- At T12

Which structures are seen at level of T12-L1?
- Pancreas, spleen, kidneys (particularly left)
- Gallbladder, portal triad, biliary tree
- SMA, left renal vein, aorta, IVC
- View of small bowel, left colon, duodenum

Identify this structure; seen best at which level?

- SMA
- T12-L1

Which strucutres are seen at level of L3-L4?
- Right kidney
- Gallbladder
- View of small bowel, ascending/descending colon, 3rd part of duodenum
- Abdominal and post-abdominal musculature well visulaized

Identify this structure; well visualized at what level?

- Psoas Muscle
- L3-L4
What is the modality of choice for diagnosing problems w/ the Biliary Tree?
- Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopanreatography (ERCP)

What is the imaging modality of choice for visualizing the abdominal aortic vasculature?
- Digital subtraction arteriography

What is the pathology seen here; causes?

- Ascites (fluid accumulation in abdomen)
- Liver cirrhosis, salt/water retention, heart failure, cancer
What is a mid-sagittal view in CT useful in identifying?
Useful in assessing the SMA and “Nutcracker” syndrome

What is SMA syndrome?
- 3rd part of the duodenum is compressed between aorta and SMA
- Results in partial or complete blockage of the duodenum

What is Nutcracker Syndrome?
- Compression of the left renal vein between the SMA and aorta

What type of hernia is this?

- Sliding hiatal hernia
- Bulge of stomach through esophageal hiatus into thorax
What type of hernia is showed here?

- Paraesophageal hiatal hernia
What pathology is seen here; common presenting sx’s?

- Zenker’s Diverticulum
- Diverticular formation in the esophageal wall adjacent to the inferior pharyngeal constrictor and cricopharyngeus muscle
- Severe halitosis (bad breath)
What pathology is seen here?

- Ulcerative Colitis
- Classic “lead pipe” apperance due to loss of the haustral marking throughout the colon
What pathology is seen here; cause?

- Cholithiasis (gall stones)
- High concentrations of bilirubin in bile and/or inefficient emptying
What is this pathology?

- Shatzki Ring
- Narrowing of esophagus caused by ring of mucosal tissue


