Lecture 2: Anterior Abdominal Wall Flashcards
What 9 structures are found in the RUQ?
Liver: right lobe
Gallbladder
Stomach: pylorus
Duodenum: parts 1-3
Right suprarenal gland
Right kidney
Right colic (hepatic) flexure
Ascending colon: superior part
Transverse colon: right tail
What 10 structures are found in the LUQ?
Liver: left lobe
Spleen
Stomach
Jejunum and proximal ileum
Pancreas: body and tail
Left kidney
Left suprarenal gland
Left colic (splenic) flexure
Transverse colon: left half
Descending colon: superior part
What 10 structures are found in the RLQ?
Cecum
Appendix
Most of ileum
Ascending colon
Right ovary
Right uterine tube
Right ureter: abdominal part
Right spermatic cord: abdominal part
Uterus (if enlarged)
Bladder (if very full)
What structures are found in the LLQ?
Sigmoid colon
Descending colon: inferior part
Left ovary
Left uterine tube
Left ureter: abdominal part
Left spermatic cord: abdominal part
Uterus (if enlarged)
Bladder (if very full)
Label A-I (9 regions of the anterior abdominal wall)

A) Right Hypochondrium
B) Epigastric
C) Left Hypochondriac
D) Right Flank (lateral)
E) Umbilical
F) Left flank (lateral)
G) Right inguinal (groin)
H) Pubic
I) Left inguinal (groin)

Label the Transverse planes A-G

A) Xiphisternal
B) Transpyloric
C) Subcostal
D) Supracristal
E) Transtubercular
F) Interspinous
G) Suprapubic
What structures are found within the Transpyloric plane (L1)?
Gallbladder fundus
Pylorus
Pancreatic neck
SMA origin
Hepatic portal vein
Root of transverse mesocolon
Hila of kidneys
The subcostal plane (L3) is at the level of which organ?
Transverse colon
The transtubercle plane (L5) is at the level of which organ?
Iliocecal junction
The interspinous plane (S2) is at the level of which organs?
Appendix and sigmoid colon
What is the superficial and deep layers of the anterior abdominal wall called?
Superficial: Campers (fatty)
Deep: Scarpa’s (membranous)
What are the layers of the anterolateral abdominal wall, starting with the skin?
Skin
Campers fascia (superficial)
Scarpa’s (deep membranous)
External oblique
Internal oblique
Transversus abdominis
Transversalis fascia
Extraperitoneal fat
Parietal peritoneum
What is the target layer of liposuction?
Removal of the superficial fatty layer: Camper’s
What is the origin, insertion, and innervation of external oblique muscle?
Origin: lower 6 ribs
Insertion: aponeurosis and linea alba, anterior iliac crest and pubic tubercle
Innervation: Thoraco-abdominal nerves T7-T11 and Subcostal nerve
What is the action of the external oblique muscle?
Compress abdomen and increase intra-abdominal pressure; move trunk and retain posture
What is the origin, insertion, and innervation of the Internal Oblique muscle?
Origin: iliac crest
Insertion: Lower 10-12 ribs, aponeurosis, linea alba and pubic crest
Innervation: Thoraco-abdominal nerves T6-T12
The cremasteric muscle arises from?
Some fibers of the internal oblique follow spermatic cord to make the cremasteric muscle
What is the action of the internal oblique?
Compress and support viscera, laterally flexes and rotates
What is the orign, insertion, and innervation of the Transversus Abdominis muscle?
Origin: lower 7-12 costal cartilages, thoracocolumbar fascia, iliac crest
Insertion: linea alba, pectin pubis and pubic crest
Innervation: Thoraco-abdominal nerves (T6-T12)
What is the origin, insertion, and innervation of Rectus Abdominis m.?
Origin: Pubic symphysis and pubic crest
Insertion: Xiphoid process and outer surface of 5th-7th intercostal cartilages
Innervation: Thoraco-abdominal nerves (ventral rami T6-T12)
What is the action of the Rectus Abdominis muscle?
Flexes trunk and compresses abdominal viscera; stabilizes and controls tilt of pelvis
Rectus abdominis prevents what kind of tilt of pelvis?
Prevents anterior tilt of pelvis
Above the arcuate line what makes up the anterior and posterior components of the Rectus Sheath?
Anterior: Aponeurosis of Internal and External Oblique
Posterior: Transversalis fascia and Aponeurosis of Transversus abdominis

Below the arcuate line what makes up the anterior and posterior components of the Rectus Sheath?
Anterior: Aponeurosis of external/internal oblique and transversus abdominis
Posterior: Transversalis fascia
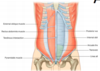
What are the nerves from T-7-T11; what anterior abdominal structures do they run between at the mid-axillary line?
- Thoraco-abodominal nerves, which are continuations of intercostal nerves.
- Run between Internal Oblique and Transversus Abdominis m.
What is the nerve at T12; runs along?
Subcostal nerve; runs along inferior 12th rib; motor; sensory is superior to iliac crest
What are the nerves at L1?
There are two branches
- Iliohypogastric goes to hypogastric region
- Ilioninguinal goes to the inguinal region.
What is McBurney’s point?
Location of the Appendix, which is right side of abdomen, 1/3 of the distance from the ASIS to the umbilicus
The internal thoracic artery comes down and branches into?
Musculophrenic a. and Superior epigastric a.
Where does the inferior epigastric artery arise from; where does it run?
Branch of the External Iliac artery; runs posterior to the Rectus abdominis m, but anterior to the posterior layer of rectus sheath.
What anastomoses around the umbilicus?
The superior and inferior epigastric arteries
Embryological origin of median umbilical fold?
Remenant of Urachus
Embryologic origin of medial umbilical fold?
Remenant of Umbilical arteries
What is found in the lateral umbilical folds?
Inferior epigastric artery and vein
The medial inguinal fossae is in which space; which type of hernia occurs here?
Inguinal triangle; direct hernia
Which hernia type occurs in the lateral inguinal fossae?
Indirect hernias
Discuss midline incisions
- The rectus sheath is strong and can support sutures
- Poor vasculature, which means no bleeding, but also slow healing
- No problems with nerves
- Not an ideal cut, but good if rapid incision necessary
What are the pros and cons of the subcostal surgical incision; organs accessed?
- Musculature is fine
- Concenred about superior epigastric artery
- Only nerves are cutaneous.
- Not a bad cut
- Access to gallbladder, bilary tract, and spleen
What are the pros and cons of a suprapubic surgical incision; common area for what surgery?
- No real problems here
- Muscles run in the same orientation as the incision
- Need to be aware of iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves
- Common area for C-section
What are the pros and cons of a paramedian surgical incision?
- Tight musculature means lots of muscular pull
- The aponeurosis is tough so holds sutures well
- Low blood supply so not too much bleeding, but slow healing
- You have all of the thoracoabdominal nerves, which means if you cut those you lose innervation to the rectus abdominis, it atrophies and dies
- Used mainly for liver transplant
What are the 3 ventral hernias?
1) Umbilical - common in newborns
2) Epigastric - thru linea alba
3) Spigelian - rare; semilunaris
Superior to the transumbilical plane where does most of the lymph drain to?
Majority to axillary LN and some to parasternal LN
Superficial vessels below umbilicus drain into which lymph nodes?
Superficial inguinal LN’s (also the scrotum, gluteal region, and lower limb)
What are the deep lymphatics and what do they accompany?
External iliac nodes, common iliac nodes, lumbar/arotic/caval nodes which accompany the deep veins of the abdominal wall.
*Testicular cancer will metastasize into the lumbar/aortic/caval lymph nodes
Label A-E and state the embryological origin?
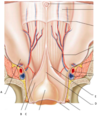
A) Lateral inguinal fossae
B) Medial inguinal fossae
C) Supravesical fossae
D) Median umbilical fold
E) Medial umbilical fold

Prune belly syndrome is a problem with development of what embryologically?
Paraxial mesoderm, specifically the hypomere and hypaxial muscles failing to form
3 main features of prune belly syndrome?
1) Anterior abdominal wall muscles deficient or absent
2) Urinary tract anomalies (i.e., very large bladder)
3) Bilateral cryptorchidism (2 undescended testicles)


