Lecture 4: Part 2 (Spinal Column) Flashcards
(97 cards)

Efferent (motor) only
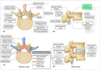
- we are looking at an axial cut of the vertebral column
- the yellow structures are ventral (anterior) side of the spinal cord
-
so what is the ventral (or anterior) root modality?
-
efferent (motor) only
-
will mix with the dorsal (posterior) root (carrying sensory only) at the intervertebral foramen where it will mix as a spinal nerve
- then we will see a seperation of the two - a dorsal ramus going dorsally to supply the intrinsic muscles of the back and a ventral ramus to take care of the rest of the body at that particular vertebral level
-
will mix with the dorsal (posterior) root (carrying sensory only) at the intervertebral foramen where it will mix as a spinal nerve
-
efferent (motor) only
ventral/anterior root carries what?
ventral/anterior root carries efferent (motor)

dorsal/posterior root carries what?
dorsal/posterior root carries afferent (sensory)

where do modalities mix as spinal nerve?
modalities mix as spinal nerve at intervertebral foramen (both motor and sensory)

dorsal/posterior ramus carries what?
dorsal/posterior ramus carries mixed sensory/motor to intrinsic back muscles and skin overlying the midline of the back

ventral/anterior ramus carries what
ventral/anterior ramus carries mixed (motor and sensory) to every else (everywhere but the intrinsic back muscles and skin overlying the midline of the back)

2 primary spinal curves (in fetus)
- kyphotic = concave anteriorly
- thoracic and sacral

2 secondary spinal curvatures
(names and what causes each)
- lordosis = concave posteriorly
- occurs because bipedal
- cervical lordosis = due to raising and holding head erect
- lumbar lordosis = due to upright posture, standind and walking

we start as kyphotic fetus and maintain kyphotic curve in thoracic and sacral regions but gain lordodic curves as we mature
kyphosis (abnormality)
kyphosis = hunchback
- abnormal exaggeration of the thoracic curvature

Dowager’s Hump
Dowagers hump = excessive thoracic kyphosis in older women resulting from osteoporosis

Lordosis (abnormality)
- Lordosis = hollowback
- an abnormal exaggerated lumbar spine
- exaggerated lumbar lordosis = common in pregnancy or with increased abdominal fat anteriorly

scoliosis (abnormality)
- scoliosis = curved back
- abnormal lateral curvature of the spine, usually in the thoracic region

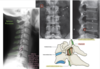
Increased pressure on the structure indicated by the arrows would diminish what functional modality(ies)?
A. efferent
B. afferent
C. both

Increased pressure on the structure indicated by the arrows would diminish what functional modality(ies)?
A. efferent
B. afferent
C. both

what are the most anterior and most posterior structures of spine
- most posterior structure = spinous processes
- __in every region except in the end of the sacral region where they fail to form and we get a sacral hiatus (gap)
- most anterior structure = vertebral bodies
- blocks of bone stacked next to each other (with intervertebral discs between them)

1 =

1 = vertebral body

2 =

2 = spinous process

3 =

3 = transverse process
4 =

4 = inferior articular process

5 =

5 = inferior articular facet

Typical Vertebra:
A =

Typical Vertebra:
A = spinous process

Typical Vertebra:
B =

Typical Vertebra:
B = vertebral body

Typical Vertebra
C =

Typical Vertebra
C = Lamina

Typical Vertebra
D =

Typical Vertebra
D = Pedicle

Typical Vertebra
E =

Typical Vertebra
E = Transverse Process