Lecture 3: The Cell (Part 2) Flashcards
(35 cards)
Ribosomes are found (2)
1) free in cytosol
2) alongside the ER

Ribosomes main job is to
- translate information that is encoded in mRNA’s –> protein
- A rapidly growing mammalian cell can contain about 10 million ribosomes

Two ribosomal subunits (and function of each)
1) Larger subunit: catalytic function
2) Smaller subunit: decoding function (what actually translated the mRNA into protein sequences)
* In total (both subunits): made up of 82 different proteins and 4 different rRNA molecules*

Ribosome microscopy
- what microscope is used
- appearance

- small (15-20 nm diameter), can only see under TEM
- look like little dots/grains of sand

sorting signals
- contained within ___
- direct ___
- begins with ___
- may move through ____
Sorting signals:
- contained in each protein’s amino acid sequence
- direct a protein’s movement through the system
- Begins with the synthesis of a protein on a ribosome in the cytosol
- May move through intermediate stations
- Additional signals direct retention or exit to the next compartment

ER membrane is attached to _____
- Forms 2 structures: ____ and ____
- ER membrane is attached to the outer membrane of the nucleus
- Forms two distinct structures that perform different functions (smooth ER and rough ER)

Ribosomes that stud the outside of the ER (aka RER) are responsible for controlling the synthesis, modification, and assembly of 2 types of polypeptides (proteins):
1) ______ (& location)
2) ______ (& location)
1) transmembrane proteins (bottom right picture)
- synthesized and found on the inside of the ER membrane)
- will have transmembrane domain
2) soluble proteins (top right picture)
- fully synthesized on ER membrane, then crosses membrane and is released into ER lumen (so they can then be further processed and released through trafficking)
- A subset of these are ultimately released into the extracellular space - secretory proteins

Postranslational modifications of proteins synthesized in the RER include:
- protein _______ unit
- location?
Protein folding unit
- In the lumen of the ER

Protein quality control process
- location
- process
Protein quality control process: (in the endoplasmic reticulum)
- if we have a protein that’s made (either a transmembrane protein or soluble protein) but is not correctly formed or folded, it will be rejected
- will stimulate the protein quality control mechanisms which lead to the activation of further genes that either produce proteins to fix the proteins or degrade misfolded proteins (so that we don’t have downstream effects and clinical disease progressions that are tied to misfolded or unavailable proteins)
-Example 1: form of emphysema where the ER quality control mechanisms continually reject an incorrectly folded protein and send it for degradation (and the lack of this protein leads to the clinical progression of this emphysema)
-Example 2: Form of cystic fibrosis where ther is just one single amino acid that is in a particular position in the protein construction that triggers the protein quality controls unfolded protein response and sends it for degradation (which leads to the clinical formation of this cystic fibrosis)

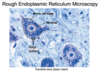
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum Microscopy
- what microscope is used
- appearance

Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum
- see with TEM
- looks like channels (parallel lines) studded with ribosomes (small dots)

thickness of plasma membrane
10 nm
Which arrow points to the lumen (inside of RER) and which points to the space between cisterns (folds)?

Ribosomes stud the OUTSIDE of RER
A) lumen (because no ribosomes on that side)
b) space between cisterns of RER

What is pictured and how do you know what it is?

Rough endoplasmic reticulum
- cut in a little bit of a different plane, so don’t see nice parallel lines like before
- know its rough ER because it’s the only thing in the cell thats studded in ribosomes (small dots)

Which area of the outlined cell (A, B, or C) contains the most rough ER?

(You cant see individual parts of RER with a light microscope, but you can see generally where things are if there is enough of it)
Answer: A
- we know that B is the nucleus because its the most basophilic structure and a circle
- C is the cytoplasm - its eosinophilic because of the proteins in the cytoplasm
- Rough ER is studded in ribosomes, which are made of rRNA (a nucleic acid), which attracts hematoxylin
- so if you see areas in the cytoplasm with a lot of purply blue instead of pink, thats where the rough ER is (we can’t see the details, but we can point out the region where it’s living)

- Nissl body:
- Nissl stain:

Nissl body – large aggregation of rough endoplasmic reticulum in a neuron (basophilic)
Nissl stain – general term for any basic stain used for Nissl bodies (ex: toludine blue is a nissl stain)

- A =
- B =
- C =

- A = nerve cell body
- B = nucleus
- C = Nissl body (aggregates of rough ER, specificially in neurons)
- -if you have cells that have a lot of rough endoplasmic reticulum, such as nerve cells (because they really need to make a lot of proteins), you might see basophilic clumps of rough ER around the nucleus instead of just like a general stained area.*
- -we’ve used a basic stain here, and anything that’s stained these Nissl bodies really well, is called a Nissl stain, so toluidine blue is an example of a Nissl stain (or it belongs that family)*
4 main functions of smooth ER
1) phospholipid biosynthesis
* synthesized on cytoplasmic face, then distributred to the cell membrane
2) storage site for calcium ions
* released in brief bursts to control the activities of calcium-dependent proteins, then quickly pumped back in to shut these proteins off
3) covert glycogen to individual glucose molecules for immediate use by cells
* used by cells like liver and muscle cells
4) contains enzymes to inactivate biochemical toxins
* found in great abundance in liver cells, which remove these toxins from the bloodstream
phospholipid biosynthesis
-performed by what?
DONE BY SMOOTH ER
- synethesized on the cytoplasmic face of its structure
- distributes to all other cell membranes and intercell membranes throughout the cell
storage site for calcium ions
SMOOTH ER
- sarcoplasmic reticulum
- •Released in brief bursts to control the activities of calcium-dependent proteins, then quickly pumped back in to shut these proteins off
Converting glycogen into individual glucose molecules for immediate use by cells (where most common?)
SMOOTH ER
-in liver and muscle cells
Contains enzymes that inactivate biochemical toxins
(where common)
Smooth ER
-liver cells (hepatocytes), which remove these toxins from the bloodstream
What is shown?

Smooth ER (in TEM appearance)
-looks like curvy channels or tubes WITHOUT ribosomes

Traffic between the RER and Golgi Apparatus is carried by:
traffic between the RER and golgi apparatis is carried by membrane-Bounded Vesicles
- Most RER synthesized proteins are carried to the Golgi apparatus
- Vesicles
- Transported by motor proteins
- Similar mechanisms to shuttle from Golgi back to the RER, & within Golgi
- Membrane trafficking

Name each pathway
Red pathway =
Green pathway =
Blue pathway =

Endocytic pathway (green)
Secretory pathway (red)
Retrieval pathway (blue)


















