Lecture 20: Anatomy Flashcards
Name these parts of the pancreas, duodenum and spleen

In a healthy adult, in which region of the abdominal cavity does the spleen normally lie
The left hypochondrium
At the level of which ribs does the spleen lie
Level of left 9th and 11th ribs
List the 4 structures that lies between the spleen and the lower left ribs
The peritoneum
The diaphargm
The left lung
The pleural cavity
Give four functions of the adult human spleen
Storage of iron
Phagocytosis of old/damaged erthryocytes
Immune response to circulating antigens
Production of B and T cells
Phagocytosis of old/damaged white blood cells
The spleen is most commonly damaged in abdominal trauma. What can happen if the spleen has ruptured
It can cause significant haemorrhage and perhaps shock
Describe the blood supply to the pancreas
Main blood supply is via splenic artery, which supplies the neck, body and tail of the pancreas.
The head of the pancreas is supplied by the superior and inferior pancreatoduodenal arteries
Describe the venous drainage of the pancreas
Mainly via the splenic vein
Trypsinogen and chymotrpsinogen are proenzymed produced by the pancreas.
Why are they stored as proenzymes?
What activates them?
The proteolytic enzymes are stored this way to avoid self-digestion.
Trypsinogen is cleaved by brush border enzymes in the duodenum into its active form, trypsin.
Chymotrypsinogen is convereted to chymotrypsin by trypsin
a patient with suspected cholecystitis comes with pain located in the right side of the upper abdomen but also radiated to the right shoulder area.
Why does the pain radiate to the right shoulder
This is referred pain
The phrenic nerve gives sensory fibres to the adjacent diaphragm and possibly to the gallbladder. Many of the fibres come from C4 spinal nerve, which is also sensory to the shoulder
Explain the hormonal control of gallbladder contraction
Cholecystokinin (CCK) release is stimulated by the presence of fatty and acidic chyme in the small intestine.
CCK stimulates the contraction of the gallbladder
By which two veins does the bound bilirubin pass from the spleen to the liver
Splenic and portal veins
Which cell organelle is responsible for conjugation of bilirubin?
Endoplasmic reticulum
Into which lumen is conjugated bilirubin directly secreted by hepatocytes?
Bile canaliculus
What is the source of the enzymes the reduce bilirubin to urobilinogen in the bowel?
Bacteria
Which vein carries resorbed urobiliogen from the terminal ileum to the portal vein?
Superior mesenteric vein
In alcoholic hepatitis what is the ratio that is important?
AST:ALT ratio is often greater than 2
Name the 4 parts of the duodenum?
Superior: 5cm in length
Descending: 7.5cm
Horizontal: 10cm
Ascending: 2.5cm

Where does the head of the pancreas sit inside?
The curvature of the duodenum
The superior porition of the duodenum is connected to the liver by what?
Hepatoduodenal ligament
Which part of the duodenum is associated with the hepatoduodenal ligament?
Superior portion of the duodenum
Duodenal ulcers are most likely to occur in the ____ portion of the duodenum.
Duodenal ulcers are most likely to occur in the superior portion of the duodenum.
The superior mesenteric artery lies ___ the neck of the pancreas
behind
The superior mesenteric artery lies ___ to the uncinate process.
Anterior
Which veins unite to form the hepatic portal vein
the splenic and superior mesenteric veins
Which part of the pancreas is framed by the duodenum
Head of the pancreas
Name these parts of the duodenum


Name these parts of the pancreas

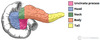
Name these parts of the biliary tree


Name these parts regarding the vascular of the pancreas


The spleen is connected to the pancreas by which parts?
The spleen is connected to the tail of the pancreas
What locations are drained by the superior mesenteric vein
venous drainage of the midgut – which spans from the major duodenal papilla (of the duodenum) to the proximal 2/3 of the transverse colon.
Which veins drain the spleen?
Describe where it drains into
Splenic veins drain the spleen
Unlike the splenic artery, the splenic vein is straight and it maintains contact with the body of the pancreas as it crosses the posterior abdominal wall. As it reaches the neck of the pancreas, the splenic vein joins the superior mesenteric vein to form the portal vein.
What locations does the inferior mesenteric vein drain
Drains the hindgut – the distal 1/3 of the transverse colon, splenic flexure, descending colon, sigmoid colon and rectum.
The inferior mesenteric vein drains into which vessel?
Splenic vein- which joins with the superior mesenteric vein to form the portal vein.
Name these parts of the venous drainage system in the abdomen

This is the Portal Venous System

The portal system carries venous blood (rich in nutrients that have been extracted from food) to the liver for processing.
This is the system for the venous drainage of the spleen, pancreas, gallbladder and the abdominal part of the gastrointestinal tract.
The portal vein is formed by the union of the splenic vein and the superior mesenteric vein, posterior to the neck of the pancreas, at the level of L2.
As it ascends towards the liver, the portal vein passes posteriorly to the superior part of the duodenum and the bile duct. Immediately before entering the liver, the portal vein divides into right and left branches which then enter the parenchyma of the liver separately.
Describe the accessory duct
The duct drains the head of the pancreas
Drains directly into the duodenum
More superior to the hepatoduodenal papilla

In the presence of portal hypertension the spleen may be enlarged. Why is this?
The splenic vein is a tributary of the portal vein.
The portal venous system does not contain valves so in portal hypertension the spleen becomes congested and enlarged


