Lecture 1 Flashcards
50% of Bos taurus cattle died with anaemia, weakness, weight loss, no death with bow inducus
Cattle ticks
Most important tick in australia
Rhipicephalus australis
How much does rhipicephalus australis cost
$150 millions
Morphology of rhipicephalus australis
Mouth as long as basis capituli

rhipicephalus australis
Lifecycle of rhipicephalus australis
One host tick - feedon host for 2 weeks, drp off and then start to lay eggs
Eggs laying can cease if temperature is below 15 degrees
How long can rhipicephalus australis larvae survive
Summer: 3-4 months
Winter: 5-6 months

rhipicephalus australis
How do rhipicephalus australis larvae get onto host
Sit on grass lwith legs up
Larvae are the infective stage
What do larvae turn into and for how long rhipicephalus australis
Nymphs after 4-5 days
How long does it take for nymph to turn into larvae
rhipicephalus australis
one week
rhipicephalus australis: how long do females feed
3 weeks after larvae attachment early in the moring they drop off.
rhipicephalus australis: host
Cattle
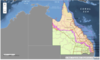
rhipicephalus australis: distribution
QLD, NT, WA, NSW