LEC 5: Microstructure of Tissues: Epithelial Tissue - 08.19.2014 Flashcards
(55 cards)
What are the four (4) specialized tissue types
- connective
- epithelial
- nervous
- muscle
* each of these tissues exist in association with each other to form organs
What germ layer does epithelial tissue derive from
all three (3) germ layers
- mesoderm
- ectoderm
- endoderm
What germ layer does connective tissue derive from
mesoderm
What germ layer does muscle tissue derive from
mesoderm
What germ layer does nervous tissue derive from
ectoderm
What type of epithelial tissue derives from the ectoderm
epidermis (skin) derives from the ectoderm
What type of epithelial tissue derives from the endoderm
the linings of the GI tract and respiratory tracts derive from endoderm
What type of epithelial tissue derives from the mesoderm
endothelium (linings of blood vessels) and mesothelium (linings of cavities) derive from the mesoderm
Describe types of epithelial tissue deriving from the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm
- ectoderm = epidermis (skin)
- endoderm = lining of GI tract, lining of respiratory tract
- mesoderm = endothelium (lines blood vessels), mesothelium (lines body cavities)
Name the (2) major types of epithelial tissue
- membranous epithelia – sheetlike tissues that cover/line surfaces, cavities, and organs of the body
- **glandular epithelia **– perform secretory functions
What is membranous epithelia
sheetlike tissues that cover/line surfaces, cavities, organs of the body
What is glandular epithelia
epithelia that performs secretory functions
Describe five (5) functions of epithelial tissue
- protection/containment (skin)
- absorption (intestines)
- secretion (glands)
- sensation (neuroepithelium)
- contractility (myoepithelium)
Are epithelial cells polar or nonpolar
polar
basement membrane
epithelial tissues are supported by the basement membrane (separates them from underlying supportive tissue)
What are the four (4) characteristics of epithelial tissue
- cells closely bound to one another by membrane specializations (cell junctions) form continuous sheets
- supported by basement membrane (separates them from underlying supporting tissue)
- not penetrated by blood vessels
- epithelial cells are polar
Label the parts of the epithelial cell

A. Apical plasma membrane
B. Lateral plasma membrane
C. Basal-lateral membrane
D. Basal membrane
E. Basement membrane
What are the three (3) ways to classify epithelial tissue
- cell layers
- morphology
- surface characteristics
If classifying by cell layers, what are the three types of epithelial cells
cell layer classification of epithelial cells
- simple-one layer
- stratified-more than one layer
- pseudostratified-nuclei at different positions
If classifying by morphology, what are the three types of epithelial cells
morphological classification of epithelial cells
- squamous (flat)
- columnar
- cuboidal
If classifying by cell characteristics, what are the three types of epithelial cells
cell characteristics classification of epithelial cells
- cilia
- keratin
- microvilli
In this slide of a small blood vessel (H&E Stain), what kind of cells are these

Simple Squamous Epithelium

Collecting tubule in the kidney (Azan stain), what kind of cells are these

Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
- note clear basement membrane (blue)

What kind of cells are these
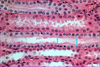
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium








































