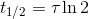Laboratory Methods Flashcards
(27 cards)
Sample variance

Simple propagation of error (for uncorrelated errors)

General propagation of error

Error on f = AB and f = A/B

Error weighted average

Error of the error weighted average

Poisson distribution
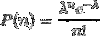
Error of the Poisson distribution for large N

Time between Poisson events
The time between Poisson events follows an exponential distribution. Specifically, if one event falls at time t = 0, the time of the next event’s arrival is distributed as

Complex impedance of a capacitor, inductor, and resistor

High-pass filter
High frequencies pass, low frequencies attenuated

Low-pass filter
Low frequencies pass, high frequencies attenuated

Diode
Allows current to flow only in one direction, from anode to cathode in the picture below. No current can flow until a minimum bias voltage is applied - typically about 0.7 V for a silicon diode. Apart from this, the voltage drop is essentially indepenent of the current. Uses: turn AC into DC, reroute current away from sensitive components (if the voltage surges, the diode starts conducting, resulting in an almost short circuit at high enough voltages)

Op-amp
(note that the op-amp has a maximum output voltage)

AND gate

OR gate
Average path length of an alpha particle

Average path of a high energy electron
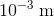
Radiation collision targets
- Nuclei interact almost exclusively with atomic electrons
- Electrons can either interact with atomic electrons or atomic nuclei (although the latter is still more rare)
Minimum ionizing particle
At relativistic speeds, all particles lose roughly similar amounts of energy per unit distance (about 1 keV / cm in air). This value is the minimum energy loss, and therefore relativistic particles are referred to as “minimum ionizing particles”.
Photoelectric effect

Compton wavelength

Radioactive decay

Half-life to mean lifetime