Electromagnetism: Essentials Flashcards
(23 cards)
Electric field of a point charge

Electric dipole orientation
Dipole moment points from negative to positive (in opposite direction of field lines)
Torque and potential for an electric dipole

Gauss’s Law (differential and integral forms)
*in linear dielectric media, use permittivity of medium, not of free space

Electric Flux

Electric field and potential in a conductor (with infinitely mobile charge)
The electric field is zero, while the electric potential is constant.
Where does exess charge lie in a conductor?
On the surface
Point charge electric potential relative to V = 0 at infinity

Definition of potential difference

Electric potential of an extended body relative to V = 0 at infinity
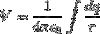
Definition of capacitance and differential relationship

Parallel Plate Capacitance

Electrical Energy Density (in vacuum and in medium)

Definition of current

Current density
Current per area
Gauss’s Law for Magnetism

Magnetic dipole moment defintion
Current times area
Magnetic dipole torque and potential

Biot-Savart Law

Maxwell-Ampere Law

Three types of magnetism
Paramagnetism: lines up with the applied field
Diamagnetism: opposes the applied field
Ferromagnetism: permanent with various domains
Lenz’s Law
Current creates field to oppose change in flux
Differential magnetic force



