Lab 7: General Muscular System Flashcards
(30 cards)
Muscle Organization
Muscle Organ (Epimysium)
Muscle Fasicle (Perimysium)
Muscle FIber (Endomysium)
Myofibrils
Myofilaments (Actin & Myosin)
Muscel Fiber Model
- Endomysium
- outermost layer
- Sarcolemma
- tan layer
- T-tubles
- holes/orange horizontal lines
- Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
- white webbing
- Terminal Cisternae
- surround t-tubule; white lines
- Myofibril
- includes myofilaments
- Myosin
- thick red lines in myofibril
- Actin
- thin red line in myofibril
- Z-line
- pink horizontal line
- Sarcomere
- z-line → z-line
- Cell Nucleus
- blue structure
- Satellite Cell
- tan structure
- Neuromuscular Junction
- Acetylcoline (yellow circles)
- Mitochondria (blue structures)
A flattened, tendinous sheet derived from interwoven fibers of the endomysium, perimysium, and epimysium of skeletal muscle
Aponeuroses
plasma membrane of a skeletal muscle cell (fiber)
Sarcolemma
actin (contractile protein)
Thin myofilament
theory on the mechanism for muscle contraction
Sliding filament theory
connective tissue (deep fascia) encircling many skeletal muscle fascicles
Epimysium
a bundle of many skeletal muscle cells (fibers)
Fascicle
connective tissue encircling a single skeletal muscle fascicle
Perimysium
skeletal muscle cell endoplasmic reticulum
Sarcoplasmic reticulum
Junction of a motor neuron and a skeletal muscle fiber
Neuromuscular junction
Myosin (contractile protein)
Thick myofilament
Connective tissue covering surrounding a skeletal muscle cell (fiber)
Endomysium
Contractile protein filaments consisting of mainly actin and myosin
Myofilaments
Bundles of myofilaments found in a single muscle cell
Myofibril

- Tendon
- Epimysium
- Endomysium
- Bone
- Perimysium
- Fasicle
- Blood vessel
- Muscle fiber

Identify, describe, and provide an example

- Parallel/ Longitudinal - fascicles parallel to long axis of muscle; Sartorius
- Parallel muscle with tendinous bands - Rectus abdominus
- Convergent - fascicles spread over a large area converge to a single tendon; Pectoralis major
- Unipennate - all fascicles converge to one side of a tendon; Semimembranosis
- Bipennate - fascicles converge to both sides of a tendon; Rectus femoris
- Multipennate - tendon branches converge to a single tendon; Deltoid
- Circular - concentrically arranged fibers surrounding an opening; Orbicularis oris

Muscle Fiber
All muscle fibers are only innervated by a single neuron
However, a single neuron can innervate many muscle fibers
A muscle fiber consists of many sarcomeres arranged side by side
Describe the difference between the origin of a muscle and the insertion of a muscle.

- Myofibril
- Myofilaments
- Thin Filament (actin)
- Thick Filament (myosin)
- Mitochondria
- Sarcolemma
- Triad
- Sarcoplasmic Reticulum
- Terminal Cisterna
- T-tubules


- Sarcomere
- H zone
- Actin
- M-line
- Myosin
- Z-line
- A-band
- I-band

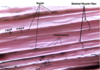
Microscope Components of Skeletal Muscle
- Individual muscle fibers
- Sarcolemma
- Nuclei
- A-band (Dark bands)
- I-band (Light bands)
- Endomysium

Skeletal Muscle
Sliding Filmaent Theory
- ATP binds to myosin cross-bridge headm which split ATP into ADP and Pi and energy. Energy is used to swivel the cross-bridges to a “ready” (90º) position
- Motor neuron at neuromuscular junction releases acetylcholine, which binds to receptors on sarcolemma, causing an action potential
- Action potential spreads throughout sarcolemma and down he t-tubules
- This causes the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) channels to open and release calcium ions (Ca2+)
- Ca2+ bind to troponin-tropomyosin complex on actin, exposing binding sites for myosin
- Myosin cross-bridges attach to actin (and release Pi) causing myosin to swivel to 45º, pulling actin and their z-lines towards cell center, shortening sarcomere


