Lab 6: General Skeletal System Flashcards
Number of bones
206
Main divisions of the bones of the skeleton
Axial Skeleton (80 bones)
Appendicular Skeleton (126 bones)
Axial Skeleton
skull, vertebral column, sternum, ribs
Appendicular Skeleton
bones of the appendages (arms and legs), and the girdles that connect the appendages to the axial skeleton
Various Connective Tissue Types
-
Connective Tissue Proper
- Adipose
- Dense Regular
- Cartilage
-
Osseous
- Spongy
- Compact
-
Blood
- Red Bone Marrow
Shapes of Bones
- Long
- Short
- Flat
- Sesamoid
- Sutural (Wormian)
- Irregular
Examples of long bones
- humerus
- radius
- ulna
- metacarpals/ metatarsals
- tibia
- fibula
- femur
Examples of short bones
- carpals
- tarsals
Examples of flat bones
- cranium
- ilium
- sternum
Examples of pneumatized bones
“air pockets”
- maxilla
Examples of sesamoid bones
- patella
Examples of sutural (wormian) bones
“fused”
-skull
Examples of irregular bones
- vertebrae
- mandible
- coxal bones
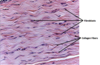
- most abundant
- collagen fibers too thin to see
- resists stretching
- Found at: Articular end of bones
Hyaline Cartilage
- matrix has elastic fibers
- tolerates repeated bending
- Found in: epiglottis and ears
Elastic Cartilage
- Resists twisting and compression
- hylaine + dense CT
- alternating rows of collagen and chondrocytes
- Found in: intervertebral discs, meniscs, pubis symphysis
Fibrocartilage
Types of osseous tissue
Compact & Spongy bone

- Concentric Lamellae
- Spongy Bone
- Canaliculi
- Lacuna
- Osteocyte within lacunae
- Periosteum
- Haversion (central) Canal
- Osteon
- Volkmann’s Canal


- Proximal Epiphysis
- Diaphysis
- Distal Epiphysis
- Epiphyseal line
- Spongy bone
- Medulary Cavity
- Endosteum
- Periosteum
- Articular Cartilage

Growth of bone or cartialge due to the addition of bony matrix or cartilage to the outer surface (deep to the periostuem)
Inceases the bone organ in width
Appositional Growth
“little canals” that connect lacunae and osteocytes to each other
Canaliculi
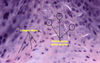
Immature cartilage cell (responsible for matrix production)
Chondroblast
Mature cartilage cell (usually trapped in lacunae)
Chondrocyte
Canal lined with endosteum to supply blood vessels, lymphatics, and nerve to bone
Haversian (central) Canal