Lab #4: Muscles of Upper Body Flashcards
3 types of joint MOVEMENTS
- Angular Movements
- Circular Movements
- Special Movements
4 types of Angular Movements
- Flexion
- Extension & Hyperextension
- Adduction
- Abduction
3 types of Flexion
- Dorsiflexion
- Plantar flexion
- Lateral flexion
2 types of Circular Movements
- Rotation
- Circumduction
2 types of Rotation
- Supination
- Pronation
6 types of Special Movements (PRIeDE)
- Protraction
- Retraction
- Inversion
- Eversion
- Depression
- Elevation
Frontal Belly of Occipitofrontalis
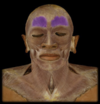
O: Frontal Bone & skin of eyebrows
I: Galea Aponeurotica
A: moves scalp, wrinkles forehead, elevates eyebrows
Occipital Belly of Occipitofrontalis

O: Superior Nuchal Line
I: Galea Aponeurotica
A: moves scalp slightly posteriorly
Orbicularis Oris **

O: Mandible & Maxillae, fascia & fibers from other facial muscles
I: skin & lips surrounding the mouth
A: closes lips, puckers up lips
*1st sphincter of digestive tract
*“kissing” muscle
Masseter *

O: Zygomatic arch
I: lateral surface of coronoid process, lateral surface & angle of mandible
A: elevates & protracts mandible, prime mover of jaw closure
* feel contraction near angle of mandible when clenching teeth
Temporalis *

O: superior & inferior portions of temporal bone
I: Coronoid process of mandible
A: elevates & retracts mandible
* palpate on temple while clenching teeth
Buccinator **

O: alveolar processes of mandible & maxillae
I: Orbicularis Oris
A: compresses cheek, holds food between teeth, aids in sucking & blowing
* “trumpeter” muscle
*composes fleshy wall of cheeks
Medial & Lateral Pterygoids

O: pterygoid processes of sphenoid bone
I: mandible
A: elevate & protract mandible, move it from side to side during chewing
Sternocleidomastoid *
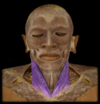
O: manubrium & sternal ends of clavicle
I: mastoid processes of temporal bones
A: both- head is pulled forward & down (flexion of cervical vertebrae & flexion of atlanto-occipital)
one- turns head sideways, in opposite direction of contracting muscle
* form lateral borders of suprasternal fossa
Platysma

O: Fascia of deltoid & pectoralis major muscles, and acromion of scapula
I: Skin of cheek and mandible
A: Pulls lower lip inferior, tenses skin of neck, contributes to depression of the mandible
Serratus Anterior *

O: Anterior and superior margins of upper ribs
I: Medial (vertebral) border of scapula & anterior surface of scapula
A: Prime mover that protracts & depresses scapula (synergistic to pec. minor), stabilizes scapula, superiorly rotates scapula (glenoid cavity moves superior)
* “saw toothed” appearance
Pectoralis Minor *

O: Sternal ends of upper ribs
I: Coracoid process of scapula
A: Protracts & depresses scapula (Hunched over shoulders)
* deep to Pec. Major
simple movement in which two opposing surfaces slide slightly back-and-forth or side-to-side to one another and the angle between teh bones doesn’t change
gliding
either increases or decreases angle between articulating bones
angular motion
movement in an anterior-posterior plane of the body that decreases the angle between bones
flexion
movements in an anterior-posterior plane that increases the angle between bones
extension
movement that typically returns body part to the anatomical position
extension
an angular motion in which the angle between the bones is >180
hyperextension
severe example of this motion occurs in tetanus and is termed “opisthotonos”
hyperextension


