Exam 4 lectures HEART Flashcards
consists of the heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins.
The cardiovascular system
The pumping action of the heart is essential to maintain blood circulation. It beats about ____ times per minute. The amount of blood pumped from one ventricle per minute is called the cardiac output.
75
The continual circulation of blood throughout the body is essential for maintaining
homeostasis (a state of equilibrium within the body).
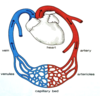

which sides of the heart pump where
The right side pumps blood to the lungs. The left side pumps to the rest of the body.
define blood pressure
The heart develops “blood pressure” through alternate cycles of heart wall contraction and relaxation. Blood pressure is essential to push the blood through the vessels.
consists of the right side of the heart (right atrium and right ventricle), the pulmonary arteries, which convey poorly oxygenated blood to the lungs, and the pulmonary veins, which convey oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left atrium.
The pulmonary circulation
consists of the chambers on the left side of the heart (left atrium and left ventricle) and all the named blood vessels that carry blood to the tissues (arteries) and all the named blood vessels that return the blood from the tissues (veins) back to the right atrium of the heart. The tissue capillaries are included.
The systemic circulation
where is the heart located?
is located left of the body midline posterior to the sternum in the mediastinum
The heart is located in the mediastinum

The heart is contained within
the pericardium, a fibrous sac and double-layered serous lining. It is fused to the diaphragm.
is composed of two parts: the outer fibrous pericardium and the inner, double-layered serous pericardium.
The pericardium
is divided into two layers that are actually continuous with each other: the parietal layer, which is lines the inner surface of the fibrous pericardium, and the visceral layer, which is fused to the outer surface of the heart (this layer is also called the epicardium).
The serous pericardium
is inflammation of the visceral and parietal layers of the serous pericardium, usually accompanied by excess fluid between the two membranes. This excess fluid can cause pressure on the heart (cardiac tamponade) and impair the function of the heart.
Pericarditis
cardiac tamponade

Blows to the chest can lead to __________ caused by bleeding between the visceral and parietal pericardial membranes.
pericardial tamponade
If the heart is unable to pump blood properly, then the venous blood traveling towards the heart backs up. This will lead to
external jugular vein distention (JVD). One cause of JVD is cardiac tamponade.
A common treatment for cardiac tamponade is to
carefully insert a needle through the parietal pericardium and aspirate off some of the excess fluid to relieve the pressure on the outside of the heart.


The heart wall consists of
three distinctive layers: the epicardium (visceral layer of serous pericardium), the myocardium, and the endocardium (which is continuous with the endothelium of vessels)
the heart is composed of ___ chambers
4
The anterior portion of each atrium is a wrinkled, flap-like extension called
an auricle.
So, the auricle is just a portion of the atrium.


receives blood from the systemic circulation.
The right atrium
receives blood from the pulmonary circulation.
The left atrium
The ventricles are the
inferior chambers. The right ventricle pumps to the pulmonary trunk, while the left ventricle pumps to the aorta.
There are one-way valves to
guide the flow of blood through the chambers of the heart.
The fibrous skeleton of the heart is located
between the atria and the ventricles, and is formed from dense irregular connective tissue. It is electrically non-conductive!
The right atrium receives venous blood from the
systemic circulation and the heart muscle itself (via the coronary sinus).
Poorly oxygenated blood is returned to ________ the of the heart from the arms and head by the __________while poorly oxygenated blood from the torso and legs is returned to the right atrium by the _____________. The venous drainage from the myocardium also empties into the right atrium via the coronary sinus (not shown).
right atrium
superior vena cava
inferior vena cava
is a depression in the interatrial septum between the left and right atria.
The fossa ovalis
Blood from the right atrium flows through the ________ into the right ventricle.
tricuspid valve
When the right ventricle contracts the _____________shuts and is supported by the chordae tendineae that are anchored in the papillary muscles.
tricuspid valve
_________________receives deoxygenated blood from the right atrium. The interventricular septum separates the left and right ventricles. The internal walls of the ventricles have muscular ridges called trabeculae carneae. Projecting from the ventricular walls are papillary muscles which anchor the chordae tendineae.
The right ventricle
Like the shroud lines of a parachute, the __________________ are tight when the atrioventricular valves (tricuspid and bicuspid) are closed. This supports the AV valves during times of high reverse pressure.
chordae tendineae
When the right ventricle contracts, and the tricuspid valve closes, the only exit for the blood is the
pulmonary semilunar valve
After blood flows through the pulmonary semilunar valve it enters the_______________ . This trunk soon branches into the left and right pulmonary arteries which deliver poorly oxygenated blood to the lungs so CO2 can leave the blood and O2 can enter the blood.
pulmonary trunk




Note there are no _______________\_ to support the pulmonary semilunar valve. It closes when the back flow of blood fills its cusps
chordae tendineae
Highly oxygenated blood from the lungs travels to the left atrium via one of the four
pulmonary veins (two from each lung).


Blood from the left atrium passes through the into the_______________________ left ventricle.
left atrioventricular valve (bicuspid or mitral valve)
The left AV valve (bicuspid valve) is also called the _____________ because it resembles a bishop’s hat, or mitre.
mitral valve
The ________ ventricle has thinner walls since it pumps blood to the lungs nearby more slowly for gas exchange.
right
The ______ ventricle has the thickest walls because it pumps the blood to the entire arterial system.
left




Because the myocardium is thick muscle, it needs its own blood supply via___________
the coronary arteries.
are the only branches of the ascending aorta. They exit the ascending aorta immediately superior to the aortic semilunar valve.
The left and right coronary arteries
can lead to narrowing of the myocardial arteries. This can cause myocardial ischemia and angina pectoris
Atherosclerosis
Reduction of blood flow ________ through a branch of the coronary arteries causes pain _______________
ischemia
angina pectoris
Blockage of blood flow through a branch of the coronary arteries can cause an area of the myocardium to become infarcted ___________
This is commonly called a “heart attack”.
myocardial infarction
or MI


The venous drainage from the myocardium collects in the cardiac veins, which in turn flow to the _____________ which drains into the posterior of the right atrium.
coronary sinus


can reduce essential blood flow to the myocardium of the ventricles.
Tachycardia and/or hypotension
is when a chamber of the heart is relaxed (dilated).
is when a chamber of the heart is contracted.
“Diastole”
“Systole”
At the beginning of the beginning of the cardiac cycle the left and right atria……
contract simultaneously (atrial systole), forcing blood through the open AV valves.
When the ventricles contract
(ventricular systole)………
the atrioventricular valves close and the semilunar valves are forced open, allowing blood to enter the pulmonary trunk and aorta.
When the ventricles are relaxed (diastole)…..
blood soon flows passively from the atria into the ventricles through the open atrioventricular valves. For a brief period all four chambers are in diastole.
When the ventricles contract (ventricular systole)…..
the atrioventricular valves close and the semilunar valves are forced open, allowing blood to enter the pulmonary trunk and aorta.
for a period of time both the atria and ventricles are relaxed and all four chambers of the heart are…..
filling simultaneously. Most of the ventricular filling (70%) occurs during this time.
Why are there no one-way valves at the inlets of the atria?
By being partially empty and stretchable, atria prevent the interruption of venous blood flow to the heart that would occur during ventricular systole if the veins ended at heart inlet valves.
By preventing the inertia of interrupted venous flow that would otherwise occur at each ventricular systole
atria allow approximately 70% more cardiac output that would otherwise occur!
the key benefit of the atria
is in preventing circulatory inertia and allowing uninterrupted venous flow to the heart!
an atypically slow heartbeat of less that 50 beats per minute.
Bradycardia
Athlete’s bradycardia
a beneficial adaptation resulting from a muscular heart, healthy circulatory system, and excellent lung capacity.
In the fetal heart most of the blood bypasses the pulmonary circulation by traveling through the
foramen ovale directly from the right atrium to the left atrium. A flap of tissue, the septum , is pushed aside as the blood flows through the foramen ovale
When a baby is born and the lungs are fully functional, the blood from the left atrium
pushes the septum primum closed, creating a closed interatrial septum.


