L3 - Anterior Abdominal Wall Flashcards
Name the organs in the Right Upper Quadrant
- Liver (Right Lobe)

- Gallbladder
- Stomach (Pylorus)
- Duodenum
- Right Kidney
- Pancreas (Head)
- Ascending Colon: Superior Part
- Transverse Colon: Right Half
Name the organs in the Right Lower Quadrant
- Cecum
- Vermiform Appendix
- Most of Ileum
- Ascending Colon: Inferior Part
- Uterus (If enlarged)
- Urinary Bladder (If very full)

Name the organs in the Left Upper Quadrant
- Liver: Left Lobe
- Spleen
- Stomach
- Jejunum and Proximal Ileum
- Pancreas: Body and Tail
- Transverse Colon: Left Half
- Descending Colon: Superior Part

Name the organs in the Left Lower Quadrant
- Sigmoid Colon
- Descending Colon: Inferior Part
- Uterus (If enlarged)
- Urinary Bladder (If very full)

Which of these are in the RLQ?
A. Liver
B. Transverse Colon
C. Cecum
D. Stomach
E. Sigmoid Colon
Cecum
What are the layers of the Anterior Abdominal Wall?
Skin →
Camper’s Fascia →
Scarpa’s Fascia →
External Oblique →
Internal Oblique →
Transversus Abdominus Muscle →
Transversalis Fascia →
Parietal Peritoneum

In the lower abdomen, there are two distinct layers
What are they?
Superficial fatty
- Camper’s fascia
- contains superficial veins
Membranous
- Scarpa’s fascia
- Gives rise to fundiform ligament of penis
- Can be sutured
**Superficial Fascia contains both Camper’s and S_carpa’s Fascia_
Scarpa’s Fascia turns into all the following EXCEPT:
Fundiform Ligament of the Penis
Superficial penile Fascia
Tunica Dartos of the Scrotum
None of the above
None of the above
Scarpa’s Fascia turns into:
- Fundiform Ligament of the Penis
- Superficial penile Fascia
- Tunica Dartos of the Scrotum
True or False
You CANNOT suture Camper’s Fascia, you CAN suture Scarpa’s Fascia
True
A lot of anastomose is in the:
- umbilical cord
- esophagus
- rectum
What can Portal Hypertension lead to?
Caput Medusae

Membranous Layer of Superficial Fascia aka Scarpas Fascia is continuous with the
Tunica Dartos of the scrotum
and
Superficial penile fascia

What is the Deep Inguinal Ring made by?
Transversalis Fascia
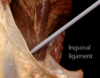
What structure is this?

Inguinal Ligament
What structure is this?

Lacunar Ligament

What structure is this?

Anterior Inguinal ligament
What structure is this?

Conjoint tendon

What structure is this?

Superficial inguinal ring

The superior and inferior crus are also known as
medial crus
lateral crus

External Oblique Muscle
Name its origin and insertion
Origin
Outer surface of ribs 6-12
Insertion
Linea alba
Pubic tubercle
Anterior ½ of iliac crest
*Aponeurotic fibers form external spermatic fascia
Same direction as the external intercostals
when it goes into the scrotum, External Oblique →
External Spermatic Fascia

Internal Oblique Muscle
Name its origin and insertion
Origin
Thoracolumbar fascia
Anterior 2/3 of iliac crest
Lateral ½ of inguinal ligament
Insertion
Inferior borders 10-12th ribs
Linea alba
Pubis via conjoint tendon
Gives rise to the cremaster muscle

when it goes into the scrotum, Internal Oblique →
Cremaster Muscle

Transversus Abdominis Muscle
Name its origin
Origin
Inner surfaces of 7th-12th costal cartilages
Thoracolumbar fascia
Iliac crest
Lateral 1/3rd of inguinal ligament

Transversalis Fascia
- Helps form posterior wall of rectus sheath above arcuate line
- Forms posterior wall of rectus sheath below arcuate line
- Continues over spermatic cord as internal spermatic fascia
ALWAYS on the posterior wall of the rectus sheath

when it goes into the scrotum, Transveralis Fascia →
Internal Spermatic Fascia

Inner View of Anterolateral Abdominal Wall
What are the five folds of the peritoneum?

Median umbilical fold (1)
(down the midline)
- over remnant of urachus
Medial umbilical fold or ligaments (2)
- over obliterated fetal
- umbilical arteries
Lateral umbilical folds (2)
- over inferior epigastric
- vessels
only fold functioning in our body right now

What is the site of the direct inguinal hernia and where does it occur?
Inguinal triangle
occur medial to the inferior epigastric vessels

Direct vs. Indirect Hernias
Direct:
- MEDIAL to the Inferior Epigastric Vessels
Inside the Inguinal Triangle
Indirect:
LATERAL to the Inferior Epigastric Vessels

True or False
The rectus sheath only surrounds the anterior rectus abdominal muscle
False
rectus sheath surrounds both the anterior and posterior rectus abdominal muscle
Above Arcuate Line
What is found on the Anterior and Posterior to Rectus Abdominus?
Anterior to Rectus Abdominus:
- External Oblique
- Internal Oblique (1/2)
Posterior to Rectus Abdominus:
- Internal Oblique (1/2)
- Transversus Abdominus
- Transversalis Fascia
- Parietal Peritoneum

Below Arcuate Line
What is found on the Anterior and Posterior to Rectus Abdominus?
Anterior to Rectus Abdominus:
- External Oblique
- Internal Oblique
- Transversus Abdominus
Posterior to Rectus Abdominus:
- Transversalis Fascia
- Parietal Peritoneum

The lateral folds on the anterior abdominal wall contain which structure(s)?
A. Inferior Epigastric Vessels
B. Remnant of the Urachus
C. Remnant of the Obliterated Umbilical Arteries
D. Superior Epigastric Vessels
A. Inferior Epigastric Vessels
Inguinal Ligament
What does it represent
where does it run,
and what does it form?
Represents –> inferior border of the abdomen
Runs –> from the anterior superior iliac spine to the pubic tubercle
Forms –> the major part of the floor of the inguinal canal

What is the External/Superficial Ring made by?
What is the Internal/Deep Ring made by?
Made by External Oblique Aponeurosis
Made by the Transversalis Fascia



What is the Conjoint Tendon: made by?
Made by Internal Oblique and Transversus Abdominus

The external spermatic fascia, cremaster muscle, and the internal spermatic fascia the spermatic cord
SURROUND
Testicular artery & vein + Vas deferns =
Transversus Abdominus + Internal Oblique =
Spermatic Cord
Conjoint Tendon

Which structure helps form the deep/internal inguinal ring?
A. Transversalis Fascia
B. External Oblique
C. Internal Oblique Aponeurosis
D. Transversus Abdominus Muscle
A. Transversalis Fascia
For Females:
The only thing that runs through the inguinal canal (that we need to know) is
- round ligament of the uterus
- the ilioinguinal nerve
- the genital branch of the genitofemoral nerve
True or False
The ilioinguinal nerve runs through the inguinal canal but is not inside the spermatic cord.
True
These rings of inguinal canal allow for protection of the peritoneum during increased abdominal pressure

Arterial, venous, and lymphatic supply to the testes originates from where?
the abdominal area
Female Inguinal Canal

What are the Floor, Roof, and Walls of the Inguinal Canal?
Roof fibers of internal oblique and transversus
Anterior Wall aponeurosis of external oblique and internal oblique
Floor lower edge of inguinal ligament and lacunar ligaments
Posterior wall conjoint tendon and transversalis fascia
MALT stands for what?
M: Muscles
Roof:
Internal Oblique and Transversus Abdominus Muscles
A: Aponeuroses
Anterior Wall:
Aponeuroses of External and Internal Oblique
L: Ligaments
Floor:
Inguinal and Lacunar Ligaments
T: Tendons
Posterior Wall:
Conjoint Tendon and Transversalis Fascia

When does the Processus Vaginalis fuse together?
once the testes has descended
True or False
Rectus Abdominus and Transversus Abdominus contribute to the surrounding of the testes
False
Rectus Abdominus and Transversus Abdominus do NOT contribute to the surrounding of the testes
What is the covering of the indirect Hernia?
What is the covering for the Direct Hernia?
Indirect Hernia = Peritoneum AND Spermatic Cord
Direct Hernia = ONLY Peritoneum

Indirect Hernia Pathway:
Deep inguinal ring → Superficial inguinal ring → Into the scrotum

Direct Hernia associated with:
Indirect hernia associated with:
- side of finger
- tip of finger


