L16-17: Office ergonomics Flashcards
What is the prevalence of musculoskeletal problems associated with computer use in Australia?
- 61% reported neck symptoms lasting greater than 8 days in the last 12 months
- 75% of public service employees reported low back problems in last 12 months

What are the 2 risk factors for MSD in office workers? Why?
- repetitive movement – fingers, wrist, head, shoulder
- sustained, static and/or awkward postures of head, neck, upper limb, trunk, legs
Mechanical and /or metabolic loading of the same muscle group(s) repeatedly or at low force results in fatigue and without sufficient rest or interruption can result in discomfort, tension, MSK symptoms
What are the 3 sources of risk for sustained and/or awkward postures of head, neck, upper limb, trunk, legs as risk factors for MSD in office workers?
- Head – visual correction, height / distance of monitor, high job demands
- Shoulder – mouse use/position
- Low back – lack of task variety; prolonged sitting/ sedentary work
What are the 2 sources of risk for repetitive movement – fingers, wrist, head, shoulder as risk factors for MSD in office workers?
- Wrist/fingers – nature of work (data entry/CAD), task monotony
- Head – typing style (hunt n peck), uncorrected vision, location of documents
What are 4 factors with evidence for musculoskeletal symptoms in office workers?

What are 3 factors increasing the risk of neck pain?
- Longer sitting time (home & work)
- Higher job strain
- Higher psychological stress
What are 3 factors decreasing the risk of neck pain?
- Longer time walking
- Greater cervical extensor endurance
- Neutral head and thorax posture
What is the aim of factors increasing/decreasing the risk of neck pain?
Identify risk factors for development neck pain in office workers.
What are the individual and workplace risk factors for neck pain (multifactorial)?

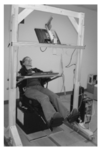
What are the risk factors and sources of risk in this photo?

Risk factors – sustained & awkward posture of neck
Sources of risk – height of desk too low; chair too high
What are the 6 effects of job stress/job strain?

What are 2 steps when conducting a workstation assessment?
- Identify the risk factors
- Talk to worker
- Task analysis: observe interaction between worker and environment
- Assess the risk for injury
- A checklist or tool
- Assess the risk for injury
What are 8 characteristics of “1. Indentify the risk factors- Talk to the Worker” when conducting a workstation assessment?
- Any current problems – headaches, back/neck, pregnant, CTS
- Take photos – if not, sketch the layout
- Hours of work, number and duration of breaks? Activity during breaks?
- Training on how to set up workstation provided?
- Do they wear glasses – bifocals, single focal length
- Are you comfortable in your workstation?
- Work at one or more workstations?
- Open plan office or Activity Based Office Design
*Not a musculoskeletal assessment*
Why is it important to take photos or make sketches of “1a. Indentify the risk factors- Talk to the Worker” when conducting a workstation assessment?
A sketch can show relationship between worker and environment

What are 7 characteristics of “1. Indentify the risk factors- Psychosocial factors” when conducting a workstation assessment?
- What do you enjoy about your job?
- In general, do you have enough time to get your work done?
- Do you work overtime /shift work / take work home?
- During busy times, can you get assistance from colleagues or supervisor?
- Do you have any control over the type, timing and flow of work tasks?
- Doing these fiscal times, are you concerned about your job security? (restructuring/ right sizing)
- Working with customers can be stressful – how do you manage this?
What are 4 characteristics of “1b. Identify the risk factors- Observe how the worker interact with environment” when conducting a workstation assessment?
- What are they required to do, how long? (task demands) – reading from screen, data entry, customer service, document reading/writing; reconciliation of invoices; telephone work
- Ask them to give percentage of time spent doing each task; rate level of pain/discomfort with each task
- Do they rotate jobs with other staff?
- Is there electronic performance monitoring (eg call centre workers) ?
What are 6 characteristics of “2a. Assess the risk for injury- Checklists and Tools” when conducting a workstation assessment?
- ROSA (Rapid Office Strain Assessment)
- RULA (Rapid Upper Limb Postural Assessment tool)
- Quantifies risks associated with computer work
- Good for determining action level for change eg office ergonomic audit
- Good validity and reliability
- Don’t evaluate environmental or psychological factors, eye strain
What are 7 features in the the “ideal” workstation set-up?
- Chair (and seated posture)
- Monitor – position, distance, angle
- Keyboard position (and use)
- Mouse position and use
- Telephone position and use
- Documents – position, angle
- Other features in environment eg lighting, air quality, temperature
What are 7 chair features?
- Easily adjustable in height and angle
- Adjustable back rest height, depth, angle
- Cloth covered seat (non slippery)
- Seat should accommodate thighs and have curved edge
- 5-point castor base for stability
- Should enable neutral spine posture with hips slightly higher than knees
- Arm rests – reduce forces and flexion moments on Lx spine, unload the shoulders when hand activity is not continuous but if not correct height they induce asymmetrical posture of trunk
What determines the correct seat height?

If chair too high, may experience tingling, numbness in legs and feet due to _________
XXX
What are 5 ideal characteristics of seated posture?
- Upright or slight backward lean (10-20˚) is good especially to take phone calls or ‘think’
- Thighs should be fully supported with 2-3 finger width space behind knee
- Feet flat on the floor or use a footrest or telephone book to relieve pressure on thighs (i.e. parallel to floor)
- Work surface should be at elbow height or just above for writing
- For comfortable keyboard use, desk should be just below elbow height
What is a forward lean?

What is a backward lean or ‘executive’ position?