Implantation and Pregnancy Flashcards
What is the normal site of implantation?
The ampulla of the fallopian tube
During the ___________ phase, there is a refurbishing of ciliated epithelial cells of the fallopian tubes.
Late follicular
At higher levels of __________, the isthmus of the fallopian tube starts to cotnract with sympathetic innervation.
Estrogen
NOTE: It allows spermatoza into the ampulla, but prevents the oocyte from moving to the uterus before fertilization occurs.
Overview of Ovum transport
- Ovulation
- Ovum expelled
- Ovum drawn into fallopian tube, due to fimbriae and cilia
- Oocyte is trapped in the ampulla of the fallopian tube, due to estrogen action causing the isthmus to constrict
* Dwells for maximum of 32 days - Fertilization occurs
- Progesterone inhibits estrogen, which releases the ampuloisthmic block
- Fertilized ovum transported to uterus, via action of ciliated epithelial cells
- Fertilized ovum floats free for as much as 4-5 days before implantation
Capasitation
- Removal of inhibitory glycoproteins from spermatozoa
What are the results of capasitation?
- Sperm motility
- Sperm metabolic activity
- Ability to fertilize oocyte
Acrosome reaction
Rupture of the outer acrosomal membrane and rease of acrosomal enzymes.
*Provides ability to penetrate the culumus oophorus and zona pellucida
Where does the acrosome reaction occur?
In the ampulla of the fallopian tube
Function of hyaluronidase
Provides ability to penetrate the culumus oophorus
Function of acrosin
Provides ability to penetrate the zona pellucida
During fertilization, the sperm heads stops in the ___________ and fuses with the __________.
Perivitelline; oocyte vitelline membrane
NOTE: Fertilization occurs in the amplulla of the fallopian tube
Mechanism of fertilization
- At ejaculation, sperm cells are deposited in the vagina.
- Once deposited, they travel through the cervical canal, through the uterus, and then up to the ovum in the upper third of the oviduct.
- Movement and hyaluronidase facilitate penetration of culumus oophorus
- Movement and acrosin facilitate penetration of zona pelucida
- Sperm head stops in perivitelline space and fuses with oocyte vitelline membrane
- Sperm head contents enter vitelline space, initiate cortical reaction (to block polyspermy) and completion of meiosis II
- Extrusion of 2nd polar body
- Fusion of male and female pronuclei
Where does implantation occur?
In the endometrium of the uterus
What are the events of implantation?
- 1st mitotic cell division occurs within 24 hrs of fertilization
- Growth-> Morula stage-> blastocyst stage
- Arrival in uterus 4-5 days postovulation
- Blastocyst settles near a blood vessel and attachement begins (between days 5-9)
- Trophoblast invasion begins
* Requires low levels of estrogen
6. Synthesis and secretion of hCG begins
- Rescue of corpus luteum
NOTE: If the blastocyst implants too far away from a blood vessel, it will not be able to recieve nutirents by diffusion in the first 10 days
When is pregnancy detectable?
Prior to implantation and 1st missed menstrual flow
______ allows for rescue of the corpus luteum.
hCG
What role does estradiol play in fertilization, transport, and implantation?
- Stimulates growth of fallopian tube ciliated epithelial cells
- Facilitates adrenergic induction of “ampulloisthmic block”
- Facilitates trophoblast invasion of the endometrium
- May induce contraction of fallopian tube musculature
What role does progesterone play in fertiliztion, transport, and implantation?
- Stimulates beating activity of fallopian tube epithelial cilia
- Blocks E2 effect on fallopian tube ampulla isthmus muscle
What is the function hPL?
Modifies the metabolic state of the mother during pregnancy to facilitate the energy supply of the fetus.
NOTE: hPL acts as a growth hormone
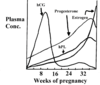
What hormonal changes are seen throughout pregnancy?
- Prolacting rises throughout pregnancy
- hCG rises early in pregnancy
- Progesterone rises until about two weeks berfore parturition
- Estrogen constantly rises
- FSH and LH remain low throughout pregnancy
What changes occur with the pituatary gland and its secretions during pregnancy?
- Increase in gland size
- Increases in prolatin, ACTH, TSH
- Decrease in GH
NOTE: GH decreases or stays the same
What changes occur with the andrenal gland and its secretions during pregnancy?
- Increased glucocorticoids
- Mineralocorticoids
What changes occur with the thyroid gland and its secretions during pregnancy?
- Increase in size
- Increase in hormone secretion
What changes occur with the parathyroid gland and its secretions during pregnancy?
- Increase in size
- Increase in hormone secretion
What changes occur with the placenta and its secretions during pregnancy?
- Increase in human chorionic thyrotropin, cGH
- Increase in cACTH, cTRH, cGnRH
Sheehen’s syndrome
Hypopituitarism (decreased functioning of the pituitary gland), caused by ischemic necrosis due to blood loss and hypovolemic shock during and after childbirth
NOTE: May result from pituatary enlargement during pregnancy. Pituatary can be squished by the sella turcica
As placental GH increase, there is an increase in _____.
IGF-1, which plays a role in feedback inhibition of pituatary GH production
NOTE: As the placental GH increases, materal GH decreases
Why is the placenta not able to convert C21 steroids (pregnenolone, progesterone) into C19 steroids (testosterone)?
It lacts the cytochrome P-450-17 hydroxylase enzyme
The ________ is required for the synthesis of estrogen during pregnancy.
Fetal adrenal gland
NOTE: The pregnenolone from the placenta to the fetal compartment to make DHEA-S (Dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate)
What happens to th DHEA-S after it has been produced in the fetal adrenal gland?
It is transported to the fetal liver, where it is converted to estroil (E3)
NOTE: Estriol can work in the fetal and maternal system to regulate blood flow
___________ serves as a substrate for the production of fetal cortisol.
Progesterone
What roles does estrogen play in pregnancy?
- Increases uterine size
- Increase external genitalia size
- Increases mammary gland ductile proliferation
- Increases pelvic ligaments relaxation with relaxin
- Increases uteroplacental blood flow
What roles does progesterone play in pregnancy?
- Increase decidual cell development
- Increases uterine and oviductal secretion
- Increseas loculo-alveolar breast development
- Decreases myometrial contractility
- Increases immunosuppression of the uterus
- Prevents the uterus from rejecting the fetus as a foreign body
What two substances are released as result on increased angiotensin?
Aldosterone
- Increases blood volume
Prostaglandins/ Prostocyclin
- Increases vascular constriction
NOTE: Normal pregnancy induces an increase in blood volume through an increase in angiotensin II and a blockage of the AII pressor effects on the maternal musculature. This allows us to have hemorrhaging during parturition without severely decreasing blood volume
What would happen if during pregnancy both the blood volume increases and the vascular wall tension occur?
Pre-eclampsia
NOTE: This may resut in brain damage to the fetus, due to the reduced blood flow.
What changes are seen in glucose, alanine, free fatty acid, and B-hydroxybutyrate levels during pregnancy?
Glucose
- Decrease, due to accelerated depletion
Alanine
- Decrease due to accelerated depletion
- Decreases severly during preganancy to maintain glucose levels
Free Fatty Acids
- Increase due to accelerated lipid mobilization and metabolism
- Assists in maintaining blood glucose levels
B-Hydroxybutyrate
- Increase due to accelerated lipid mobilization and metabolism
NOTE: Post-meal increases in insulin are elevated three fold. This indicates an reduced control of plasma glucose.

A progressively increased turnover of lipid occurs during pregnancy. This increased turnover has been associated mainly with the dibetogenic action of ______ and __________.
hPL; placental GH
NOTE: These hormones normaly oppose insulin activities.
An elevation of __________ may be the direct inducer of initial contractions.
Prostaglandins
NOTE: Oxytocin from the placenta and pitiutary stimulate a continuation of the contractions but do not initiate parturition.
Which ratio is implicated as the inital change induced by the fetal signal?
E2/P ration increases
What is the positive feedback mechanism that regulates parturition?

What are the 4 phases of lactation?
Mammogenesis
- Preparation of mammary gland
Lactogenesis
Milk secretion
Milk letdown
What are the steps of mammogenesis?
- The atrophic duct is primed by adequate levels of insulin, adrenal, steroids and GH
* Estrogen induces ductile growth
__2. After ductile growth, the ducts will be primed by insulin, estrogen, adrenoL, steroids, and GH
- Progesterone and prolactin induce growth of alveoli
NOTE: After ductile growth from the 1st pregnancy, most of the ducts will stay in place for future pregnancies.
What hormones stimulate milk secretion? Which hormones inhibit milk secretion?
Stimulate: Prolactin, insulin, and adrenal steroids
Inhibit: Estrogen and Progesterone
What are the steps lactogenesis and milk secretion?
Late pregnancy aspects
- Development of cellular secretory apparatus
* Increases in ER, synthetic pathway enzymes, and # of secretory vesicles - Small amount of secretion
Post parturition aspects
- Further increases in secretory machinery
- Cells swell with secretory vesicles
Progressive increases in secretion
- Secretion is maintained by suckling stimulation of prolation release.
- It also induces the release of oxytocin
Milk let down is stimulated by _______.
Oxytocin
REMEMBER: Release of oxytocin is maintained by the suckling stimulus
Gestational diabetes mellitus
Diabetes first recognized during pregnancy
NOTE: GDM occurs when the pancreas cnanot secrete sufficient insulin to overcome the relative insulin resistance and increased fuel consumption during pregnancy
What is a diabetogenic hormone?
Any hormone that opposes the effect of insulin
- GH
- CRH
- hPL
- Progesterone
What are some abnormalities associated with infants of diabetic mothers?
- Macrosomia **
- Hypoglycemia **
- Hypocalemia and Hypomagnesemia **
- Respiratory Distress Syndrome **
- Polycythemia
- Hyperbilirubinemia
- Renal Vein Thrombosis
- Persistance of Fetal Circulation
- Cardiomyopathy
- Congenital Heart Disease*
- Caudal Regression Syndrome *
- Miscellaneous Congenital Anomalies *
*= Higher frequency in infants of non GDM mothers
**= Pathophysiology to be considered
Why would macrosomia and hypoglycemia result in a baby of a mother with GDM?
If we have materal hyperglycemia during pregnancy, it dumps much glucose into the baby. The baby will respond by increasing insulin levels. Thus the baby will be hyperinsulinemic. The hyperinsulinemic status produces macrosomia and hypoglycemia once that baby is born and no longer recieving the glucose supply from mom.
What accounts for the hypocalcemia and hypomagnesemia seen in baby with a mom with GDM?
- During the last two months of gestation, a lot of Ca2+ moves from mom to baby. If the mom is diabetic, she will spill Mg through her kidneys and end up with low Mg.
- At the time of parturition, there are high levels of Ca2+ and calcitonin to store Ca2+ i bones.
- Mg2+ is required for the release of PTH from vesicles. With low Mg, there will be low PTH, and thus a hypocalemic state
How can respiratory distress syndrome occur in a baby with a mom that has GDM?
- Lung glycogen is needed to produce surfactant
- However, elevated circulating glucose will result in low lung glycogen, and thus low surfactant. This results in infantile respiratory distress
Hormone factors involved in regulating fetal growth
NOTE: Every place we see that has mahor growth of fetus has to do with insulin. Hyperinsulinemia is associated with excessive fetal growth. This reuires insulin binding to IGF-1 receptor.

Pathophysiology of infants of diabetic mothers



