Immunisations Flashcards
(14 cards)
What are some success vaccination programs that can be used as examples for patients?
- smallpox
- polio - only remaing in 3 endemic countries
- measles - WHO has significantly decreased its effects in developing countries
What are some diseases that are increasing despite vaccination? Why?
- Pertussis is increasing:
- immunity wanes in later life (isn’t lifelong)
- People after 30 years old are generally not immune
- you get a modified infection with it being less severe, but you can still transmit the disease.
- target parents to get the pertussis vaccine.
- Measles:
- travellers bringing it back to australian communities
- primarily thailand, indonesia, india.
What does this picture show? What vaccine protects from this?

Diptheria:
- school aged children, sore throats.
- Respiratory difficulties from obstruction, can have rare outcomes of death
- can affect smooth muscle (heart muscle) and cause arrhythmias
What is the diagnosis? What vaccine can prevent this?

Pertussis
- still very common
- cough - whoop at the end, known as the 100 day cough
- get hypoxic encephalopathy
- cyanosed and hypoxic (oxygen and NG feeding tube)
- petechiae and vomiting in older children
- diagnosis using nasal swab, PCR (NAT), blood test for serology (bordetella specific IgA) or PT antigen
- management:
- antibiotics (make it less infective don’t change the course unless there in catarr stage (before the cough)
- macrolides e.g. clarithromycin
- antibiotics (make it less infective don’t change the course unless there in catarr stage (before the cough)
What is the disease? What vaccine can prevent this?

Periorbital cellulitis secondary to HiB
- do eye movements, visual acuity
- usually caused by staph or strep but very common with HiB too.
- HiB can also cause meningitis and epiglotitis (pic)
- Treatment:
- flucloxacillin but in unvaccinated use 3rd gen cephalosporin

What is the Diagnosis? What vaccine is used? What are the effects of the disease?

Polio
- spread via fecal oral route, an enterovirus.
- most people develop flacid paralysis
- Sabin vs Salk
What vaccine can prevent this condition? What is the problem shown here?

Rotovirus
- commonest cause of viral gastro before the vaccine now overtaken by norovirus
- mainly morbidity through admissions through dehydration.
- it is an oral vaccine.
What causes this condition? What is the complications of this disease?

Mumps
- virus spread by droplet
- admission because can’t eat or drink due to swelling of the parotids. Often bilaterally but occasionally unilateral.
- Can cause severe disease:
- orchitis (infertility)
- encepahlitis
What is the diagnosis of this picture? What complications are related to this condition?
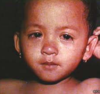
Measles
- 3Cs and 1 K of Measles:
- conjunctivitis
- cough
- coryzal symptoms
- Koplik spots
- maculopapular rash starts on the face and spreads
- Complications:
- pneumonia
- encephalitis (1 in 1000)
- Subacute scelerosis SSPE - happening years later.
What is the Diagnosis? What disease causes this process?

Congenital Rubella
- rubella - often seen overseas
- Complications:
- growth retardation
- deaf
- intellectual impairment
- congenital cardiac defect
- only slight disease as an adult (get a cold)
What is this disease? What are its effects?

Varicella Zoster Virus (chickenpox/shingles)
- fever and rash,
- come out in crops and get variation of progression
- risk of teratogenic if baby is small
- adults it can be dangerous:
- bacterial infection secondarily
- post viral cerebellitis
What is the disease behind this sick child? What vaccinations can you use?

Meningococcal
- bacterial infection - purpitic non-blanching rash
- we only vaccinate against meningococcal C. Can get B on private health or if immunosuppressed.
- in travellers you get the polysaccharide vaccine due to outbreaks A and W135
- other serotypes are out there now
- if you are exposed prophylactic rifampicin (covers urine and tears)
A mother comes in and is concerned about vaccines overwhelming the immune system and is concerned about the side effects of vaccines (esp autism). Counsel her about vaccines.
Pros:
- MMR has been disproven to cause autism in multiple studies
- delaying them means more risk - (pertussis, pneumococcal) but there might be problem giving too many.
Anti:
- herd immunity, but against this argument:
- some need very high amounts,
- protecting immunodeficient (babies, elderly, others)
- travel
- complications:
- local (swelling)
- general - mold fever, irratability/aches
- might get a mild form of disease:
- MMR - 1 in 10 get maculopapular rash
- Varicella - unusual but some get vesicles at the site
- Rotavirus - diarrhoea within a day or 2 and occasionally some vomiting
- rare:
- hypotonic hyperresponsive episode (scary) - vasovagal
- anaphylaxis
- intussusception
18 mthh old twins one with neuroblastoma for chemo. Due for a non-live vaccine and a non-live booster (MMRV and DTPa). What should you do? What are the contraindications for immunisations?
- None for neuroblastoma child - Absolute contraindications:
- anaphylaxis
- unexplained encephalopathy (post pertussis)
- live vaccines in:
- pregnancy
- immunosuppression
- previous live virus
- everyone else in household should get live vaccine and wait 6 months post chemo to give the child his.
- relative contraindications:
- evolving neurological disease
- high temperature (>38.5)


