ID & Immunizations Flashcards
Lyme Disease - bug and tick name
- Borellia burgdoferi
- Ixodes deer tick (black-legged tick)
Malaria Prophylaxis
- malarone
- 1 day before to 7 days after (daily)
- don’t use in preg
- chloroquine
- weekly, 1 week before to 4 weeks after
- OK in preg
- mefloquine
- 1 week before to 4 weeks after
- OK in preg
Travel immunizations
Twinrix – Hep A/B
- Regular schedule : day 0, 30 and 180
- Accelerated schedule: day 0, 7, 21 and 365
Typhoid Fever – Salmonella
- Typherix: single dose and repeat in 3 years
- Typhim Vi: single dose and repeat in 3 years
Traveller’s Diarrhea - ETEC/V.cholera
- Dukoral: two doses q weekly starting 2 weeks ac travel (6 years to adults) three doses q weekly starting 3 weeks ac travel (2 to 6 years)
- Booster - if all pts have had their last dose within 5 years a single oral booster dose is needed; if the last dose was > 5 years then a complete primary vaccination series as per age is indicated
Tetanus/diphtheria
- All travelers should have this UTD
Modified Centor Criteria
Presence of tonsillar exudates: 1 point
Tender anterior cervical adenopathy: 1 point
Fever by history: 1 point
Absence of cough: 1 point
Age less than 15 years,* add 1 point to total score
Age more than 45 years,* subtract 1 point from total score
0-1 = no treatment, no testing
2-3 = RAT, treat if +ve, send culture if -ve (in kids only)
4 = treat, send culture
If no RAT
0-1 = no treatment
2 = no treatment unless outbreak, or known recent gabs exposure
3-4 = treat
Treatment for GABS strep Pharyngitis
Peds: Amoxicillin 50 mg/kg PO daily X 10 days (max 1000 mg)
or Amoxicillin ER tablet 775 mg PO daily X 10 days (children >12)
Adult: Pen V 300 mg PO TID X 10 days
or
Peds: Clindamycin 20-30 mg/kg/day PO divided TID X 10 days
Clindamycin 300 mg PO TID X 10 days
Indications for Abx prophylaxis for IE
- Invasive Dental Procedure
AND
- Prosthetic heart valve, hx IE, or unrepaired congenital cyanotic heart defect
Uncomplicated UTI Tx options
Macrobid 100 mg PO BID X 5d
Cipro 250 mg PO BID X 3d
TMP-SMX (Septra DS) i tab PO BID X 3 d
Pyelonephritis (Inpatient) Treatment
Ceftriaxone 1-2g IV
or
Gentamicin 5 mg/kg IV
or
Cipro 400 mg IV
*add ampicillin 1-2 g IV if enterococcus suspected
Pyelonephritis (Outpatient) Treatment
Cipro 500 mg PO BID X 7d
or
Septra DS i tab PO BID X 10-14d
*add ampicillin 500 mg PO TID if enterococcus suspected
Pyelonephritis Tx in Pregnancy
Inpatient: Amp + Gent or Ceftriaxone
Outpatient: TMP/SMX* or Keflex
*Not for late third trimester due to risk of kernicterus
Outpatient Pneumonia Treatment
Amox/Clav 875/125 mg PO BID X 7d
Pen allergic:
levofloxacin 750 mg PO daily X 5d
or
moxifloxacin 400 mg PO daily X 5d
Pneumonia: Inpatient Treatment
Amox/Clav 875/125 mg PO BID +- Azithro 500 mg PO daily
or
cefotaxime 1g Q8h IV or ceftriaxone 1g q24h IV +- Azithro 500 mg IV daily
+- Vancomycin 15-20 mg/kg IV Q12h
Pen allergic:
levofloxacin 750 mg PO/IV daily
or
moxifloxacin 400 mg PO/IV daily
Cellulitis treatment
Nonpurulent: Keflex 500 mg PO QID X 5-7d
(levo/moxi/clinda if allergic)
Purulent: Septra DS i BID X 7d
(or doxycycline 100 mg PO BID)
Diabetic foot infections treatment
Minor (ulcer : Keflex +- Septra
Moderate to Severe:
Amox/Clav + Septra
or
Ceftriaxone + Flagyl + Vanco
or
Pip-Tazo + Vanco
SIRS Criteria
Two of:
T >38.3 or
HR > 90
RR >20 or PCO2
WBC 12,000, or >10% immature forms
Triggers for treating AOM
>6 months with otorrhea OR severe (mod otalgia/>48h/T>39) X 10d
6-23 months with bilat AOM X 10d
6-23 months unilat, not severe = Obs or Abx X 10d
>2 years, not severe = Obs or Abx X 5-7d
Persistent Symptoms of AOM after 48-72h
Initiate or change Abx therapy, consider IM ceftriaxone, clinda, or tympanocentesis
AOM Abx Choice
1st line: Amoxicillin 80-90 mg/kg divided BID or Amox/Clav 90 mg/6.4 mg/kg
Pen Allx: Cefuroxime 30 mg/kg divided BID
Dose of Acyclovir for suspected HSV Encephalitis
10 mg/kg IV q8h X 10-14 d (assuming normal renal function)
Stages of Lyme Disease
- first stage: erythema migrans, sometimes malaise/LAN, resolves 3-4 weeks
- second stage: fever, LAN, neuropathies, heart block, arthralgias, multiple target lesions. Unilateral or bilateral facial nerve palsy.
- late disseminated stage: months/years later. Chronic arthritis, myocarditis, polyneuropathy, subacute encephalopathy.
What to do with a tick bite?
- no need to test serum or tick if no EM
- IDSA recommends prophylaxis (200 mg doxy or 4 mg/kg up to 200 mg in children > 8 as single dose) if all of:
- ixodes tick
- engorged or > 36 h attached
- within 72 h of bite
- if doxy contraindicated, do not offer alternative abx
Rocky Mountain Spotted Fever (read-through)
- rickettsia rickettsii
- fever, malaise, conjunctivitis
- rash (80%) days 2-4 of fever
- small blanching erythematous macules –> becomes petechial
- begins on hands/feet, centripetal spread up the trunk
-
Labs
- normal WBC + Hb
- Low Plt
- mild + LFTs
- Low Na
- acute + convalescent serum
-
Tx
- Doxy
- Risk of teeth staining low, recommended for children of all ages
Rabies incubation period
- 20-90 days, but cases up to 5 years
- stays localized in soft tissues during incubation, but rapidly spreads to CNS thereafter
Rabies Clinical Features
- encephalitis
- 80% encephalitic, 20% paralytic
- 50% have hydrophobia - drinking causes choking/spasms
- aerophobia - grimacing when air blown on face
What does/does not constitute a rabies exposure?
Which animals are low/high risk?
- petting a rabid animal or contact with urine/blood/feces is not an exposure (unless fresh wound on skin)
- being in same room as bat with no known bite is NNT ~2.7 million, but PEP often still recommended
- If asleep, if child, if mentally disabled, then PEP
- healthy cat/dog –> observe animal for 10 days before offering vaccine
- 2x vaccinated cat/dog no reported cases
- skunks, raccoons, foxes, most carnivores, and bats need prophylaxis
- squirrel, rats, rabbits, rodents almost never require prophylaxis (no reported cases)
Ehrlichiosis
- tick-borne illness
- WBC infection
- lone-star tick, southeastern US
- 30% get nonspecific rash
Anaplasmosis
- tick-borne illness
- ixodes tick, common in Lyme endemic areas
- fever, malaise
- no rash
- doxy
Tularemia
- Francisella tularensis
- transmitted by ticks and flies
- several forms
- ulceroglandular (most common)
- glandular
- typhoidal
- oculoglandular
- pneumonic
- doxy, cipro, gent if severe
Babesiosis
- malaria-like parasite
- co-infection with lyme common
- 7-10 days atovaquone + azithromycin
West Nile Virus
- arbovirus
- transmitted by mosquitoes
- 20% infected develop symptoms, 1% severe infection
- Ab testing available, not specific
- treatment supportive
Anthrax
- bacillus anthracis
- unsterilized, imported animal hides/raw wool
-
pulmonary
- generally fatal inhaled mediastinitis
-
cutaneous
- most common
- painless macule –> ulcerative site with serosanguineous vesicles – > painless black eschar
- untreated mortality 5-20%
Brucellosis
- unpasteurized dairy, slaughterhouse workers
- endemic in Mediterranean basin
- nonspecific symptoms
Psittacosis
- chlamydophila psittaci
- from birds
- pneumonia + endocarditis, hepatitis, CN palsies, AIN
Q Fever
- coxiella burnetii (rickettsial infection)
- inhalation or arthropod from cattle, sheet, goats
Hantavirus
- inhalation from rodents
- 3-4 d flu-like illness –> APE, hypotension, metabolic acidosis
- supportive treatment
Cutaneous Larva Migrans
- migrating cutaneous hookworm larva from contaminated soil
- single-dose ivermectin
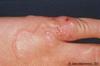

Disseminated Gonorrhea
(painless)

- chancre or primary syphilis
Rash of secondary syphilis
- dull red-pink papular
- starts on trunk, spreads to flexor surfaces, palms + soles

(painful)

- chancroid
- haemophilus ducreyi
(painless chancre —> painful LAN)

- lymphogranuloma venereum
Nongonococcal Urethritis
- usually chlamydia
- sometimes ureaplasma urealyticum, mycoplasma genitalium, HSV, adenovirus (no need to treat)
- if WBC >5/HPF –> treat for chlamydia
- if symptoms persist, culture for trichomonas vaginalis + treat with Flagyl 2 g PO x 1
Syphilis
- treponema pallidum
- primary
- painless chancre, indurated borders
- secondary
- 3-6 weeks after end of primary phase
- rash, lymphadenopathy, sore throat/fever/headaches/malaise
- dull red-pink, papular
- starts on trunk, spreads to palms/soles, flexor surfaces
- tertiary
- 3-20 years later, in 1/3 of patients
- widespread granulomatous lesions (gummata)
- meningitis, dementia, neuropathy (tabes dorsalis), thoracic aneurysm
Genital Herpes
- genital usually HSV-2, but indistinguishable from HSV-1
- prodrome of pain/tingling x 24h
- vesicles heal within 3 weeks
- shedding for 10-12 days after onset of rash
- to culture, deroof/puncture vesicle and scrape base with swab
- first episode (primary) treated longer than second episode
Chancroid
- Haemophilus ducreyi
- painful genital ulcers + lymphadenitis (may lead to buboes if untreated)
- dx clinical (cultures poor, no PCR available)
- single dose zithromax or ceftriaxone tx
Lymphogranuloma Venereum (tropical bubo)
- painless chancre x 2-3 days
- unilateral suppurative inguinal LAN 1-3 wks later
- scarring linear depressions parallel to inguinal ligament
- somtimes rectal ulcers, bleeding, discharge
- dx clinical, no great tests
- doxy x 21 days
Granuloma Inguinale (Donavanosis)
- Klebsiella granulomatis
- endemic in India, south Africa
- painless subcutaneous nodules –> painless beefy red, fragile ulcers
- dx clinical, no great test
- doxy x 3 weeks
Cognitive Force
WBC > 20
- CXR
- Urine
- Skin check
Sporotrichosis
- Sporothrix schenckii fungus
- mostly in tropical zones, in soil, common among florists
- dx fungal cultures/tissue biopsy cultures
- tx itraconazole x 3-6 months
Acute Herpetic Gingivostomatitis
- common primary infection at 6 mo. - 5 yrs
- 90% HSV 1, 10% HSV 2
- abrupt high fever, drooling, swollen + friable gingiva + vesicular oral lesions, tender cervical LAN
- lasts 1-3 weeks
- acyclovir 15 mg/kg PO divided 5x/day x 7d
Treatment of Varicella + Shingles
-
Varicella
- h/a, malaise, fever
- 2-3 crops of lesions focused on torso/face over 1 week
- consider PO acyclovir if > 12 y old, chronic skin or lung disorder, or immunocompromised
- acyclovir 20 mg/kg PO QID x 5 days
- start within 24h of rash if possible
-
pregnancy
- 30% varicella pneumonia, mortality 40%
- congenital varicella syndrome
- usually in first 20 weeks of pregnancy
- <2% risk at < 20 weeks, lower after
- diagnosis
- clinical
- 4x rise in varicella-specific IgG Ab over 14-21d period
- management
- if history of chickenpox –> reassure
- if unknown, and able to get results within 96h, draw VZV IgG Ab
- if unable to get labs within 96h or if no immunity
- give VZIG 625 units IM
- if develops severe disease
- acyclovir 10 mg/kg IV Q8h or 800 mg PO QID x 5 d
-
Shingles
- valacyclovir 1 g PO TID x 5 days for adolescents/adults
- maternal HZV not harmful but exposure to HZV without varicella immunity is
Poor Man’s CD4 Count
- < 200 is ~ < 1700 cells/mm^3 total lymphocyte count
- < 200 CD4 and viral load > 50 k is associated with AIDS-defining illnesses and is common cutoff for antiretroviral therapy
oral hairy leukoplakia (OHL)
- oral hairy leukoplakia (OHL)
- EBV infection
- lateral border tongue white plaques, cannot scrape off
- acyclovir

HIV Optho Emergency
- CMV Retinitis
- low CD4 count (often < 50) + ssx retinal detachment
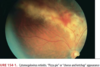
PJP Pneumonia
- fever, nonproductive cough, SOB
- Xrays diffuse infiltrates but 25% neg
- sometimes elevated LDH
- ABG –> increase in Aa gradient
- walk test –> desat
- septra DS 2 TID x 3 weeks
- prednisone 40 mg BID and 21 day taper if PaO2 < 70 mm Hg or Aa > 35 mm Hg
Endocarditis
Review Evernote
Tetanus
Review Evernote
Occ Health and HIV PEP
see note “Occ Health”
C. Diff Infection
- symptom onset usually 7-10 days post abx, but up to 60d
- sometimes two-step test
- step 1: test for glutamate dehydrogenase (present in all strains)
- step 2: if +ve, test for toxin A/B which is present only in toxic strains, treat if step 2 positive
- initial mild episode: Flagyl 500 mg PO TID x 14 d
- initial moderate episode: Vanco 125 mg PO QID x 14 d
- severe: Flagyl 500 mg IV + Vanco 500 mg PO
- Relapse: see stanford
- fidaxomicin 200 mg PO BID x 10 d (alternative to vanco for moderate)
- treatment does not eradicate, so do not test/treat asymptomatic patients
Scombroid Poisoning
- tuna, mackerel, bonito, mahi-mahi
- histadine in fish transformed into histamine by bacteria when stored too warm
- 30 min-24h after eating
- flushing, headache, abdo cramping, vxdx
- self-limited
- tx with H1 + H2 blockers
Ciguatera Poisoning
- large reef predator fish contaminated with Gambierdiscus toxicus –> ciguatoxin
- grouper, snapper, amberjack, barracuda
- heat resistant
- acts on Na channels causes depolarization
- nxvxdx –> hypesthesias, paresthesias, numbenss, weakness
- temperature sensitivity +- heat/cold reversal
- supportive treatment
Tetrodotoxin
- puffer fish
- paresthesias, h/a, vx, ddx, ascending paralysis
- death in 4-6 h
- anticholinesterases such as neostimine and edrophonium
Tetanus Clinical Syndromes
- uncontrolled muscle spasms
- may start with mild trisumus –> risus sardonicus
- opisthotonos
- hypersympathetic state
- HTN, fever, sweating
- normal LOC
-
localized tetanus
- rigid just muscles prox to wound
- may progress to generalized
-
neonatal tetanus
- improper stump care, born to unimmunized mother
- weak cry, poor suck
-
cephalic tetanus
- from HI or otitis
- CN 7th and other CN palsies
Who needs airborne precautions?
- Measles
- Tuberculosis (primary or lanryngeal)
- Varicella (airborne + contact)
- Zoster (disseminated or immunocompromised patient; (airborne and contact )
- SARS (Contact+airborne )
Sexual Assault
See Evernote
Treatment of First Stage vs. Second Stage Lyme
See Evernote
Asplenic patient with fever
- start broad spectrum abx
- consider admission


