Histology - Musculoskeletal Block (I) Flashcards
True/False.
Neurons are both irritable (responsive to stimuli) and conductive.
True.
The CNS is made up of what major portions?
Brain,
spinal cord
What are the major portions of the brainstem?
Midbrain
pons,
medulla oblongata
The peripheral nervous system is made of what major parts?
How many of each?
Cranial nerves (12);
spinal nerves (31)
The brain is made up of what major portions?
Cerebrum,
cerebellum,
brainstem
What is another term for neuronal cytoplasm?
What is another term for neuronal RER?
Perikaryon;
Nissl bodies
Neurons typically have a maximum of how many dendrites?
Neurons typically have a maximum of how many axons?
15;
1
Dendritic branches are called:
gemmules (spines)
Axons originate at the:
What happens here?
Axon hillock;
summation (temporal and spatial)
What basic neuron configuration (i.e. axonal and dendritic branching) do motor neurons have?
Multipolar
(multiple dendrites + 1 axon)
What basic neuron configuration (i.e. axonal and dendritic branching) do general sensory neurons have?
Pseudounipolar
(sensory side + laterally removed soma + transmitting side)
What basic neuron configuration (i.e. axonal and dendritic branching) do special sensory neurons have?
Bipolar
(sensory side and transmitting side bisected by soma)
What neuron type is responsible for circuit formation and creating high neuronal interconnection?
Interneurons
(typically multipolar)
Motor neurons are:
Sensory (general) neurons are:
Special sensory neurons are:
Interneurons are:
Multipolar;
pseudounipolar;
bipolar;
multipolar
Bipolar neurons are:
Multipolar neurons are:
Pseudounipolar neurons are:
Special sensory;
motor (or interneurons);
sensory (general)
Where is the most obvious location of a collection of pseudounipolar cell soma?
Any dorsal root ganglion
True/False.
Interneurons are often multipolar.
True.
Pyramidal cells and Purkinje cells receive large amounts of input from what type of neuron?
Interneurons
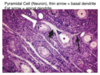
What type of multipolar neuron is found primarily in the cerebrum?
What type of multipolar neuron is found primarily in the cerebellum?
Pyramidal cells;
Purkinje cells
What type of cell is a pyramidal cell (e.g. multipolar, unipolar, bipolar, pseudounipolar, etc.)?
Multipolar
What type of cell is a Purkinje cell (e.g. multipolar, unipolar, bipolar, pseudounipolar, etc.)?
Multipolar
What basic neuron configuration (i.e. axonal and dendritic branching) do interneurons have?
Multipolar
Where are pyramidal cells found?
The cerebrum
Where are Purkinje cells found?
The cerebellum
In what layers of the cerebrum are pyramidal cells found?
With what functions are they associated?
Layers III and V;
memory, learning, sensory information integration, motor response initiation
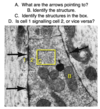
The large motor neurons seen in the anterior horn are what kind of neuron?
What is found in abundance in their cytoplasm?
Multipolar;
Nissl bodies
What is the name of the extracellular space surrounding motor neurons found in the anterior horn?
What is found here?
Neuropile;
axons, dendrites, blood vessels, and glial cells
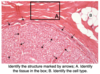
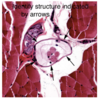
The lines coming from the right side of the image are indicating what structures?
What type of cell is this likely to be?
What is the extracellular space called?
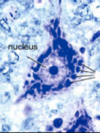
Nissl bodies;
a motor neuron;
neuropile
What is the ratio of glial cells to neurons in the CNS?
10:1
What are the four glial cells of the CNS?
Astrocytes,
ependymal cells,
oligodendrocytes,
microglia
What shape are ependymal cells?
Columnar
What are the two main types of astrocyte?
Where does each (mainly) occur?
Protoplasmic (gray matter),
fibrous (white matter)
Glial tumors mostly arise from which type of astrocyte?
Fibrous astrocytes
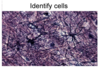
What type of cell is shown in this micrograph?
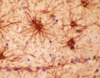
Astrocytes
(here shown under fluorescence)
Astrocyte foot projections mostly wrap around what two structures?
Blood vessels (contributing to the BBB);
neurons (providing support, repair, and K+ / neurotransmitter removal)

What type of cell is shown in this micrograph?
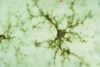
A microglial cell
(small, fibrous, dark-staining)
How many types of oligodendrocyte are there?
What are they?
3;
perivascular,
satellite,
interfascicular
What cells are stained ‘G’ and what cells are stained ‘N’ in this micrograph?
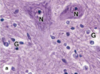
Glial cells;
neurons
What type of cell is shown in this micrograph?
Name the structure indicated by the ‘P.’

Astrocytes;
foot processes
What are the main glial cells of the PNS?
Satellite cells;
Schwann cells
Peripheral nerve axon bundles are known as:
These bundles are surrounded by:
Fascicles;
connective tissue sheaths
What is the name for the connective tissue sheath surrounding each individual fascicle (bundle of axons)?
What is the name for the connective tissue sheath surrounding several fascicles (bundles of axons)?
Perineurium;
epineurium
A group of axons makes up a ________, a group of which makes up a ________.
Fascicle, nerve
What thin layer of connective tissue surround an individual axon and its associated Schwann cell?
Describe this connective tissue.
Endoneurium;
loose reticular fibers (type III collagen)
The permeability barrier of a nerve is made of what type of junctions?
This barrier is found in what layer of connective tissue?
Tight junctions;
perineurium
Describe the perineurium.
Flattened cells surround groups of axons that form fascicles

What type of tissue makes up the epineurium?
Dense irregular connective tissue
True/False.
One individual Schwann cell pairs with one individual axon at a particular point and wraps around it once.
False;
one Schwann cell wraps around one neuron many times at a particular point, making multiple layers of insulation
(from a few up to 150 layers from a single Schwann cell)
The length of axon that is covered by a Schwann cell is called the _________.
The short gaps of exposed axon between Schwann cells are called ______________.
Internode (1 - 1.5 mm);
nodes of Ranvier
How long is the typical length of axon covered by a Schwann cell? What is this space called?
How many Schwann cells can be needed to myelinate a single axon?
1 - 1.5 mm, the internode;
100s
What type of myelinating cell is found in the PNS?
What specific type of myelinating cell is found in the CNS?
Schwann cells;
interfascicular oligodendrocytes
One Schwann cell can be attached to how many neurons?
One oligodendrocyte cell can be attached to how many neurons?
1;
up to 30
True/False.
Many PNS axons are not sheathed by Schwann cells and are not myelinated.
False;
although it is true that many are unmyelinated, all PNS axons are protected and supported (‘sheathed’) by Schwann cells

True/False.
A single oligodendrocyte can myelinate several internodes of the same axon.
True.
What term describes nervous conduction down myelinated axons from node of Ranvier to node of Ranvier?
Saltatory conduction
What is the purpose of nervous ganglia?
Sensory ganglia send information to the:
Autonomic (motor) ganglia send information to the:
To act as relay stations;
CNS;
effector organs
True/False.
Motor ganglia are synaptic stations.
True/False.
Sensory ganglia are synaptic stations.
True;
false
Which has its nucleus in a central position within the cell, a large multipolar neuron (e.g. a motor neuron) or a neuron found in a sensory ganglion?

Sensory ganglia neurons
(motor neurons have peripherally displaced nuclei as seen in this image)
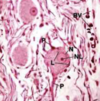
What are the two major types of plexi (nets of ganglia) found in the enteric nervous system?
Submucosal (Meissner’s);
myenteric (Auerbach’s)
This micrograph shows nervous tissue between two separate layers of muscular tissue that have differing orientations.
This is most likely to be from what organ system?
What is this collection of nervous tissue called?

The gut;
the myenteric (Auerbach’s) plexus
(of the enteric nervous system)

Name the type of synaptic junction:
an axon synapsing on a non-neuronal cell
Axosomatic synapse
Name the type of synaptic junction:
an axon synapsing on a dendritic spine
Axodendritic synapse
Name the type of synaptic junction:
an axon synapsing on an adjacent axon
Axoaxonic synapse
How long is the average synaptic cleft?
~25 nm
Presynaptic cholinergic neurons have what type of appearance to their vesicles?
Clear vesicles

Presynaptic adrenergic neurons have what type of appearance to their vesicles?
Dense vesicles
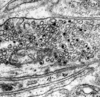
Which horns of the gray matter in spinal cord cross section will reach the outer surface of the cord?
What horns appear largest?
(Options: ventral, lateral, and dorsal horns)
Dorsal horns;
ventral horns

From superficial to deep, what are the three layers of cerebellar cortex in terms of type of neuron?
Molecular (synaptic);
Purkinje;
granular
What is the outer layer of the cerebellar cortex in terms of type of neuron?
Molecular (synaptic)
What is the middle layer of the cerebellar cortex in terms of type of neuron?
Purkinje (functional; motor)
What is the inner layer of the cerebellar cortex in terms of type of neuron?
Granular
(small, densely packed neurons)
How many cellular layers of cerebral cortex are there?
From superficial to deep, what are the outer three cellular layers of the cerebral cortex?
6;
molecular (I),
external granular (II),
external pyramidal (III)
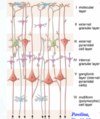
How many cellular layers of cerebral cortex are there?
From superficial to deep, what are the inner three cellular layers of the cerebral cortex?
6;
internal granular (IV),
internal pyramidal (ganglionic) (V),
multiform (polymorphic) (VI)

How many cellular layers of cerebral cortex are there?
From superficial to deep, what are they?
6;
molecular (I),
external granular (II),
external pyramidal (III),
internal granular (IV),
internal pyramidal (ganglionic) (V),
multiform (polymorphic) (VI)
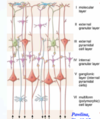
What are the main functional cells of the cerebral cortex?
In what layers are they found?
Pyramidal cells;
layers III and V

What percent of interneurons are found in the CNS?
99.9%
Are any inclusions common in neurons?
Lipofuscin (especially in the elderly);
melanin (from the substantia nigra pars compacta)
For what types of movement is fast axonal transport used?
For what types of movement is slow axonal transport used?
Movement of vesicles and mitochondria;
cytoplasmic proteins for the assembly of microtubules and neurofilaments
What type of CNS cell is particularly small and not typically seen in normal brain tissues?
Microglia
True/False.
Ependymal cells can be either columnar or cuboidal.
True.
True/False.
Ependymal cells can have both cilia and microvili.
True/False.
If the above is true about either cilia or microvili, this means that the ependymal cells are epithelial cells.
True
(for movement or absorption purposes);
false
What shape is a Schwann cell nucleus?
Flat and small
What type of tissue is shown in this micrograph?
What are some of its defining characteristics?
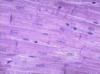
Cardiac muscle;
striations, intercalated discs
What type of tissue is shown in this micrograph?
What are some of its defining characteristics?

Skeletal muscle;
striations
What type of tissue is shown in this micrograph?
What are some of its defining characteristics?

Smooth muscle;
non-striated
Which of these types of muscle is striated?
Cardiac
Smooth
Skeletal
Cardiac,
skeletal


Astrocytes

A. Autonomic ganglia
B. Smooth muscle

A. Myelinated nerve axon
B. Unmyelinated nerve axon
C. Schwann cell
D. Fibroblast

A. Purkinje cells
B. Molecular layer
C. Granular layer
A - F
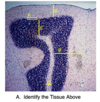
A. Cerebellar tissue
B. Cortex
C. Medulla
D. Molecular layer
E. Granular layer
F. Purkinje cells




A. Dorsal root ganglion pseudounipolar cells
B. Satellite cells

Multipolar neuron

Myelin sheath

A. Cerebellar cortex
B. Pyramidal neurons

Nodes of Ranvier


(Note: the synapse is just the tiny line. There is a synapse on either side of the central axon in the image)


Autonomic ganglion

Peripheral nerves
Nervous tissue is composed of two major types of cells?
Neurons;
neuroglia (glial cells)
True/False. Unmyelinated peripheral neurons are often still enveloped in Schwann cell cytoplasm?
True.
(just not wrapped in multiple layers to create the myelination effect)
What type of cell is this and where is it likely to be found?
What are its cytoplasmic aggregates?

A motor (multipolar) neuron,
the ventral horn;
Nissl substance
Is Nissl substance basophilic or eosinphilic?
Why?
Basophilic;
high concentrations of rRNA
You identify a motor neuron in a section of spinal cord histology. Where did you find it?
In what parts of the neuron are you not likely to find Nissl substance?
The ventral horn;
the axon hillock and axon
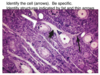
What types of cell are most prominent in this slide?
What smaller cells surround these prominent cells?
Where is a likely location of the PNS where this slide was found?

Sensory neurons (pseudounipolar);
satellite cells;
dorsal root ganglion
This slide shows a portion of a sympathetic autonomic ganglion.
What inclusions are see in the cytoplasm?

Lipofuscin
(in lysosomes)
True/False.
Dorsal root ganglia are synaptic locations.
True/False.
The ventral horns are synaptic locations.
True/False.
The dorsal horns are synaptic locations.
True/False.
Autonomic ganglia are synaptic locations.
False;
true;
true;
true
Name the three layers of connective tissue associated with nerves.
Endoneurium (surrounds each nerve fiber)
Perineurium (surrounds bundles of nerve fibers (i.e., fascicle))
Epineurium (dense irregular connective tissue that surrounds an entire nerve)
Endoneurium surrounds:
Perineurium surrounds:
Epineurium surrounds:
Each nerve fiber;
each bundle (fascicle) of nerve fibers;
an entire nerve
Why are longitudinally cut nerves “wavy” in appearance?
To allow stretching and movement with tissues
What type of connective tissue is epineurium?
Dense irregular connective tissue
What type of connective tissue fiber is associated with endoneurium?
Type III collagen
What type of connective tissue fiber is associated with epineurium?
Type I collagen (dense irregular connective tissue)
What type of connective tissue fiber is associated with Schwann cell basement membranes?
Type IV collagen
What type of connective tissue fiber is associated with Schwann cell basement membranes?
What type of connective tissue fiber is associated with endoneurium?
What type of connective tissue fiber is associated with epineurium?
Type IV collagen;
type III collagen;
type I collagen
Neurons releasing adrenergic products are characterized by what type of vesicle in their axons?
Dense (dark) vesicles

Neurons releasing cholinergic products are characterized by what type of vesicle in their axons?
Clear (light) vesicles

Which type of secretory axon is this more likely to be, cholinergic or adrenergic?

Cholinergic
(clear vesicles)
Which type of secretory axon is this more likely to be, cholinergic or adrenergic?

Adrenergic
(dense vesicles)
What are four primary types of motor neuron found in the body?
Where are their respective soma found?
Somatic motor neurons in the ventral horn;
autonomic motor neurons in the autonomic ganglia;
Purkinje cells in the cerebellum (between the granular and molecular layers);
*pyramidal (Betz) cells in the cerebrum (layers III and V)
(note: *pyramidal cells are also responsible for cognition and many other tasks)
What pyramidal (Betz) cell structure extends towards the superficial cerebral layers?
What pyramidal (Betz) cell structure extends towards the deep cerebral layers?
Apical dendrites;
the axon

Pyramidal (Betz) cells are characterized by ___________ extending superficially, ___________ extending laterally, and ___________ extending deeply.
apical dendrites,
basal dendrites,
axons

How does the rabies virus get to the host CNS from the original wound (often a peripheral bite mark)?
How does the rabies virus get to the host salivary glands from the CNS?
It rides dyneins back to the CNS;
it rides kinesins back to the salivary glands
How does the rabies virus get to the host CNS from the original wound (often a peripheral bite mark)?
It rides dyneins in the peripheral nerves
How does the rabies virus get to the host salivary glands from the CNS?
It rides kinesin proteins down microtubules in the peripheral nerves
What explains the extremely high latency period between a person being bitten by a rabid animal and that same person showing signs/symptoms of the disease?
(sometimes years)
The rabies virus rides dyneins back to the CNS and then kinesins down to the salivary glands from there
(this can be an extremely long process, especially if the initial rabid bite was far in the periphery (e.g. the hand or foot) and a small, slow nerve was infected)
Which of these types of muscle is striated?
Cardiac
Smooth
Skeletal
Cardiac,
skeletal
What type of tissue is shown in this micrograph?
What are some of its defining characteristics?

Skeletal muscle;
striations
What type of tissue is shown in this micrograph?
What are some of its defining characteristics?

Cardiac muscle;
striations, intercalated discs
What type of tissue is shown in this micrograph?
What are some of its defining characteristics?
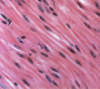
Smooth muscle;
non-striated
When we say some muscle tissue is striated, what does that mean?
The tissue has alternating dark and white lines that are perpendicular to the direction of the muscle fibers

Dystrophin connects what filament type to protein complexes of the plasma membrane?
These plasma membrane complexes connect to what extracellular structure?
F-actin;
laminin

State the proper terminology for the following in relation to a myocyte:
Plasma membrane
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Cytoplasm
Sarcolemma;
sarcoplasmic reticulum;
sarcoplasm
What type(s) of muscle is(are) striated?
Skeletal;
cardiac
What type of muscle is striated and involuntary?
What type of muscle is striated and voluntary?
What type of muscle is non-striated and involuntary?
What type of muscle is non-striated and voluntary?
Cardiac;
skeletal;
smooth;
none (does not exist)
What are the two main myofilaments?
Myosin (thick);
actin (thin)
What proteins are associated with myosin?
Titin (anchors thick filaments to Z lines)
In striated muscle, the dark bands are called __ bands.
The light bands are called __ bands.

A
(dArk bands);
I
(lIght bands)

What proteins are associated with actin?
Tropomyosin (covers myosin-binding sites);
troponin (binds calcium, moves tropomyosin);
nebulin (stabilizes and aligns actin polymers);
dystrophin (anchors thin filaments to plasma membrane protein complexes)
What protein runs alongside myosin, anchoring it to the Z-lines and running the entire length of a sarcomere?
Titin
What type of protein gives muscle its elasticity?
Titin
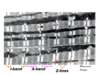
Name 1, 4, 5, 7, 9, 10, and 11.

1 - Z-line
4 - M-line
5 - titin
7 - sarcomere (Z-to-Z)
9 - H-zone
10 - A-band
11 - I-band
What proteins are found in the I band?
Actin,
tropomyosin,
troponin,
nebulin,
z-line proteins,
titin

What proteins are found in the A band?
Myosin, M-line proteins
+ I band proteins
(actin, tropomyosin, troponin, nebulin, titin)

What proteins are found in the H-zone?
Myosin, myomesin (M-line protein), titin

What are two unique facts about skeletal muscle nuclei?
Skeletal myocytes are multinucleated;
the nuclei are peripherally located
Skeletal myocytes are basically elongated plasma membranes filled with:
and peripherally lined by:
myofibrils;
many nuclei
In striated muscle, what dark line bisects each I band?
In striated muscle, what light area bisects each A band?

The Z-line;
the H band
What type of cell has a very limited role in providing regenerative effects in damaged skeletal muscle?
Satellite cells
Many __________ fuse into a single elongated ___________ that runs with other similar cells to make up a muscle fascicle.
Myoblasts;
myofiber (myocyte)
How is myocyte contraction linked to surrounding connective tissue?
Dystrophin (intracellular) connects actin to plasma membrane protein complexes;
these complexes connect to laminin in the endomysium basement membrane (extracellular)
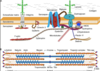
Name as many proteins of the sarcomere as you can.
Myosin, titin, myomesin (and C-proteins);
actin, tropomyosin, troponin, nebulin, alpha-actinin
(peripherally associated: dystrophin, desmin)

What type of cell junction unites myocytes?
None!
They are held together by layers of connective tissue (endomysium, perimysium, epimysium)
What layer of muscle connective tissue carries most of the vasculature and nervous innervation for the muscle?
Epimysium
1st step - myosin bound to actin
What is the 2nd step of the actin-myosin crossbridge cycle?
What is the 3rd step of the actin-myosin crossbridge cycle?
What is the 4th step of the actin-myosin crossbridge cycle?
What is the 5th step of the actin-myosin crossbridge cycle?
ATP binds myosin (myosin releases actin);
ATP hydrolysis (myosin bending);
force generation (contraction, phosphate release);
reattachment (myosin inactive, bound to actin)

What are the triads extending down into each myocyte?
One T-tubule + two sarcoplasmic reticula
(i.e. a long, narrow sarcolemma invagination with two long, narrow smooth endoplasmic reticula on either side)

Epimysium surrounds bunches of muscle fascicles. It is made of what type of connective tissue?
This is associated with what type of connective tissue fiber in particular?
Dense irregular connective tissue;
type I collagen
In close examination of striated muscle, a thin line can be seen bisecting each I band (lIght band). What is that line?
Z lines
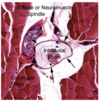
Identify the muscle spindle apparatus in this cross-section of skeletal muscle.
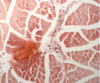
(Blue circle)
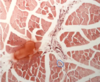
What type of tissue is shown here?
Outline one single cell in this cross-section.

Skeletal muscle
(blue line)
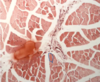
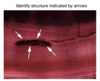
What structure is shown in this slide?

A myotendinous junction
(skeletal muscle attaching to tendon)
A sarcomere is defined as the space from one __ line to the next.
Z
In striated muscle, which are the A bands and why are they called this?
In striated muscle, which are the I bands and why are they called this?
Dark bands (dArk), they are anisotropic;
light bands (lIght) they are isotropic
Which striation bands shorten during muscle contraction?
Which striation band remains the same length during muscle contraction?
The I and H bands;
the A band
What are the two binding sites of a myosin head?
Actin-binding;
ATP-binding
When activated, protein 1 pulls protein 2 off the myosin-binding site on F-actin.
What is protein 1 and what is protein 2?
Troponin;
tropomyosin
What type of myofilament is found in the A band but not in the H band?
Light myofilaments (actin + associated proteins)
Why are smooth myocytes not striated?
The sarcomeres are randomly arranged in various directions
(i.e. not in myofibrils)

Instead of Z-lines, smooth myocytes have:
Dense bodies

What band of the sarcomere is thick filaments only?
What band of the sarcomere is both thick and thin filaments?
What band of the sarcomere is thin filaments only?
H band;
A band (length of thick filaments);
I band
What structure connects two adjacent thick filaments within one sarcomere?
Myomesin (M-line protein)
What is the difference in myosin between cardiac, skeletal, and smooth muscle?
Skeletal/cardiac muscle = bipolar;
smooth muscle = side polar

Dense bodies in smooth muscle are analogous to what structure in skeletal and cardiac muscle?
The bodies are attached to what proteins and what other structure?
Z-lines;
intermediate filaments (vimentin, desmin), the sarcolemma

What protein binds F-actin to Z-lines?
Alpha-actinin
The specific protein found in the M-line of a sarcomere is called:
Myomesin
Abnormalities in the dystrophin protein are liked to what two disorders?
Duchenne muscular dystrophy (dystrophin nearly completely absent);
Becker muscular dystrophy (dystrophin partially absent)
Duchenne muscular dystrophy is linked to mutations in what protein?
Becker muscular dystrophy is linked to mutations in what protein?
Dystrophin;
dystrophin
What role does desmin play in myocytes?
Does it assist in contraction?
It anchors Z-lines to the sarcolemma;
no (it is structural, maintaining shape)
What protein anchors actin to Z-lines?
What protein anchors myosin to Z-lines?
What protein anchors Z-lines to the sarcolemma?
What protein anchors F-actin to the sarcolemma?
Alpha-actinin;
titin;
desmin;
dystrophin
What protein anchors actin to Z-lines?
Alpha-actinin
What protein anchors myosin to Z-lines?
Titin
What protein anchors Z-lines to the sarcolemma?
Desmin
What protein anchors F-actin to the sarcolemma?
Dystrophin
Dense bodies are analogous to __________ in skeletal muscle.
Two proteins (which?) and what other structure anchor these bodies in place?
Z-lines;
vimentin, desmin
(intermediate filaments),
the sarcolemma
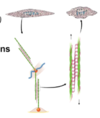
Name the differences in myosin orientation between smooth, cardiac, and skeletal muscle.
Skeletal/cardiac = bipolar myosin;
smooth = sidepolar myosin

Starting at the initial influx of calcium into the myocyte, what happens next in smooth muscle activation?
Ca2+ binds/activates calmodulin;
this complex than activates myosin light-chain kinase (MLCK);
the kinase phosphorylates the circular (self-bound) myosin to unbind/activate it

What causes rigor mortis?
The lack of ATP prevents actin-myosin dissociation
What types of tissue are the three with boxes obscuring them in this slide?

Smooth muscle cross-section;
smooth muscle longitudinal section;
dense irregular connective tissue


Cardiac muscle

Smooth muscle
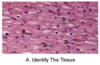
Cardiac muscle
(Bs indicate intercalated discs)





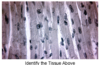
Skeletal muscle fibers

Skeletal muscle
Cardiac muscle
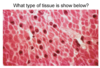
Smooth muscle (cross-section)

What structure stores calcium within myocytes?
Sarcoplasmic reticula
Myasthenia gravis involves antibodies to cholinergic receptors in what location?
The sarcolemma (at the neuromuscular junction)
What two special sensory organs relate information back to the CNS about the degree of stretch and tension in skeletal muscle?
Muscle spindles (within the muscle fibers);
Golgi tendon apparatus (within the myotendinous junctions)
Tendons attach to what bony structure?
Periosteum
(both are types of dense connective tissue)
What are the three main types of skeletal muscle according to function?
Type I;
type IIa;
type IIb
What type of tissue is shown in this slide?
What is the yellowish substance seen in some cells?

Cardiac muscle;
lipofuscin
What type of skeletal muscle fiber is slow oxidative and fatigue-resistant?
Type I (red)
Some cardiac myocytes stain an intense magenta if treated with periodic Acid-Schiff stain (PAS). What are these cells and why do they stain this way?

Purkinje cells
(modifed myocytes that conduct electrical impulses);
abundant glycogen inclusions
What type of skeletal muscle fiber is fast oxidative glycolytic?
Type IIa (intermediate)
What type of tissue is indicated by the circles in this slide?
(Orange, red, green, purple)

Orange - dense irregular CT fibers
Red - smooth muscle (longitudinal)
Green - a parasympathetic ganglion
Purple - smooth muscle (cross-section)
What type of skeletal muscle fiber is fast glycolytic and fatigue-prone?
Type IIb (white)
What type of skeletal muscle fiber is ‘red?’
What type of skeletal muscle fiber is ‘intermediate?’
What type of skeletal muscle fiber is ‘white?’
Type I;
type IIa;
type IIb
Which of the following is more prevalent in each type of skeletal muscle (red or white):
1. Mitochondria
2. Vascularity
3. Myoglobin
4. Sarcoplasmic reticulum
1 - Red
2 - Red
3 - Red
4 - White
What type(s) of muscle is(are) characterized by a high quantity of gap junctions?
Cardiac;
smooth
Which type of muscle is characterized by branching and anastomosing between fibers?
Cardiac
What type(s) of muscle is(are) characterized by centrally located nuclei?
What type(s) of muscle is(are) characterized by peripherally located nuclei?
Smooth, cardiac;
skeletal
Intercalated disc are made up of what type of cellular junction(s)?
Gap;
desmosomes
What type of muscle is not characterized by the T-tubule system?
What does it have instead?
Smooth myocytes;
caveolae (smaller invaginations)
Are any muscle types able to easily regenerate?
Only smooth muscle
What type of tissue is shown here?
How can you tell?
A leiomyoma (benign tumor of smooth muscle);
whorled (fascicular) pattern of smooth muscle bundles separated by well-vascularized connective tissue
< 5 mitotic figures per HPF, no significant atypia
What proteins anchor smooth muscle dense bodies in place?
Vimentin, desmin
(intermediate filaments)
What type of tissue is this?
How can you tell?

Leiomyosarcoma;
atypia + either mitotic activity, tumor cell necrosis, or size > 10cm

Skeletal myocytes gets calcium from:
Smooth myocytes gets calcium from:
Cardiac myocytes gets calcium from:
The sarcoplasmic reticulum
The extracellular fluid; adjacent smooth muscle cells
The sarcoplasmic reticulum; adjacent cardiac muscle cells
What shape are skeletal myocytes?
What shape are smooth myocytes?
Polygonal;
fusiform
Where are skeletal myocyte nuclei?
Where is a cardiac myocyte nucleus?
Where is a smooth myocyte nucleus?
Peripheral;
central;
central
A skeletal muscle fiber (myofiber) is just one, long:
Myocyte
One single myofiber (myocyte) is filled with many, many chains of:
myofibrils
Where are muscle satellite cells found?
On the surface of skeletal muscle cells
Are muscle striations parallel lines or perpendicular lines to the direction of the myocyte and its myofibrils?
Perpendicular lines
What is here described:
“fluid-filled capsules enclosing a few small muscle cells and nerve fibers”
Muscle spindles
How many nuclei are typically present in cardiac myocytes?
1
(but may be 2)
Do any types of muscle cell exhibit branching?
Yes, only cardiac myocytes
What are the three types of cellular junction found in cardiac myocyte intercalated discs?
Gap;
macula adherens (desmosome);
fascia adherens (specialized Z-lines)
How does a smooth myocyte nucleus appear when the myocyte is relaxed?
How does a smooth myocyte nucleus appear when the myocyte is contracted?
Cigar-shaped;
corkscrew-shaped
What disorder is characterized by antibodies (IgG) to the cholinergic receptors on the motor end plate?
Myasthenia gravis
Is there any type of muscle that is able to actively regenerate?
Smooth muscle
How does smooth muscle regenerate?
Simple mitosis of smooth myocytes
Upon injury to skeletal muscle, what normally quiescent cells are responsible for some very limited regeneration?
Where are they found?
Satellite cells;
the external lamina
Which type of muscle shows no regenerative capacity beyond simple scar formation?
Which type of muscle shows some very limited regenerative capacity through satellite cells?
Which type of muscle shows active regeneration through simple mitosis?
Cardiac;
skeletal;
smooth
Does cardiac muscle contain satellite cells?
How is damage addressed?
No;
fibroblast proliferation and scar tissue formation
What term refers to an increase in cell number?
Hyperplasia
What term refers to an increase in cell size?
Hypertrophy
During pregnancy, does the uterus undergo hyperplasia or hypertrophy?
Both
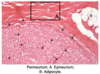
What is the most common tumor found in females?
What is the most common tumor found in males?
Leiomyomas (fibroids);
lipomas
How does weightlifting result in skeletal muscle hypertrophy?
Through repair of microtraumas
What effect can each of the following have on skeletal muscle?
- Inactivity, bedrest, cancer, congestive heart failure,*
- COPD, burns, liver failure, glucocorticoids -*
Atrophy
Cardiac ventricular hypertrophy can result from anything that causes what?
Increases in afterload
What are the changes in color seen in myocardium as a result of ischemia?
(Start with normal myocardium and end with a scar)
No change –>
dark mottling –>
hyperemia –>
yellow-brown softening –>
gray-white scar
During what time period following infarction will myocardial histology show no color changes?
1 - 4 hours
During what time period following infarction will myocardial histology show dark mottling?
4 - 24 hours
During what time period following infarction will myocardial histology show hyperemia?
1 - 5 days
During what time period following infarction will myocardial histology show hyperemia?
5 - 14 days
During what time period following infarction will myocardial histology show gray-white scar formation?
2 - 8 weeks
How does skeletal muscle regenerate?
How does cardiac muscle regenerate?
How does smooth muscle regenerate?
Satellite cells (VERY limited);
it doesn’t (no satellite cells);
simple mitosis


