Histology - Cardiology Block (I) Flashcards
What hematopoeitic cells are shown here?

Red blood cells
What hematopoeitic cell is shown here?

A neutrophil
What hematopoeitic cells are shown here among the red blood cells?
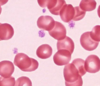
Platelets
What hematopoeitic cell is shown here?

An eosinophil
What hematopoeitic cell is shown here?

A basophil
What diameter are red blood cells?
7 - 8 μm
What diameter are platelets?
2 μm
Does any type of cell in the red blood cell lineage have granules?
No.
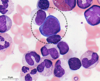
What type of hematopoeitic cell is this?

A proerythroblast
Describe proerythroblasts in regards to nucleus, cytoplasm, and granules.
Nucleus - very large
Cytoplasm - characteristic pale blue
Granules - none
What gives proeyrthroblast cytoplasm their characteristic pale blue color?

A high abundance of ribosomes

Are proerythroblasts capable of mitosis?
Yes
What type of hematopoeitic cell is shown here?

A basophilic erythroblast
True/False.
This is a basophilic erythroblast.
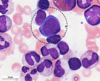
False.
(That’s a proerythroblast; attached here is a basophilic erythroblast)

Describe basophilic erythroblasts in regards to nucleus, cytoplasm, and granules.
Nucleus - round, large; full of condensed chromatin
Cytoplasm - dark blue
Granules - no

Are basophilic erythroblasts capable of mitosis?
Are proerythroblasts capable of mitosis?
Yes;
yes
What type of cell is this?

A polychromatic erythoblast
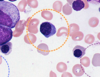
Why do polychromatic erythroblasts have their characteristic staining?

A mixture of ribosomes and hemoglobin

Are polychromatic erythroblasts capable of mitosis?
Yes
What type of hematopoeitic cell is this?

An orthochromatic erythroblast

What type of erythroblast has a light, pink-ish cytoplasm and no granules?
An orthochromatic erythroblast

Are orthochromatic erythroblasts capable of mitosis?
No
What are the three stages of erythroblast coloring?
Basophilic –> polychromatic –> orthochromatic
Are orthochromatic erythroblasts capable of mitosis?
No
What is the first type of cell in the red bood cell lineage that is not capable of mitosis?
Orthochromatic erythroblasts
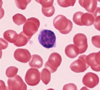
What type of hematopoeitic cell is shown here?
A reticulocyte
What is the order of cells in the RBC lineage from a proerythroblast to an erythrocyte?
Proerythroblast –>
basophilic erythroblast –>
polychromatic erythroblast –>
orthochromatic erythoblast –>
reticulocyte –>
erythrocyte
Which of these cells is the last to have a nucleus?
- Proerythroblast –>*
- basophilic erythroblast –>*
- polychromatic erythroblast –>*
- orthochromatic erythoblast –>*
- reticulocyte –>*
- erythrocyte*
Orthochromatic erythroblasts

Which of these cells is the last to be able to undergo mitosis?
- Proerythroblast –>*
- basophilic erythroblast –>*
- polychromatic erythroblast –>*
- orthochromatic erythoblast –>*
- reticulocyte –>*
- erythrocyte*
Polychromatic erythroblasts

What is the last cell in the RBC lineage to have a nucleus?
What is the last cell in the RBC lineage that is able to undergo mitosis?
Orthochromatic erythroblast;
polychromatic erythroblast
What is the first cell in the RBC lineage to not have a nucleus?
The reticulocyte
What is the first cell in the RBC lineage to not be able to undergo mitosis?
The orthochromatic erythroblast

Why are RBCs so eosinophilic?
High hemoglobin concentrations
What percentage of leukocytes are neutrophils?
What percentage of leukocytes are eosinophils?
What percentage of leukocytes are basophils?
50 - 70%
2 - 5%
< 1%
What percentage of leukocytes are neutrophils?
50 - 70%
What percentage of leukocytes are eosinophils?
2 - 5%
What percentage of leukocytes are basophils?
< 1%
What percentage of leukocytes are lymphocytes?
What percentage of leukocytes are monocytes?
25 - 30%
3 - 8%
What percentage of leukocytes are lymphocytes?
25 - 30%
What percentage of leukocytes are monocytes?
3 - 8%
What two broad categories of granules are found in white blood cells?
Azurophilic granules (primary granules);
Specific granules (secondary granules)
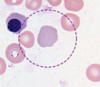
What type of hematopoeitic cell is shown here?

Monocyte
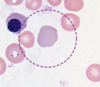
What type of hematopoeitic cell is shown here?
A lymphocyte
What is another name for a neutrophil?
A polymorphonuclear leukocyte (PMN)
How many lobes does a neutrophil nucleus typically have?
2 - 5
Do neutrophils contain either azurophilic or specific granules?
Both
What color are the azurophilic granules found in neutrophils?
What color are the specific granules found in neutrophils?
Light peach;
purple
Describe a typical eosinophil nucleus.
Do eosinophils contain either azurophilic or specific granules?
Bilobed;
both

What type of cell is this?

A basophil

Describe the shape of a basophil nucleus.
Variable: bilobed, S-shaped, or indented

Do basophils contain either azurophilic or specific granules?
Both
What are the two types of lymphocyte in regards to size as seen on histology?
Small and large
Which is more common, small or large lymphocytes?
Small (97%)
Do lymphocytes contain either azurophilic or specific granules?
A few azurophilic may be present
Do lymphocytes contain either azurophilic or specific granules?
A few azurophilic may be present
How long do monocytes typically stay in the blood?
About a day before entering the tissues
(to become macrophages)
What type of hematopoeitic cell is this?

A platelet
What cell is the initial precursor to all three types of granulocyte?
Myeloblast
What is the order of differentiation from myeloblast to neutrophil?
Myeloblast –>
promyelocyte –>
neutrophilic myelocyte –>
neutrophilic metamyelocyte –>
neutrophilic band cell –>
neutrophil
What is the order of differentiation from myeloblast to eosinophil?
Myeloblast –>
promyelocyte –>
eosinophilic myelocyte –>
eosinophilic metamyelocyte –>
eosinophilic band cell –>
eosinophil
What is the order of differentiation from myeloblast to basophil?
Myeloblast –>
promyelocyte –>
basophilic myelocyte –>
basophilic metamyelocyte –>
basophilic band cell –>
basophil
What are the first two cells of myeloblastic differentiation (common to all three myelocytes)?
Myeloblast;
promyelocyte
After a myeloblast becomes a promyelocyte, what are the next three cells before it becomes a mature cell (basophil, eosinophil, or neutrophil)?
Myelocyte –>
metamyelocyte –>
band cell –>
Mature cell (basophil, eosinophil, or neutrophil)
What is the last cell type before a cell differentiates into a neutrophil, eosinophil, or basophil?
Band cell (either neutrophilic, eosinophilic, or basophilic)
At what point in myeloblast differentiation is a cell first differentiated towards either neutrophil, eosinophil, or basophil?
Myelocyte
(e.g.,
Myeloblast –>
promyelocyte –>
basophilic myelocyte –>
basophilic metamyelocyte –>
basophilic band cell –>
basophil)
How does the nucleus:cytoplasm ratio change as a cell differentiates from myeloblast to mature cell (neutrophil, basophil, eosinophil)?
It decreases
How can a specific individual’s blood volume be estimated according to their weight?
50 - 70 ml / kg
What is the normal male hematocrit?
What is the normal female hematocrit?
42 - 52%
37 - 47%
What is the normal male hematocrit?
42 - 52%
What is the normal female hematocrit?
37 - 47%
How can plasma volume be estimated if hematocrit and total blood volume are known?
TBV * hematocrit
What is the normal percentage of blood that is made up of plasma?
45 - 55%
What is the small layer between the hematocrit and plasma in a centrifuged blood sample?
The Buffy coat (leukocytes)
(< 1% of fluid)
What is a normal male hemoglobin level?
What is a normal female hemoglobin level?
14 - 16 g / dl
12 - 14 g / dl
What is a normal male hemoglobin level?
14 - 16 g / dl
What is a normal female hemoglobin level?
12 - 14 g / dl
How much of plasma is water by weight?
90%
What is blood serum?
Plasma - the clotting factors
A normal RBC is ~7.5 μm.
Microcytic RBCs are < __ μm.
Macrocytic RBCs are > __ μm.
6
9
What is the term for RBC shrinkage?
What is a principal reason of tonicity that it would happen?
Crenation;
hypertonic solution
What is a term referring to RBC stacking?
Rouleaux
RBCs in hypertonic solutions will:
RBCs in hypotonic solutions will:
Crenate;
swell / lyse
What is the term for hemoglobin bound to O2?
What is the term for hemoglobin bound to CO2?
What is the term for hemoglobin bound to CO?
Oxyhemoglobin;
carbaminohemoglobin;
carboxyhemoglobin
Carboxyhemoglobin refers to hemoglobin bound to:
Carbon monoxide
How long does it take for reticulocytes to mature?
They make up what percentage of red cells in circulation?
1 - 2 days;
1%
What differentiates granulocytes from agranulocytes?
The presence of specific granules
(both have azurophilic granules)
Which leukocytes are also phagocytic?
Neutrophils;
eosinophils;
monocytes (and macrophages)
True/False.
Basophils are only phagocytic in the presence of antigen-antibody complexes.
False.
Basophils are not phagocytic leukocytes.
Are any agranulocytes phagocytic?
Are any granulocytes not phagocytic?
Monocytes and macrophages;
basophils
Are any agranulocytes not phagocytic?
Are any granulocytes phagocytic?
Lymphocytes;
neutrophils, eosinophils
What type of hematopoeitic cell category refers to lobed cells?
Granulocytes
(these are polymorphonuclear cells)
What type of hematopoeitic cell category refers to non-lobed cells?
Agranulocytes
(these are mononuclear cells)
Via what process do leukocytes leave circulation?
Diapedesis / extravasation
How long do neutrophils stay in the blood? And in tissues?
Do they ever reenter circulation?
10 hours, 1 - 2 days;
no
What do neutrophilic specific granules contain?
What do the azurophilic (non-specific) granules contain?
Alkaline phosphatase;
peroxidase
What is serum lacking that plasma has?
Clotting factors
If you remove clotting factors from plasma, you get:
Serum
What is the term for RBCs of various shapes?
Poikilocytosis
What is the term for RBCs of various sizes?
Anisocytosis
Define anemia.
Poor oxygen-carrying capacity
What types of hematopoeitic nucleated cell have specific granules?
What types of hematopoeitic nucleated cell have non-specific (azurophilic) granules?
Granulocytes;
all of them (granulocytes + agranulocytes)
Which are larger, the specific or non-specific (azurophilic) granules found in some hematopoeitic cells?
Non-specific (azurophilic)
A band neutrophil has what shape nucleus?
Horseshoe-shaped
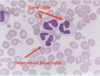
What type of leukocyte both inactivates inflammatory mediators and also phagocytizes antigen-antibody complexes?
Eosinophils
What is unique about the specific granules contained in eosinophils?
What is inside these granules?
They have a crystal-like internum surrounded by externum;
major basic protein, histaminase, aryl-sulfatase

What do basophilic specific granules contain?
How are these products neutralized?
Histamine, heparin;
eosinophilic aryl-sulfatase
Name the products stored in the specific granules found in each of the following:
Neutrophils
Eosinophils
Basophils
N - peroxidase
E - histaminase, aryl-sulfatase
B - histamine, heparin
Can any type of leukocyte renter circulation from the tissues?
Yes
(lymphocytes only)
Nucleoli are only present in what types of hematopoeitic cells?
Large lymphocytes;
monocytes
Do either large or small lymphocytes show any azurophilic granules?
Yes, large

How many platelets are typically found in the blood?
How long does each stay, on average?
150k - 450k
10 days
Describe the outermost layer of a platelet.
Peripheral clear layer called the hyalomere
(rings of microtubules / actin / myosin)

What are the two tubular systems found in the platelet hyalomere?
Open cannicular;
dense tubular

What are the two main portions of a platelet?
(outer ring and inner region)
Outer - hyalomere
Inner - granulomere
What are the three types of granule found in a platelet?
What do they contain?
α-granules – Fibrinogen, platelet-derived growth factor
δ-granules – Ca2+, ADP, ATP
γ-granules – lysosomal contents
What do platelet α-granules contain?
Fibrinogen, platelet-derived growth factor
What do platelet δ-granules contain?
Ca2+, ADP, ATP
Platelet γ-granules are essentially what?
Lysosomes
What factors are involved in platelet retraction?
Actin, myosin, & ATP
What are the main two substances responsible for clot removal?
Plasmin & γ-granules (platelet lysosomes)
What are the three platelet steps in clot formation?
Subendothelial attachment;
granule release;
adherence to each other
What are the two types of hematopoeisis?
Myeloid;
lymphoid

Pluripotent hematopoeitic stem cells give rise to what two types of multipotential hematopoeitic stem cells?
Myeloid stem cells;
lymphoid stem cells
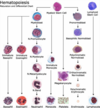
What are the largest cells in the bone marrow?
Megakaryocytes
Megakaryocyte production of platelets is controlled by what factor?
Thrombopoietin
Erythroblastic differentiation of stem cells is controlled by what factor?
Erythropoeitin
Erythrocytes are derived from what type of multipotent hematopoeitic stem cell?
Myeloid stem cells

Besides lymphocytes, what types of cell are derived from lymphoid stem cells?
(Note: lymphoid stem cells are multipotent hematopoeitic stem cells)
None;
the rest come from myeloid stem cells

Megakaryoblasts are derived from what type of multipotent hematopoeitic stem cell?
Myeloid stem cells

Ca2+, ADP, and ATP are found in which type of platelet granule?
δ-granules
(dense)
Fibrinogen and platelet-derived growth factor are found in which type of platelet granule?
α-granules
Which type of platelet granule is essentially a lysosome?
γ-granules
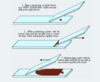
What type of smear is used in preparing peripheral smears?
Wright Giemsa
Describe the steps to prepare a peripheral smear.
Which is characterized by a block in cellular differentiation, acute or chronic leukemias?
Acute
Which is characterized by a proliferative abnormality, acute or chronic leukemias?
Chronic
What are some disorders in the differential for left shifts in leukocytes?
Infection, stress, stimulant drugs, myeloproliferative disorders, leukemia
What is a ‘left shift’ in leukocytes?
Earlier (immature) cells are seens
(bands, metamyelocytes, myelocytes, etc.)
What two hematopoeitic cells would be easy to confuse as both seem to have a horseshoe nucleus?
Monocytes and band cells
What are these two types of hematopoeitic cell?

Small lymphocyte (top);
large lymphocyte (bottom)
Where is bone marrow typically found?
The medullary area of long bones / cavities of spongy bones
What type of bone marrow is hematogenous?
What type is inactive?
Red;
yellow
What type of capillary is found in bone marrow?
Sinusoidal (discontinuous)
Pluripotent hematopoeitic stem cells give rise to what type of cell?
What are two subcategories of this type?
Multipotent hematopoeitic stem cells;
myeloid and lymphoid stem cells
What is the main role played by natural killer cells?
What is the main role played by B cells?
What is the main role played by T cells?
Immunological surveillance;
humoral immunity (i.e. antibody production);
cell-mediated immunity
What are the three broad categories of lymphocyte?
T cells
B cells
Natural killer cells
Name the alternate names used interchangably with the following:
basophilic erythroblast
polychromatic erythroblast
orthochromatic erythroblast
Early normoblast
intermediate normoblast
late normoblast
How will RBCs appear on light microscopy in iron-deficient conditions?
Hypochromic;
microcytic
Why does hereditary spherocytosis cause anemia?
The spleen destroys the spherocytes much earlier than it would otherwise
What are two major signs and symptoms of hereditary spherocytosis besides the normal S/Sy of anemia?
Jaundice
Splenomegaly
What amino acid missense mutation causes sickle cell anemia?
Glutamic acid to valine
(6th position in β-globin chain)
What general category of leukocyte is lobed?
What general category of leukocyte is non-lobed?
Granulocytes;
agranulocytes
How big is a neutrophil’s diameter in relation to an RBC?
2x
(14 - 15 in a neutrophil vs. 7.5 in an RBC)
What molecule do eosinophils release to neutralize heparin?
Eosinophil cationic protein
What autosomal dominant condition is shown in this micrograph?
Its cause is very similar to what other disease?
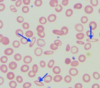
Hereditary elliptocytosis;
hereditary spherocytosis
Neutrophilia is generally due to what category of disease?
Eosinophilia is generally due to what types of disease?
Lymphocytosis is generally due to what category of disease?
Bacterial infection;
neoplasm, allergies, parasites, asthma;
viral infection
Neutropenia is generally due to what category of disease?
Bone marrow damage/destruction
What two types of tube system are found in platelets?
Open and dense cannicular systems
Why do men have higher hemoglobin concentrations (14 - 16 mg/dl) than women (12 - 14 mg/dl)?
Higher androgen levels
Hgb level x __ = hematocrit
~3
Hematocrit / ~3 = __
Hgb
What stain is used for peripheral smears?
Wright-Giemsa
How much of a normal RBC is typically pale?
1/3 - 1/2
RBCs are normally about the size of what other structure in the blood?
The nucleus of a lymphocyte
Lymphocytes on smear will often be predominantly __________ (nucleus or cytoplasm).
Nucleus

Auer rods are pathognomonic for what disease?
When present, they are seen in what type of cell?
AML;
myeloblasts
What is a way to estimate the cellularity of a patient’s bone marrow?
(Cellularity; i.e., the cell : fat ratio)
100 - the patient’s age
(e.g. a 40-year-old might have 60% cellularity
a 15-year-old might have 85% cellularity)
Is imatinib (Gleevec) still used?
Rarely;
there are many newer tyrosine kinase inhibitors which are better
(imatinib was the prototype / proof of concept)
Which has functioning cells, acute or chronic leukemias?
Chronic
(the acute are early-stage, non-functional cells - hence, why blast crises exist)
What type of named macrophage is found in the lymph node follicles (outer cortex)?
What type of named macrophage is found in the lymph node paracortex?
What type of named macrophage is found in the lymph node medulla?
Follicular dendritic cell;
dendritic cell (interdigitary);
histiocytes
Afferent lymphatic vessels can be found in what type(s) of lymphatic tissue?
Lymph nodes only


