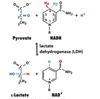
Glycolysis Flashcards
Glucose to Glucose 6 Phosphate by ____
hexokinase

hexokinase ___ glucose —> G6P
phopshorylates
hexokinase is not present in the ___
liver, there is glucokinase
what happens wtih G6P?
there is no transporter for G6P so it is stuck at the cell
γ-Phosphoryl of ATP is transferred to the ___ of Glu by Hexokinase
C6 hydroxyl

when does the liver export glucose?
when glucose is low
this is why the liver has a less aggressive heokinase (glucokinase)
difference between affinity of glucokinase compared to heoxkinase?
Liver Glucokinase has an affinity for Glu that’s 500-fold weaker than that of Hexokinase
G6P enters glycolysis?
when the cell needs energy
G6P is converted to F6P by
phopshoglucose isomerase
action of phopshoglucose isomerase on G6P
PGI isomerizes an aldose to a ketose

after phopshorylation at the C1 hydroxyl group what is produced? why?
two equal 3 carbon fragments
due to PGI setting the stage for an aldol cleavage between C3/C4 (requires a carbonyl at C2)
phopshofructokinase transfers a γ-phosphoryl of ATP to the ___ of F6P to make it F1,6 BP
C1 hydroxy

fructose 6-phopshate is converted into F 1,6 BP by
phosphofructokinase
___ plays a central role in the regulation of Glycolysis
phopshofructokinase
what cleaves fructose 1,6, biphosphate
aldose

products?


what is dihydroxyacetone converted to?
GAP, the other product of the cleavage of f 16 BP
differene between DHAP and GAP?

DHAP is a KETOSE
GAP is an ALDOSE
what converts DHAP to GAP?
tripose-P-isomerase
GAP and DHAP are both
trioses
GAP gets ____ to be converted to 1,3-BPG by GAP dehydrogenase?
oxidized and phosphorylated
____ converts GAP to 1,3 BPG
GAP dehydrogenase

first step in glycolysis where you MAKE atp?

1,3 PBG is converted to 3PG by
phosphoglycerate kinase