Energetics of Key Metabolic Steps Flashcards
Free energy change equation?
Concentrations must
be in molar units
RT log = 1.36 log
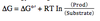
As the substrate concentration increases relative to the product concentration, the log term will become more ____ and ΔG will become more ____.

log more negeative, ΔG more negative
As the substrate concentration increases relative to the product concentration which way does the rxn proceed?

greater tendency to proceed from left to right
standard free energy chain equals
Kʹ′eq is the ratio of products to substrates at equilibrium

what is the TOTAL standard free energy chain
This relationship also holds for calculating ΔGT from ΔG for each step.

When you reverse the direction for writing a reaction, you _____ the sign of the standard free energy change.
change

how to to calculate the voltage difference between two half reactions?
ΔE°ʹ′ = E°ʹ′ (e- acceptor) - E°ʹ′ (e- donor)
The minus sign accounts for the fact that you are reversing the direction of one of the reactions to make it an oxidation. Don’t change the sign twice.
The standard free energy change, from the voltage difference between two half reactions
ΔG°ʹ′ = -nFΔE°ʹ′
n is the number of electrons transferred, F = 23.063 kcal/mol•volt, ΔE°ʹ′
the potential
difference in an oxidation reduction reaction
where reactants and products are not 1 M.

as the concentration of substrates increase, ΔE ___

increases
The actual free energy change can be calculated from
ΔG = -nFΔE
the voltage difference between two half reactions for conditions other than the standard state
ΔG, the actual free energy change which can be measured for a reaction running from left to right under a ____ conditions
given set of conditions
ΔG°, the free energy change under some ___ conditions
standard
Why is ΔG° useful?
Can calculate ΔG under any conditions if ΔG° is known.
To convert kcal/mol to kjoules/mol multiply by
4.18 kJ/kcal.
Standard State
∆G = ∆G°, when
[subst] and [prod] = 1 M
all spontaneous reactions have a
negative free energy change
biochemests standard state
if water is a product or substrate it is defined as
55.5 M = H20
biochemests standard state
if H+ is a product or substrate it is defined as

atp hydrolysis
what is the free energy change equation?


ΔG = 0, the reaction has no tendency for
net reaction in either direction

A to C free energy change?

ΔG°ʹ′1 + ΔG°ʹ′2 = -1.36 log Kʹ′eq(1) –1.36 log Kʹ′eq(2)
= -1.36 log (Kʹ′eq(1) x Kʹ′eq(2))

A to C?


Cannot use ΔG to predict ΔG at a___
catalytic site
the environemnt may be different here









