Geological traps formations rocks Flashcards
(21 cards)
Name this geological formation

Basin: A basin is a large area with thick sedimentary rocks, covered by shallow tropical water.
Name this geological formation

Reef: Reefs are mounds of rock, sand, coral or similar material lying beneath the surface of water. They are separated from land by a body of water known as a lagoon.

Name this geological formation

Ridge: A ridge is a chain of mountains or hills that form a continuous elevated crest for some distance. Ridges may be submarine ranges of mountains, including volcanoes, appearing above the surface of the ocean.
Name this geological formation

Trench: A trench is a deep, narrow channel in the sea or ocean bed. It typically runs parallel to a plate boundary, marking a subduction zone.
Name this geological formation

Delta: A delta is a mass of sediments deposited by a river flowing into a large body of water, such as a lake or ocean.
Can you label the diagram


Name this geological trap

Salt dome: Masses of salt are pushed up through clasticrocks due to their greater buoyancy, eventually breaking through and rising towards the surface. This salt is impermeable and when it crosses a layer of permeable rock, in which hydrocarbons are migrating, it blocks the pathway in much the same manner as a fault trap.
Name this geological trap
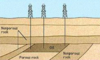
Stratigraphic: Stratigraphic traps are formed as a result of lateral and vertical variations in the thickness, texture, porosity or lithology of the reservoir rock.
Name this geological trap

Fault: This trap is formed by the movement of permeable and impermeable layers of rock along a fault line.The permeable reservoir rock faults such that it is now adjacent to an impermeable rock, preventing hydrocarbons from further migration.
Name this geological trap

Anticline traps are usually long oval domes of land that can often be seen by looking at a geological map or by flying over the land. Its formed by the accumulationof hydrocarbonsat the crest until the anticline is filled to the spill point - the highest point where hydrocarbons can escape the anticline.This type of trap is by far the most significant to the hydrocarbon industry.

Fault: A significant crackin a rock formation.

pinch out: A trap in which a sedimentary layerthins to the point where the layers above and below it come together.

Anticline: A structural trap in which the rock layers arefolded upwards.

Angular unconformity: A stratigraphictrap in which the layers have an angular tilt.
Name this organic-rich rock

Oil Shale
Name this organic-rich rock

Bitumen
Name this organic-rich rock

Granite
Name this organic-rich rock

Lignite Coal
Name this organic-rich rock

Sandstone
Name this organic-rich rock

Limestone
The rock cycle



