Genetics Predisposition to Cancer Flashcards
What do a small proportions of cancers happen due to?
Increased inherited predisposition to cancer (genetic)
What are the 2 different kinds of gene mutations that cancer can arise from?
Somatic mutations
Germline mutations
Where to somatic mutations occur?
In somatic tissue, nongermline
What can you say about the inheritability of somatic and germline mutations?
Somatic cannot be inherited and germline can
Where are germline mutations present?
In egg or sperm
What are some genetic processes associated with cancer?
Oncogenes
Tumour suppresor genes
DNA damage response genes
What are proto-oncogenes?
Normal gene that codes for proteins to regulate cell growth and differentiation
What can mutations change into oncogenes and what does this do?
Proto-oncogenes which accerlerates cell division
What are tumour suppresor genes?
Genes that inhibit cell cycle or promotes apoptosis
What happens when tumour suppresor genes fail?
Cancer arises
What are DNA damage response genes?
Repair mechanism for DNA
What happens when DNA damage response genes fail?
Cancer arises due to speeding the accumulation of mutations in other critical genes
What is an example of a DNA damage response gene?
Mismatch repair genes (MMR genes)
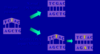
What do mismatch repair (MMR) genes do?
Corrects errors that spontaneously occur during DNA replication like single base mismatches or short insertions and deletions
What does mismatch repair failure lead to?
Microsatellite instability (MSI) where there is the addition of nucleotide repeats, which is the phenotypic evidence that MMR is not functioning normally
What is microsatellite instability (MSI)?
Where there is an addition of nucleotide repeats, which is phenotypic evidents that mismatch repair genes (MMR) are not working correctly
What are the 3 kinds of tumours?
Benign
Malignant
Dysplastic
What are some properties of benign tumours?
Lack the ability to metastasize
Rarely or never become cancerous
Can cause negative health benefits due to pressure on other organs
What are some properties of dysplastic tumours?
Benign but could progress to malignancy
Cells show abnormalities of appearance and cell maturation
What is a unique property of malignant tumours?
Able to metastasize
What are some other causes of cancer in relation to genes?
Autosomal recessive syndromes
Multiple modifier genes of lower genetic risk
What are de novo mutations?
Occur in germ cells of parents with no family history of hereditary cancer syndrome
What are de novo mutations common in?
Famial adenomatous polyposis
Multiple endocrine neoplasia 2B
Hereditary retinoblastoma
What is hereditory retinoblastoma?
Most common eye tumour in children
What is the type of inheritence of most cancer susceptability genes?
Dominant
What are some risk factors for breast cancer?
Ageing
Family history
Late menopause
Early menarche
Nulliparty (condition where woman cannot give birth)
Estrogen use
Dietary factors (alcohol)
Lack of exercise
What is nulliparty?
Condition where woman cannot give birth
What are some genes that increase hereditory susceptability to breast cancer?
BRCA1
BRCA2
TP53
PTEN
Which of BRCA1 and BRCA2 increases the risk of breast cancer the most?
BRCA1 (20-40%) whereas BRCA2 is only 10-30%
What are functions of the BRCA1 gene?
Checkpoint mediatory
DNA damage signalling and repair
Chromatin remodelling
Transcription
What is the main function of the BRCA2 gene?
DNA repair by homologous recombination
What do BRCA1 mutations increase the risk of?
Breast cancer (50-85%)
Second primary breast cancer (40-60%)
Ovarian cancer (15-45%)
Other cancers
What do BRCA2 gene mutations increase the risk of?
Breast cancer (50-85%)
Ovarian cancer (10-20%)
Male breast cancer (6%)
Other cancers
What are some risk factors for colorectal cancer?
Ageing
Personal history of colorectal cancer or adenomas
High fat, low fibre diet
Inflammatory bowel disease
Family history of colorectal cancer
What are the 2 possible hereditary colorectal cancer syndromes?
Non-polyposis (few to no adenomas)
Polyposis (multiple adenomas)
What is an example of a non-polyposis hereditary colorectal cancer?
HNPCC
What are examples of polyposis hereditary colorectal cancers?
FAP
AFAP
MAP
What are adenomas?
A beneign tumour formed from glandular structures in epithelial tissue
What are some clinical features of HNPCC?
Early but variable age in CRC diagnosis (about 45 years)
Tumour site through colon rather than descending colon
What is a clinical feature of familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP)?
Risk of extracolonic tumours (upper GI, thyroid, brain)
What is a milder form of FAP?
Recessive MYH polyposis
What do multiple modifier genes of lower genetic risk explain?
Families with history of cancer and no identified mutation
Different in cancer penetrance in families with the same mutation
What can cancer risk for patients with FAP be managed by?
Surveillance
Surgery
Chemoprevention
What are predictive gene tests used for?
To test who has genes that are associated with an increased risk in developing cancer
What is it important to remember about inherited mutations causing cancer compared to other causes?
Most cancers are sparodic, with only a small proportion being due to inherited mutations


