Gaucher's disease Flashcards
1
Q
What is Gaucher’s disease?
A
- An autsomal recessive deficiency of acid Beta glucocerebrosidase
- most common glycogen storage disease
- 1 in 40,000 incidence
- most common in **Ashkenazi Jewish origin **
2
Q
what is the pathophysiology of Gaucher’s disease?
A
- enzyme deficiency leads to disturbances in cell metabolism with accumulations of Sphingolipids in the
- liver
- spleen
- Bone marrow
3
Q
What is the classification of Gaucher’s disease?
A
-
Type 1 - Beta glucocerebrosidase deficency- most common
- adult type
- easy bruising
- Anaemia , Fx
- treatable w enzyme replacement therapy ( fatal if enzyme subsitute is not given)
-
Type 2 ( infantile)
- Lethal by age 3
- brain and organ involvement
- untreated
-
Type 3
- onset in teens
- thrombocytopenia, anaemia, enlarged liver
- fx
- gradual brain involvement
- type 3 clinical diverse
- non CNS respond well to enzymes
4
Q
What are the manifestations of Gaucher’s disease?
A
- Fatigue
- prolonged bleeding
- fever, chills, sweating
- seizure
- developmental delay
Orthopaedics
- Bone fractures/osteomyelitis
- joint pain/contractures
- bone necrosis/osteonecrosis
5
Q
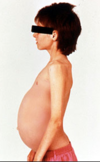
What are the signs of gaucher’s disease?
A
- Abnormal skin bruising
- Hepatosplenomegaly
- Cardiac murmur
- bone deformities
- 80% distal femur/ proximal tibia
- joint contractures
- pathological fx
6
Q
Symtpoms of Gaucher’s disease?
A
Systemic
- Fatigue ( anaemia)
- Prolonged bleeding ( thrombocytopenia)
- Fever, chills, sweats ( infection)
- Seizures, developmental delay ( CNS involvment)
Ortho
- Bone pain ( fractures, osteomyelitis)
- joint pain or contractures
- bone crisis ( osteonecrosis)
7
Q
What is seen in the labs with a pt with Gaucher’s disease?
A
- Anaemia
- Thrombocytopenia
- Dx confirmed with elevated plasma levels of Glucocerebrosides
8
Q
What does histology show on gaucher’s disease?
A
- bone marrow aspirate shows a giant binucleate storage cell filled with glucocerebrosides
- which accumulate due to deficiency of Beta- glucocerebrosides

9
Q
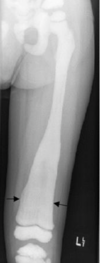
What is seen on imaging of Gaucher’s disease?
A
Xrays
- Cardiac enlargement
- pathological fx
- osteonecrosis
- abnormal bone remodelling
- Osteopenia
- ‘Erlenmeyer flask’ deformity of the distal femur- see pic
MRI/CT
- chronic vasucular insult in osteonecrosis in prox/distal femur/proximal tibia
10
Q
What is the tx of Gaucher’s disease?
A
Non operative
-
observation and support therapy
- for non affected pts ( normal bloods/xrays)
-
enzyme replacement therapy
- all children and asymptomatic pts
- not affective in type 2 gaucher’s disease
- imiglucerase
- veraglucerase alfa
-
Substrate reduction therapy
- less severely affected pts that can’t tolerate enzyme replacment therapy
- miglustat
Surgery
-
Bone marrow transplant
- if reformed early maybe curative
11
Q
What is the tx of fx mx in a pt with Gaucher’s disease?
A
- preop optimisation with enzyme therapy is critical
- availiability of additional blood, clotting products, and plaletes due to increased bleeding risk
- anaeasthetic to maintain oxygenation to prevent bone crisis
- increased risk of infection


