Foot and Ankle Review Flashcards
Foot and Ankle Review
_____% of bones in the body are in the feet
25
Foot and Ankle Review
150lb person walking 1 mile exerts ____ tons (127,000 lbs) on each foot!
~63-1/2
Foot and Ankle Review
The normal foot…
- Functions normally during a reasonable number of activities
- Relatively pain-free
- No structural deformity
- No history of significant trauma or surgery
Foot and Ankle Review
rearfoot is made of
talus and calcaneus

Foot and Ankle Review
what is the main job of the rearfoot (talus and calcaneus)?
- inversion and eversion.
- IR and ER of the tibia controls where the talus goes
- torque converter: converts IR and ER of tibia to inversion and eversion of the rearfoot
Foot and Ankle Review
what is the function of the midfoot
converts the foot into a more rigid or flexible structure
Foot and Ankle Review
what are the bones of the midfoot
navicular, cuboid and cuneiforms
Foot and Ankle Review
what is the function of the forefoot
adaptability
Foot and Ankle Review
bones of the forefoot
metatarsals and phanlanges
Foot and Ankle Review
the lateral column of the foot follows
where the cuboid is
calcaneus, cuboid and 4th and 5th metatarsal

Foot and Ankle Review
the medial column is made of
talus, navicular, cuneiforms, 1-3 metatarsals and 1-3 phalanges

Foot and Ankle Review
vestigial cleft
space between the 3rd and 4rd metatarsal that used to be used for grasping
Foot and Ankle Review
excess motion between 3rd and 4th metatarsal may create shear forces on the nerve bundle → cause inflammation

Morton’s Neuroma
Foot and Ankle Review
function of the arches
absorb shock and support
Foot and Ankle Review
arches of the foot
- medial and lateral longitudinal
- transverse

Foot and Ankle Review
plantar surface faces TOWARD midline
Inversion or VARUS:
Foot and Ankle Review
plantar surface faces AWAY from midline
Eversion or VALGUS:
Foot and Ankle Review
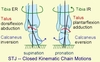
articulation between inferior talus with superior calcaneus
subtalar joint
Foot and Ankle Review
metatarsalgia
pain in the ball of the foot

Foot and Ankle Review
motion of the foot in the frontal plane
- Named by plantar surface:
- Inversion or VARUS: plantar surface faces TOWARD midline
- Eversion or VALGUS: plantar surface faces AWAY from midline
Foot and Ankle Review
motion of the foot in the transverse plane plane
abduction and adduction
Foot and Ankle Review
motions of the subtalar joint
axis?
- pronation and supination
- 42 degrees from horizontal
- 16 medially
- NOTE: the axis is variable and it moves with pronation/supination

Foot and Ankle Review
how many joints, bones, and ligaments in the foot
- 33 joints
- ~100 ligaments
- 26 bones (and 2 sesamoids)
Foot and Ankle Review
subtalar joint pronation in OKC
calcaneus abduction, DF, eversion