Fiser.08.Anesthesia Flashcards
What is a concerning finding for BMI during the standard airway examination?
BMI > or = 31
What is a concerning finding for mouth opening during the standard airway examination?
inter-incisor or inter-gingival distance > 3cm
what is a concerning finding for Mallampati classification during the standard airway examination?
Class III and IV
What is a concerning finding for mandibular protrusion during the standard airway examination?
inability to protrude lower incisors to meet or extend past upper incisors
what are two concerning findings with neck anatomy during the standard airway examination?
radiation changes; thick/obese neck
name two concerning findings with C-spine mobility during the standard airway examination
limited extension; possibility unstable C-spine
What is a concerning finding with facial hair during the standard airway examination
presence of a full beard
Mallampati classification?

class I: full visibility of tonsils, uvula, and soft palate
Mallampati classification?

class II: visibility of hard and soft palate, upper portion of tonsils, and uvula
Mallampati classification?
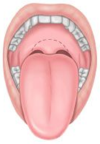
class III: soft and hard palate and base of uvula are visible
Mallampati classification?

class IV: only hard palate visible
define MAC in anesthesia
minimum alveolar concentration: smallest concentration of inhalational agent at which 50% of patients will not move with incision
how do you interpret a small MAC (minimum alveolar concentration) in terms of lipid solubility?
small MAC is more lipid soluble
how do you interpret a small MAC (minimum alveolar concentration) in terms of potency?
small MAC is more potent
what is the relationship between speed of induction & solubility in terms of inhalational anesthetics
increased speed of induction with decreased solubility (inversely proportional)
what is the fastest acting inhaled induction agent?
nitrous oxide
what is the MAC & potency of nitrous oxide?
high MAC therefore low potency
name three anesthetic effects of inhalational agents
unconsciousness; amnesia; analgesia
name the respiratory effects of inhaled induction agents
blunts hypoxic drive
name three cardiovascular effects of inhalational induction agents
myocardial depression, increased cerebral blood flow, decreased renal blood flow
name 2 advantages and 1 adverse effect of nitrous oxide (NO2)
fast, minimal myocardial depression; tremors at induction
is the onset/offset of halothane fast or slow
slow onset / offset
name 2 cardiac effects of halothane
highest degree of cardiac depression and arrhythmias
why is halothane good for children?
least pungent


