Fiser.07.Pharmacology Flashcards
What is first-pass metabolism?
Metabolism through the liver
What two modes of administration avoid first-pass metabolism?
sublingual and rectal
what aspect of a drug determines its skin absorption?
based on lipid solubility through the epidermis
What types of drugs can be absorbed into CSF? (2 characteristics)
restricted to nonionized drugs & lipid soluble
Which blood component is largely responsible for binding drugs?
albumin
what percent of penicillin is albumin-bound?
90%
what percent of warfarin is albumin-bound?
90%
why should you avoid sulfonamides in newborns?
displaces unconjugated bilirubin from albumin in newborns
what body part is tetracycline stored in?
stored in bone
what body part are heavy metals stored in?
bone
define zero-order kinetics?
constant amount of drug eliminated regardless of dose
define first-order kinetics?
drug eliminated proportional to dose
how many half-lives does it take for a drug to reach steady state?
5
define volume of distribution (formula)
amount of drug in the body divided by the amount of drug in plasma/blood Vd = (Total Drug) / (Drug in Plasma/Blood)
Where do drugs with high volumes of distribution have higher [x]? (extravascular & intravascular)
higher [x] in extravascular tissue (ex: fat)
define bioavailability
the fraction of unchanged drug reaching the systemic circulation
what is the bioavailability of IV drugs? How does this compare to PO drugs?
IV drugs assumed to have 100% bioavailability, PO drugs are less bioavailable
Define ED50
median effective dose: drug level at which desired effect is attained in 50% of patients
Define LD50
lethal dose: drug level at which death occurs in 50% of patients
What does “hyperactive” mean in pharmacology?
effect at an unusually low dose
define “tachyphylaxis” in pharmacology
tolerance after only a few doses
define “potency” in pharmacology
dose required for effect
define “efficacy” in pharmacology
ability to achieve result without untoward effect
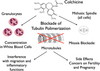
where in the hepatocyte does drug metabolism occur? (2)
smooth ER; P450 system
name four reactions that occur in Phase 1 of drug metabolism & 2 required substrates
demethylation; oxidation; reduction; hydrolysis mixed function oxidases, require NADPH / O2
name two reactions that occur in phase 2 of drug metabolism and its overall effect
glucuronic acid attaches; sulfates attach –> this results in a water-soluble metabolite to make it ready for excretion
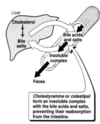
Describe the process of enterohepatic circulation of drugs and give an example of a drug that undergoes it
biliary excreted drugs may become deconjugated in intestines with reabsorption, sometimes in active form. Ex: cyclosporine
name 11 inhibitors of P450
My - Macrolides; Sullen - Sulfonamides; Robot - Ritonavir; And Amiodarone; A cute - Acute alcohol abuse; Kangaroo - Ketoconazole; Couldn’t - Ciprofloxacin; Quickly - Quinidine; Get the - Gemfibrozil; Cement -Cimetidine; Gliding on - Grapefruit juice; Ice - Isoniazid

name 8 inducers of P450
Momma - Modafinil; Da - Dilantin; Grizzly - Griseofulvin; Bear - Barbituates; Cruelly - Chronic alcohol use; Steals - St. John’s wort / Cigarette Smoke; Phen-phen (and) - Phenytoin, Phenobarbital; While - Warfarin; Racing- Rifampin; Cars - Carbamazepine / Cruciform Vegetables

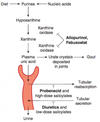
what is the most important organ for eliminating most drugs?
kidney
name two ways the kidney eliminates drugs
glomerular filtration; tubular secretion
which type of drug is water-soluble? (polar v. nonpolar)
polar drugs (ionized)
which type of drug is more likely to be fat-soluble (polar v. nonpolar)
nonpolar drugs (nonionized)
which type of drug is more likely to be eliminated in unaltered form? (polar v. nonpolar)
polar drugs (ionized)
which type of drug is more likely to be metabolized before excretion? (polar v. nonpolar)
nonpolar drugs (nonionized)
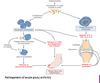
What metabolic process results in uric acid?
purine metabolism –> uric acid