Femoral Triangle Flashcards
Borders of femoral triangle
Superior: inguinal ligament
Medial: lateral border of adductor longus
Lateral: medial border of sartorius
Floor of femoral triangle
Formed by iliopsoas laterally and pectineus medially
Roof of femoral triangle
fascia lata
Contents of femoral sheath
A. Femoral, V. Femoral, Femoral canal (deep linguinal lymph nodes)
Label

Femoral ring
Proximal opening of femoral canal covered by parietal peritoneum
Femoral sheath is _____ to the inguinal ligament
Deep
Femoral herniae
protrusion of abdominal viscera (ususally SI) through the femoral ring into the femoral canal
bounded by V. femoral laterally and lacunar ligament medially
can pass inferiorly through the saphenous opening
Inguinal lymph node types
Superficial (proximal and distal) and deep
drain to external iliac lymph nodes
Proximal (horizontal) lymph nodes
inferiorly along inguinal ligament
Distal (vertical) lymph nodes
along each side of great saphenous vein
Deep inguinal lymph nodes
along medial side of V. femoral
inside femoral canal of sheath
Femoral nerve= __-__
L2-L4
Terminal cutaneous branch of N. femoral
Saphenous nerve
N. femoral innervations
Pectineus
Iliacus
Quadriceps femoris
Sartorius
4

lateral femoral cutaneous n.
7

saphenous n.
Meralgia paresthetica
compression of lateral femoral cutaneous nerve as it passes under inguinal ligament causing pain

adductor canal (subsartorial/Hunter’s canal)
femoral vessels reach popliteal fossa
begins at femoral triangle apex, ends at adductor hiatus (opening in tendon of adductor magnus)
Profunda femoris a.
largest branch of femoral artery
gives rise to medial and lateral circumflex femoral arteries
has perforating arteries that supply adductors (particularly adductor magnus) and hamstring muscles

profunda femoris a.
(deep femoral artery)
medial circumflex femoral a.
main supply to femoral head and neck
passes between iliopsoas and pectineus to reach posterior thigh

medial circumflex femoral a.
lateral circumflex femoral a.
passes laterally, deep to sartorius and rectus femoris
supplies lateral thigh muscles and femur head
Three branches of lateral circumflex femoral a.
ascending
transverse
descending

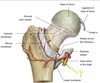
lateral circumflex femoral a.

1: medial circumflex femoral a.
great saphenous vein: clinical
can be used to administer blood, electrolytes, drugs, etc
for coronary bypass surgery
femoral pulse palpation
midway between ASIS and pubic symphysis
compression of femoral artery
reduces blood flow to femoral a. and its branches
left cardiac angiography
catheter placed into a. femoral
just inferior to midpoint of inguinal ligament
laceration of a. femoral
susceptible because superficial position
arteriovenous shunt can occur as a result of communication between injured vessels
cruciate anastomosis: 4 way common meeting of med & lat a. fem, inferior gluteal artery, and first perforating artery
saphenous varix
localized dilation of the terminal part of the great saphenous vein, may cause edema in femoral triangle
right cardiac angiography
catheter insersted into femoral vein as it passes through the femoral triangle
femoral venous puncture for administration of fluids


